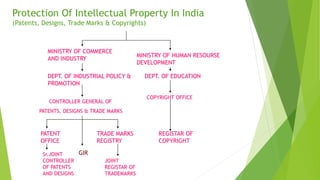
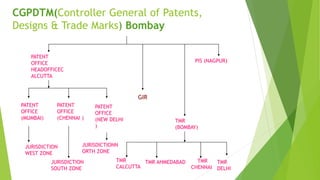
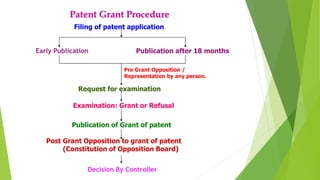
The document discusses various aspects of intellectual property rights such as patents, trademarks, and copyrights in India. It provides definitions of intellectual property and describes how patents, in particular, are important as they provide incentives for innovation and enable inventors to recoup costs. The document also summarizes India's legislative framework for IPR including amendments made to various acts over time to meet international obligations. It outlines procedures related to patent applications and grants in India.