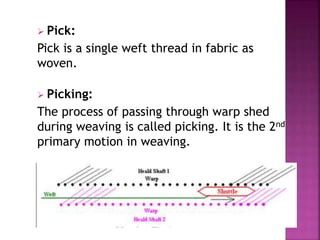
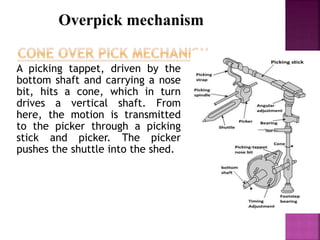
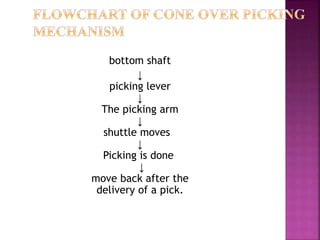
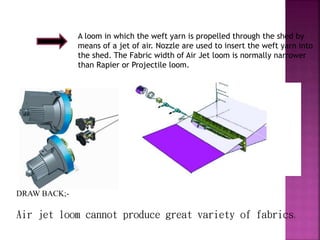
This document discusses different types of picking and picking mechanisms used in weaving. It begins with an introduction to picking, which is the process of passing the weft yarn through the warp shed during weaving. It then describes various picking mechanisms including overpicking, underpicking, and cone overpick and underpick mechanisms. The document provides details on how these different mechanisms work to insert the weft yarn through the shed. It concludes with advantages and disadvantages of different weft insertion methods like projectile, rapier, air jet, and water jet looms.