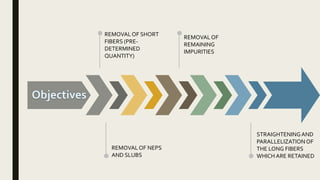
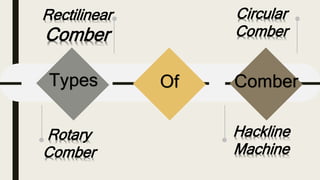
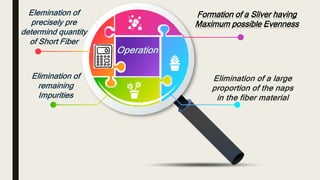
The document discusses the combing process, which takes a carded or drawn sliver and minimizes short fibers, fragments, and impurities to produce a cleaner sliver with a more rectangular staple diagram and parallel, straightened fibers. It describes the key steps in combing as removing short fibers, remaining impurities, neps and slubs, and straightening and parallelizing long fibers. Different types of combers are mentioned, including rectilinear, circular, rotary, and hackline machines. The goal of combing is to produce a sliver with maximum possible evenness. Waste removal methods are also summarized.