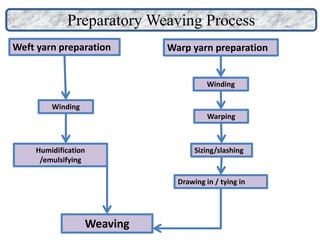
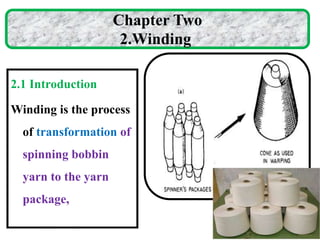
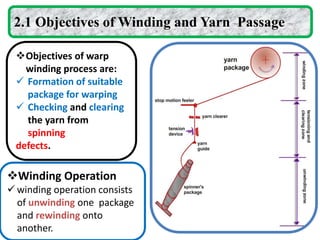
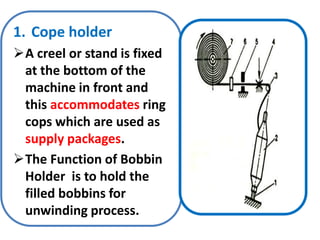
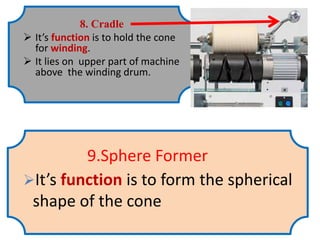
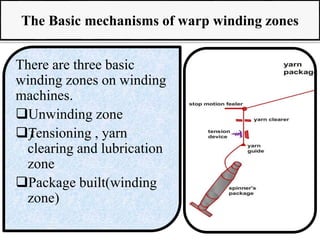
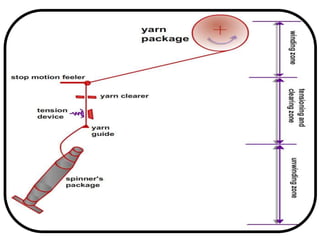
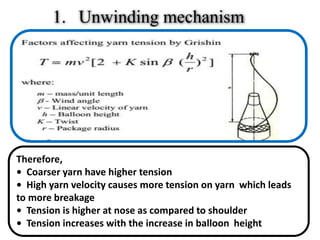
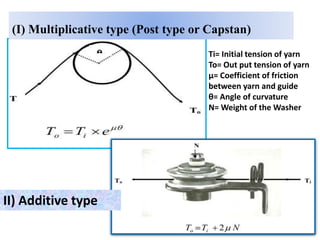
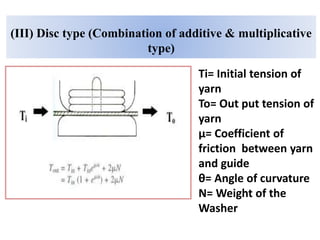
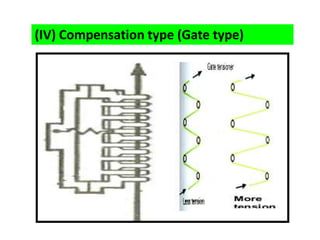
The document provides an overview of the preparatory processes for weaving, including winding, warping, sizing, and drawing-in. It focuses on winding, describing the key components of a winding machine like the balloon breaker, tensioner, and clearer. The mechanisms of winding include unwinding from the supply package, tensioning and clearing the yarn, and building the wound package. Tension is important for winding density and removing defects, and can be achieved through multiplicative, additive, disc, or compensation tension devices. The target audience is third year textile engineering students.