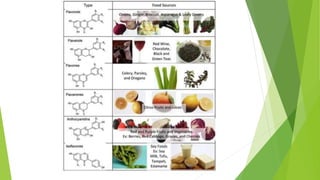
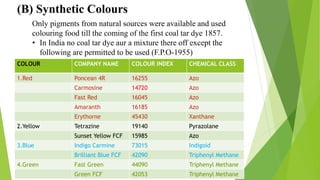
This document discusses natural and synthetic food colorings. It begins by explaining how the color of food impacts acceptance and describes the natural pigments found in fruits and vegetables, including chlorophylls, carotenoids, anthocyanins, flavonoids, and others. It then provides details on each type of natural pigment. The document also discusses the use of synthetic dyes approved for food coloring and precautions for their safe use.