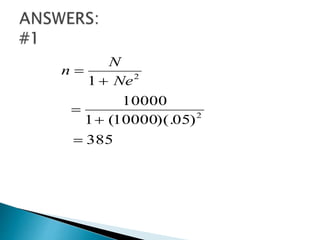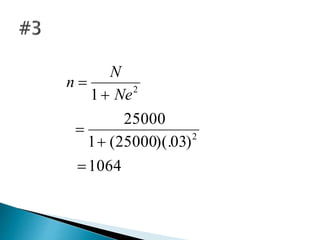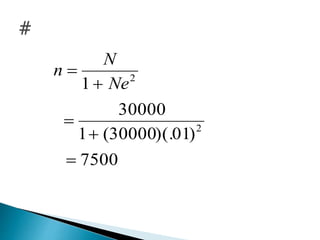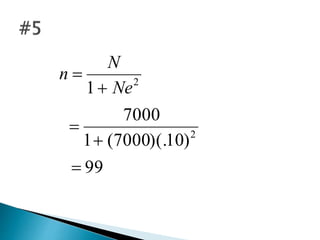This document discusses various methods for collecting data for research studies, including documentary sources, field sources, and experimental methods. Documentary sources provide detailed, accurate, and reliable data through published and unpublished reports from primary or secondary sources. Field sources involve collecting data directly from individuals through interviewing or questionnaires. Interviewing allows for consistent data but is time-consuming, while questionnaires are inexpensive but have low response rates. Experimental methods determine cause-and-effect relationships and are used in scientific inquiries. The document also provides formulas for calculating sample sizes from populations with given margin of errors.