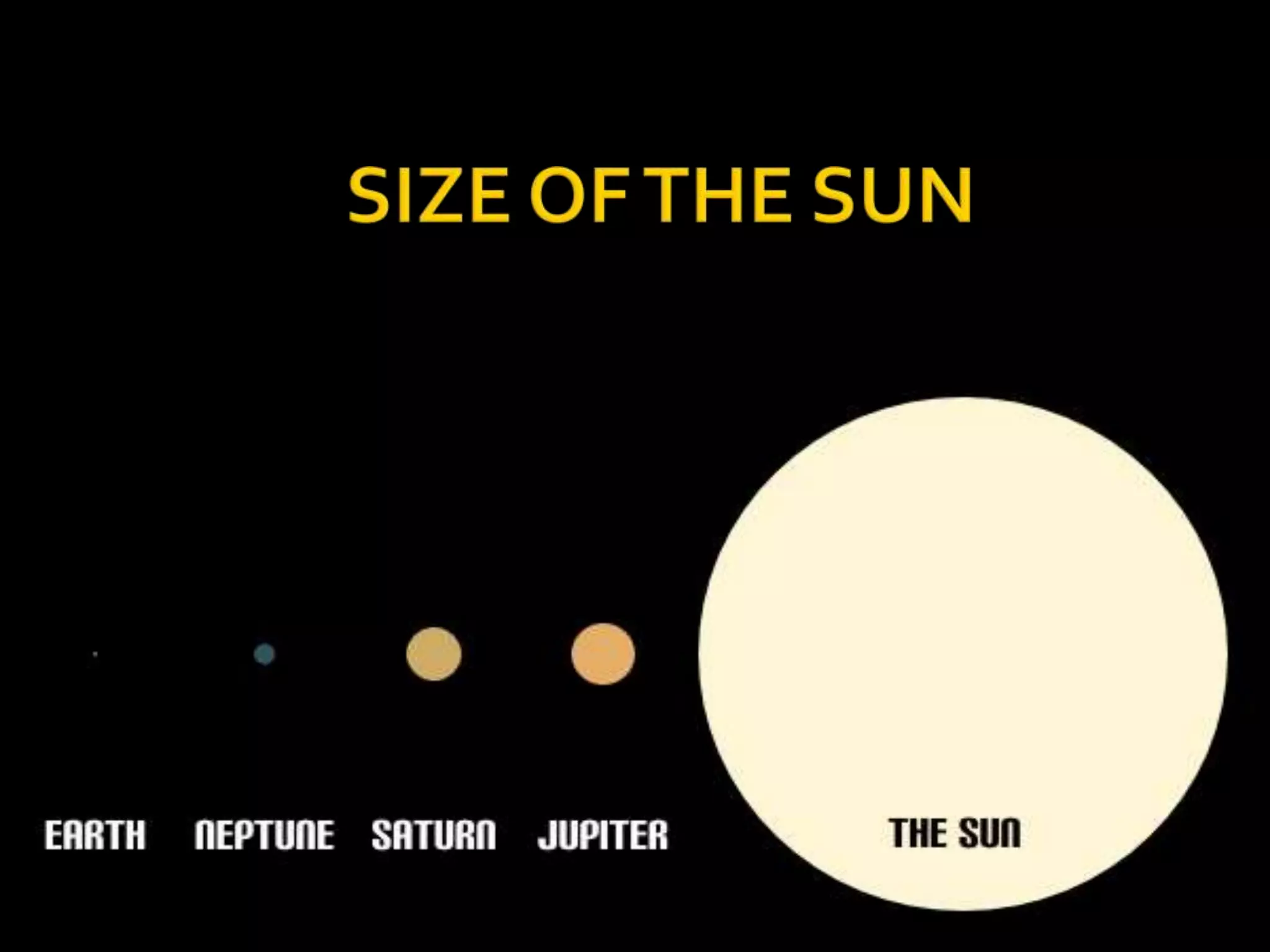
The Solar System formed approximately 4.6 billion years ago from the collapse of a giant molecular cloud. It consists mainly of the Sun and eight planets that orbit it. The four inner terrestrial planets are composed of rock and metal, while the four outer gas giants are substantially larger and composed of hydrogen, helium, and ices. Other objects in the Solar System include dwarf planets, moons, asteroids, and comets. The Sun contains over 99% of the mass in the entire system.