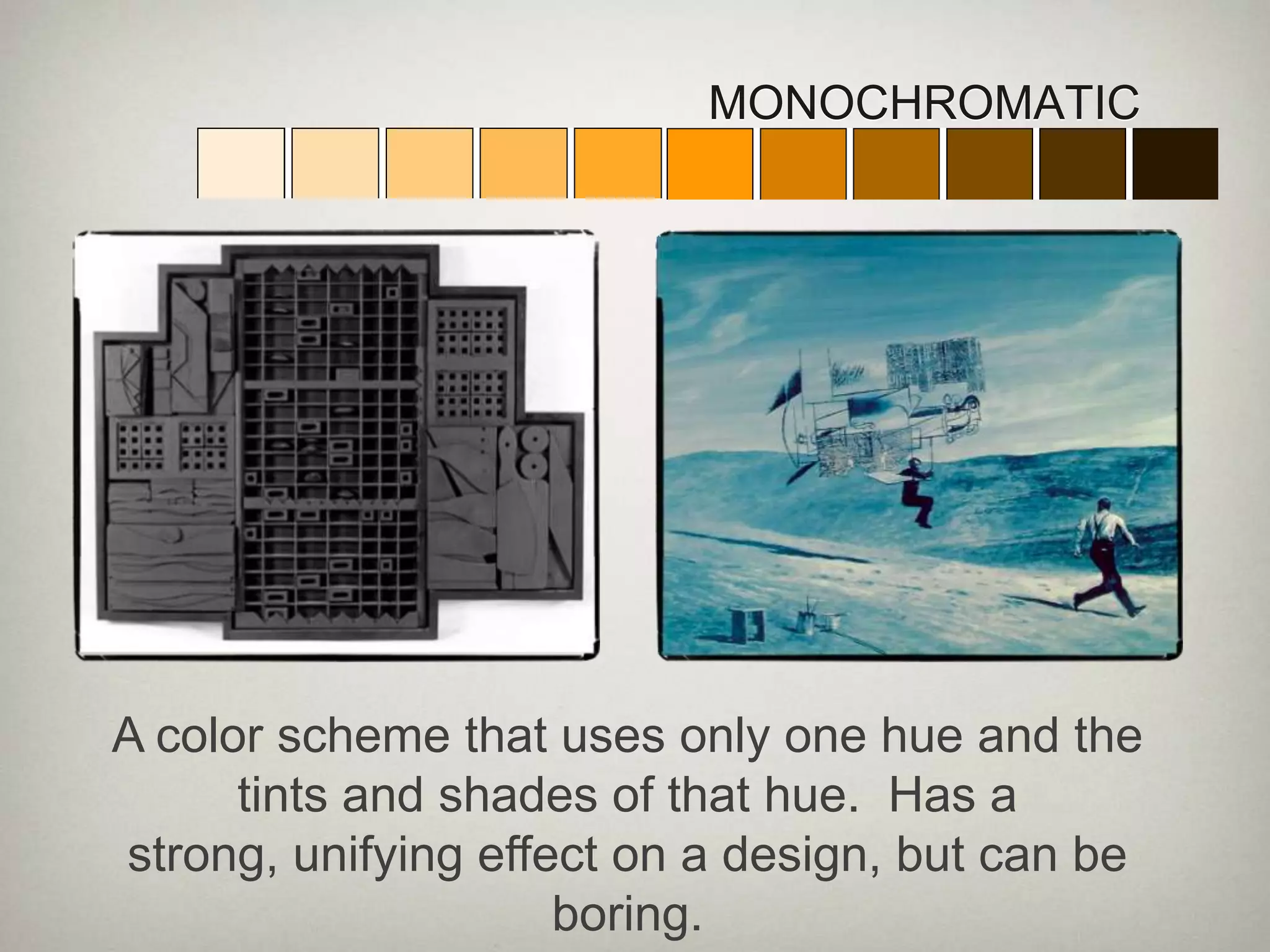
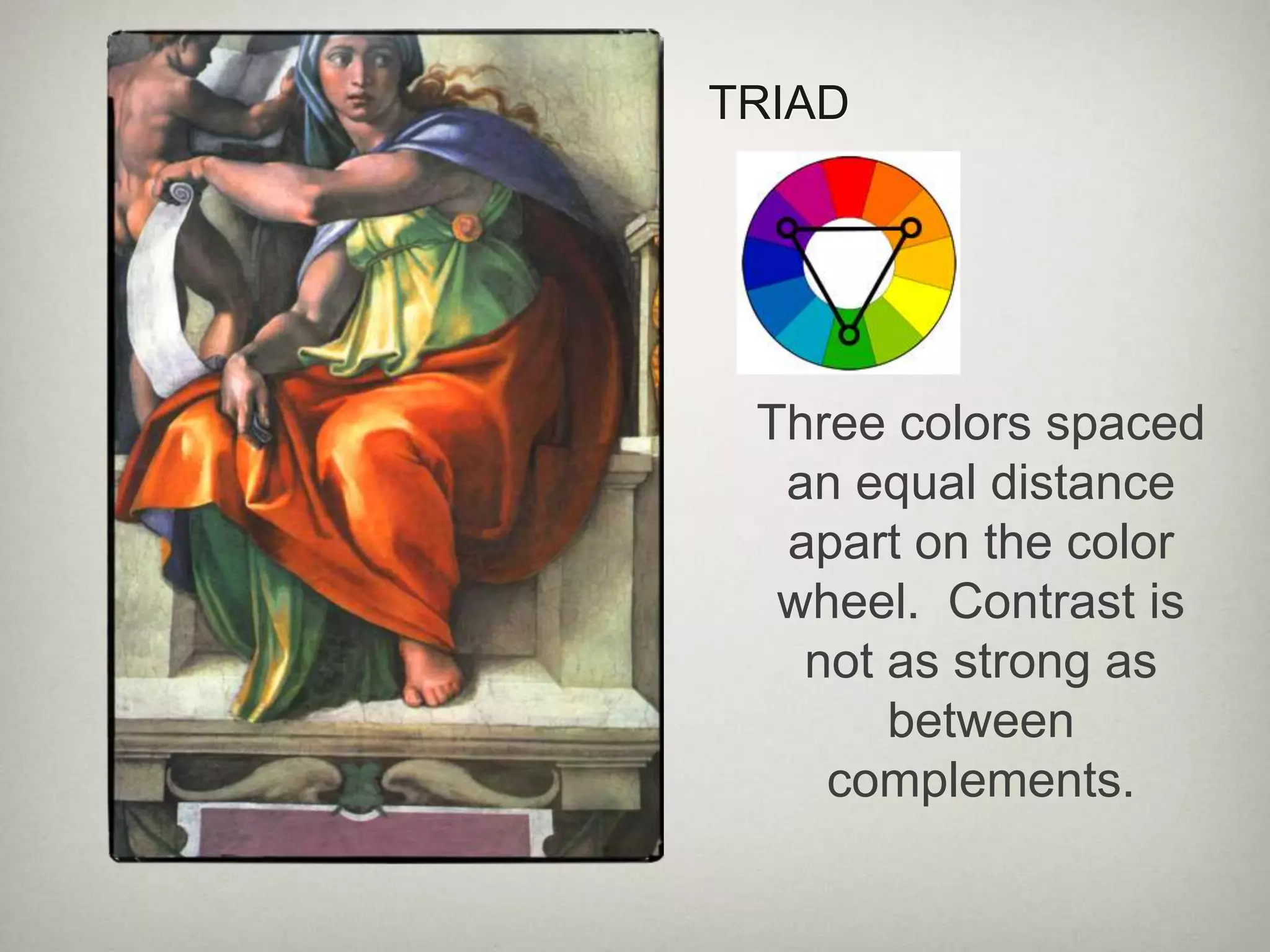
The document defines key color properties and color schemes. It describes hue as the name of a color, value as its lightness or darkness, and intensity as its brightness. It lists red, yellow and blue as primary colors that can produce other hues when mixed. Secondary colors are made from two primaries, and tertiary colors combine a primary with a secondary. Monochromatic uses one hue in different tones, while complementary mixes a hue with its opposite on the wheel. Analogous uses adjacent hues, and warm colors seem to advance while cool colors recede.