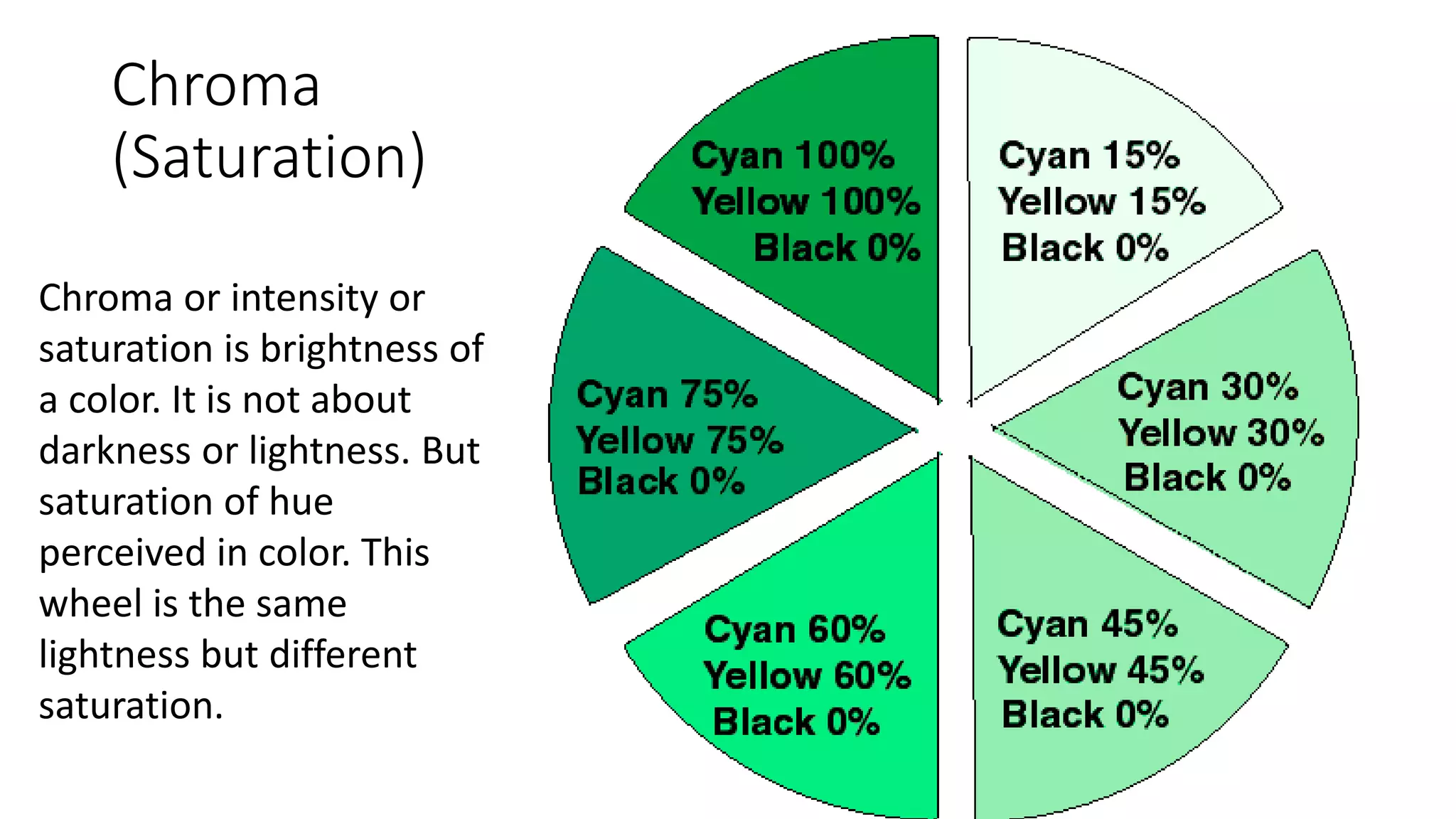
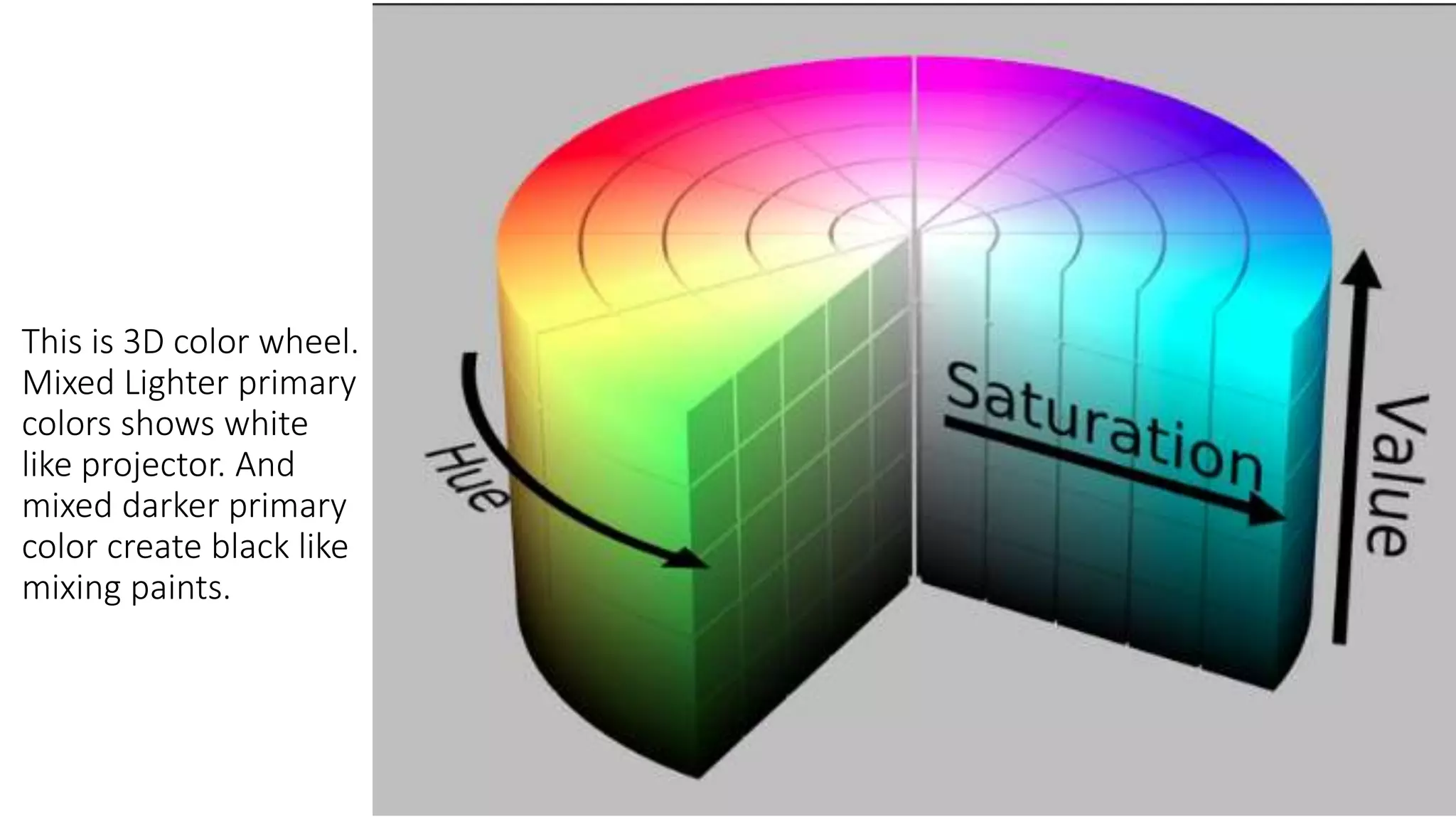
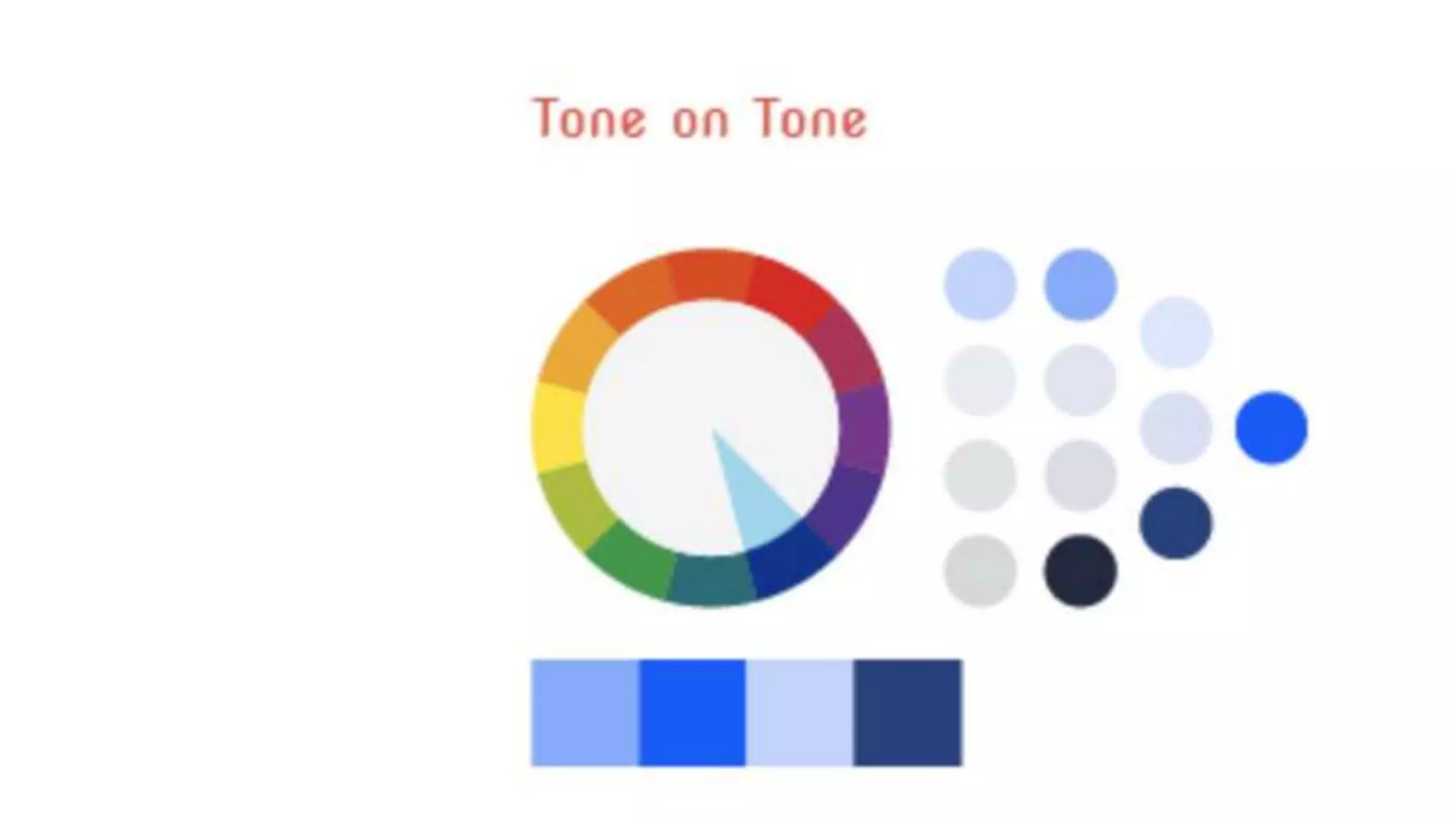
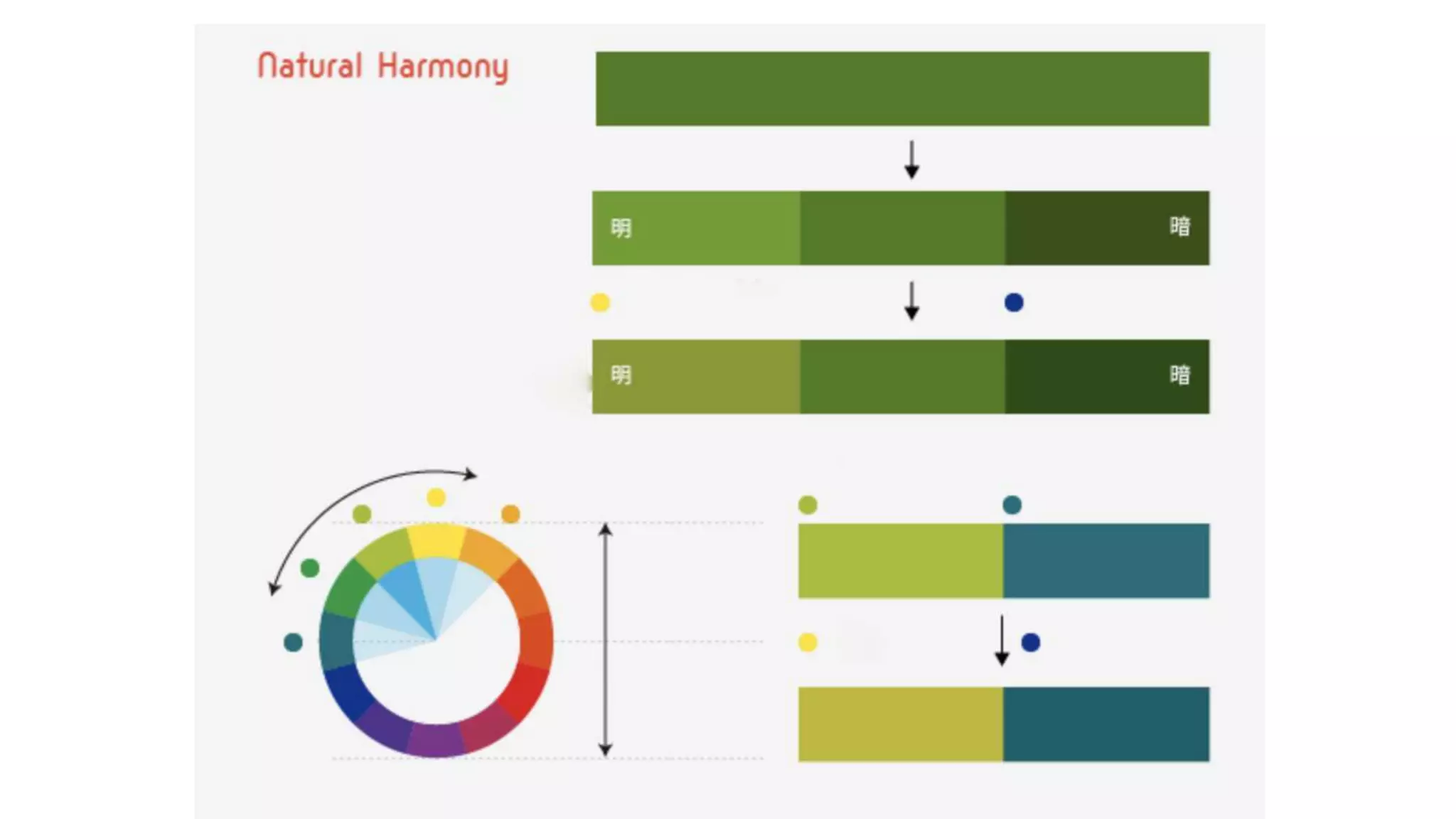
This document discusses color theory and the key elements of color including hue, value, chroma, temperature, and basic color combinations. It explains that hue is the name of a color, value is the lightness or darkness, and chroma is the brightness or saturation. The color wheel is presented showing primary, secondary and tertiary colors. Color mixing and perception are also covered along with how color is used differently based on season. Proportions of base, main and accent colors are important in design as well as line, saturation and temperature.