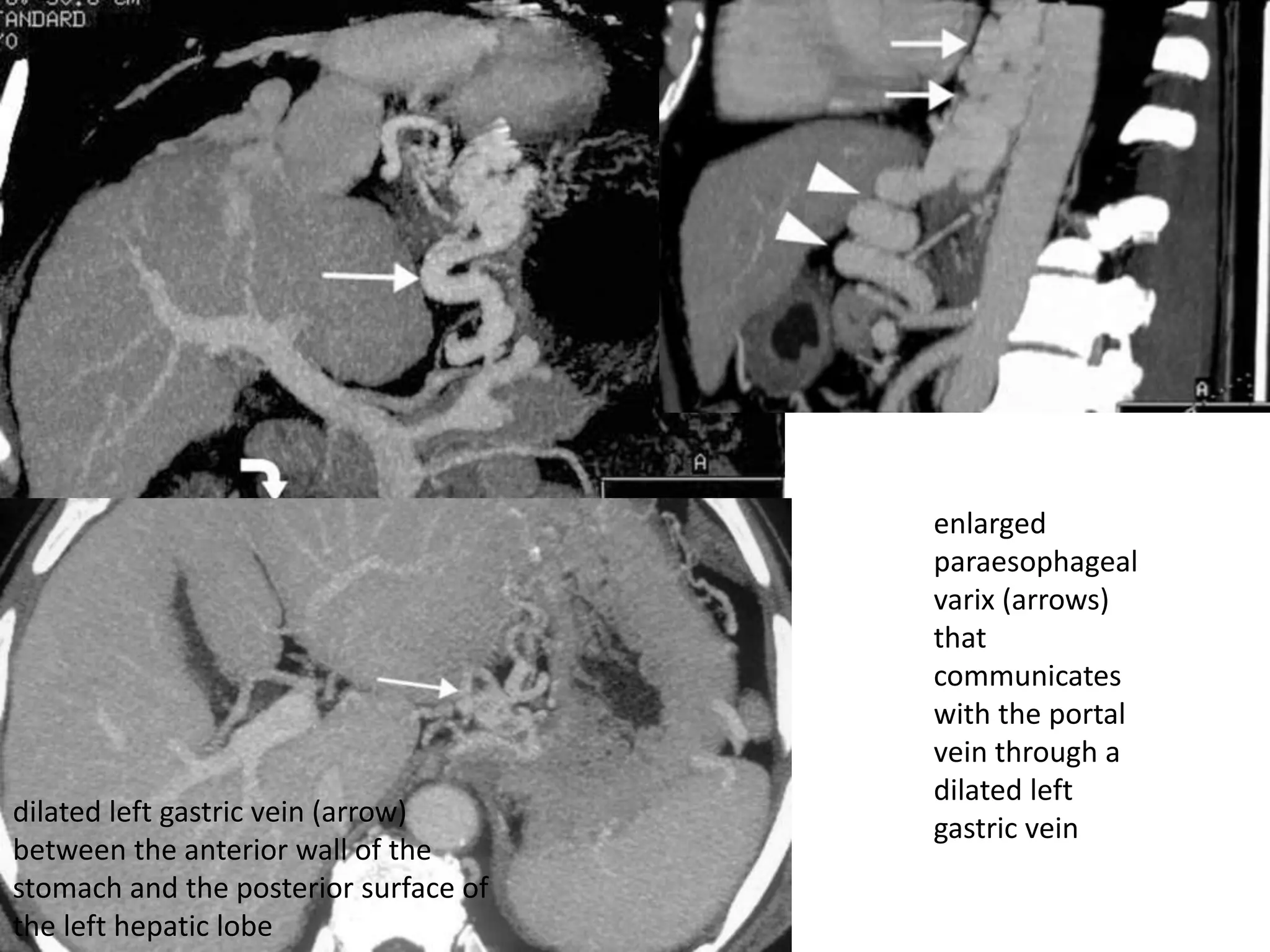
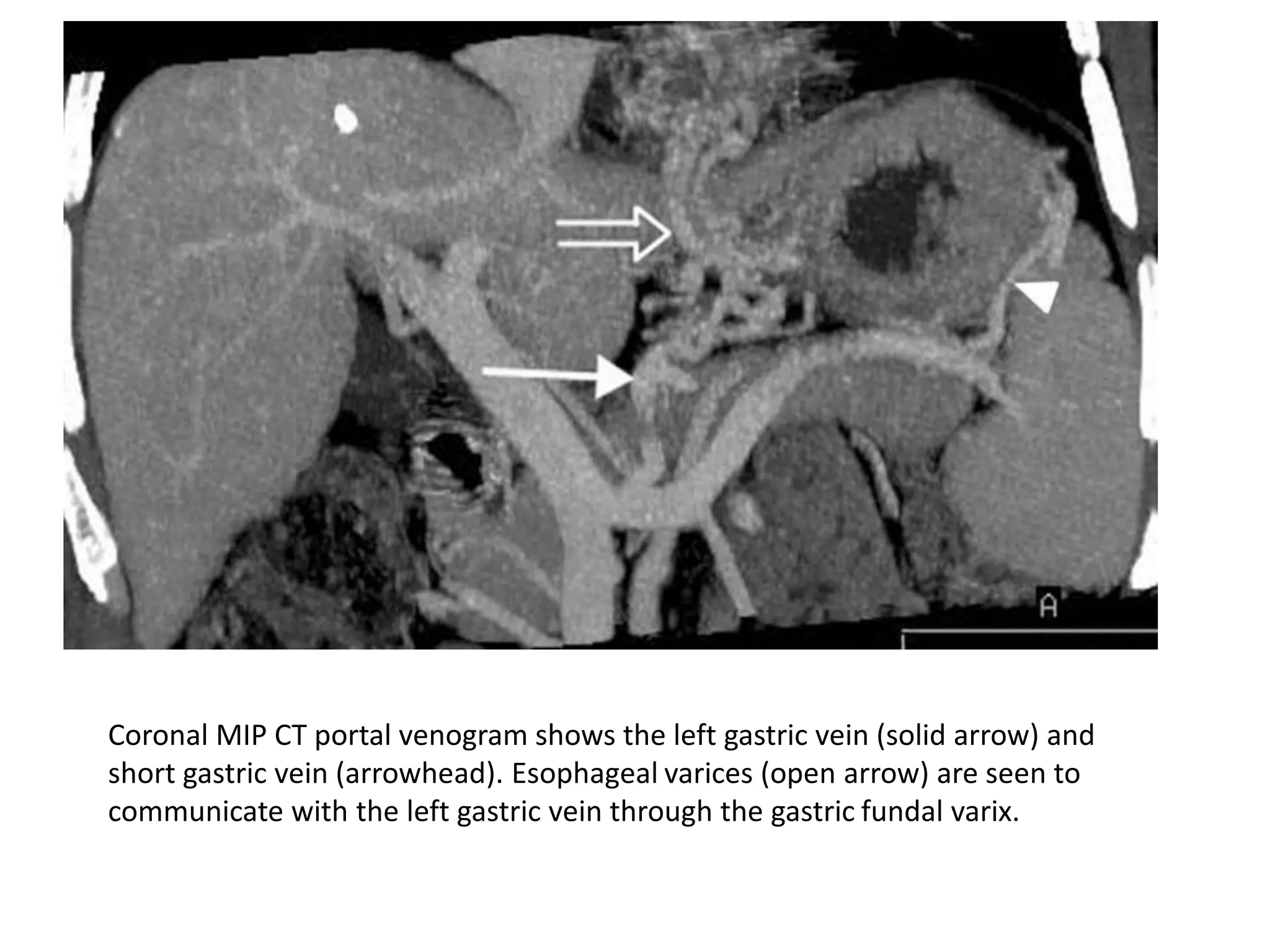
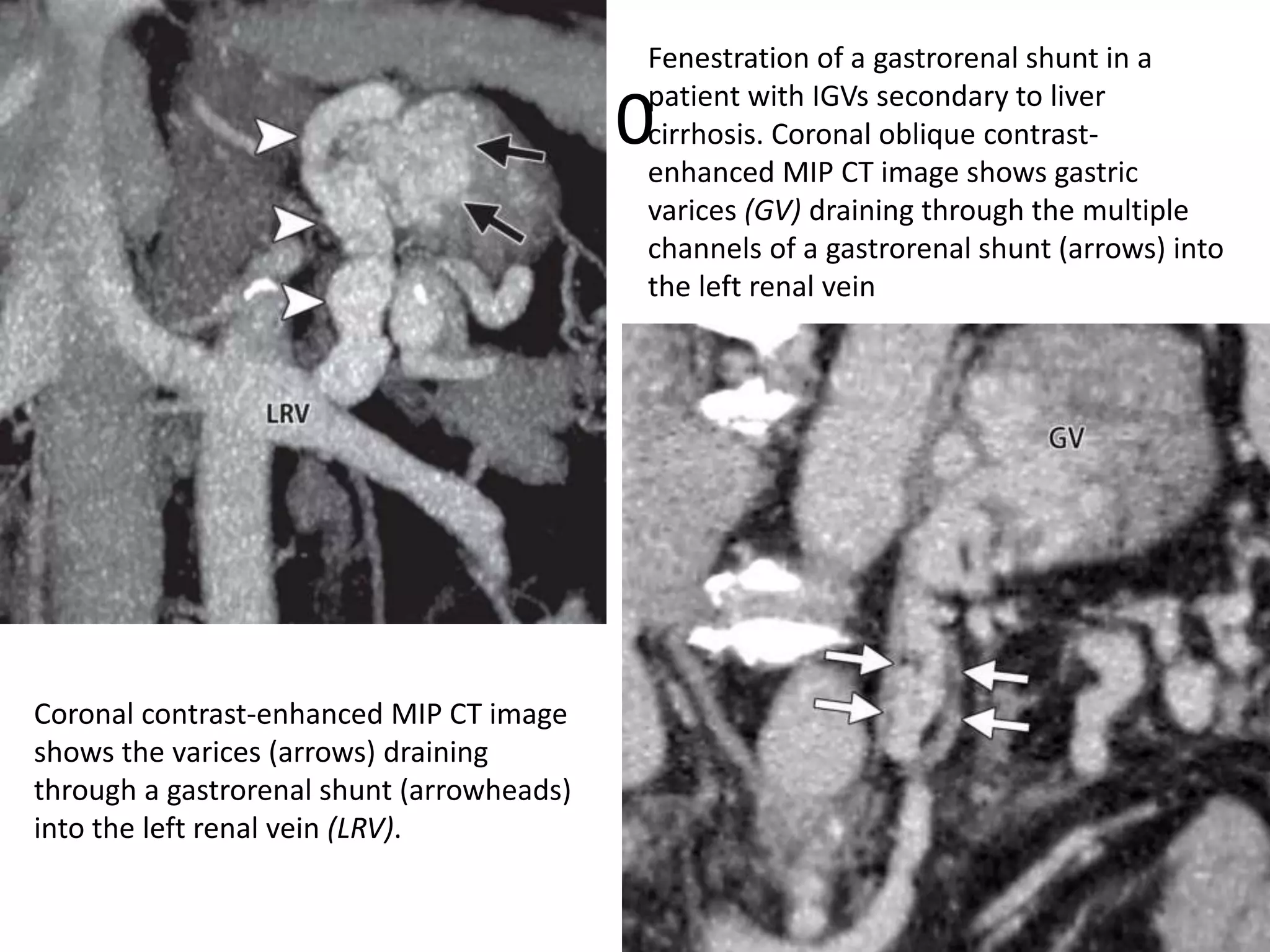
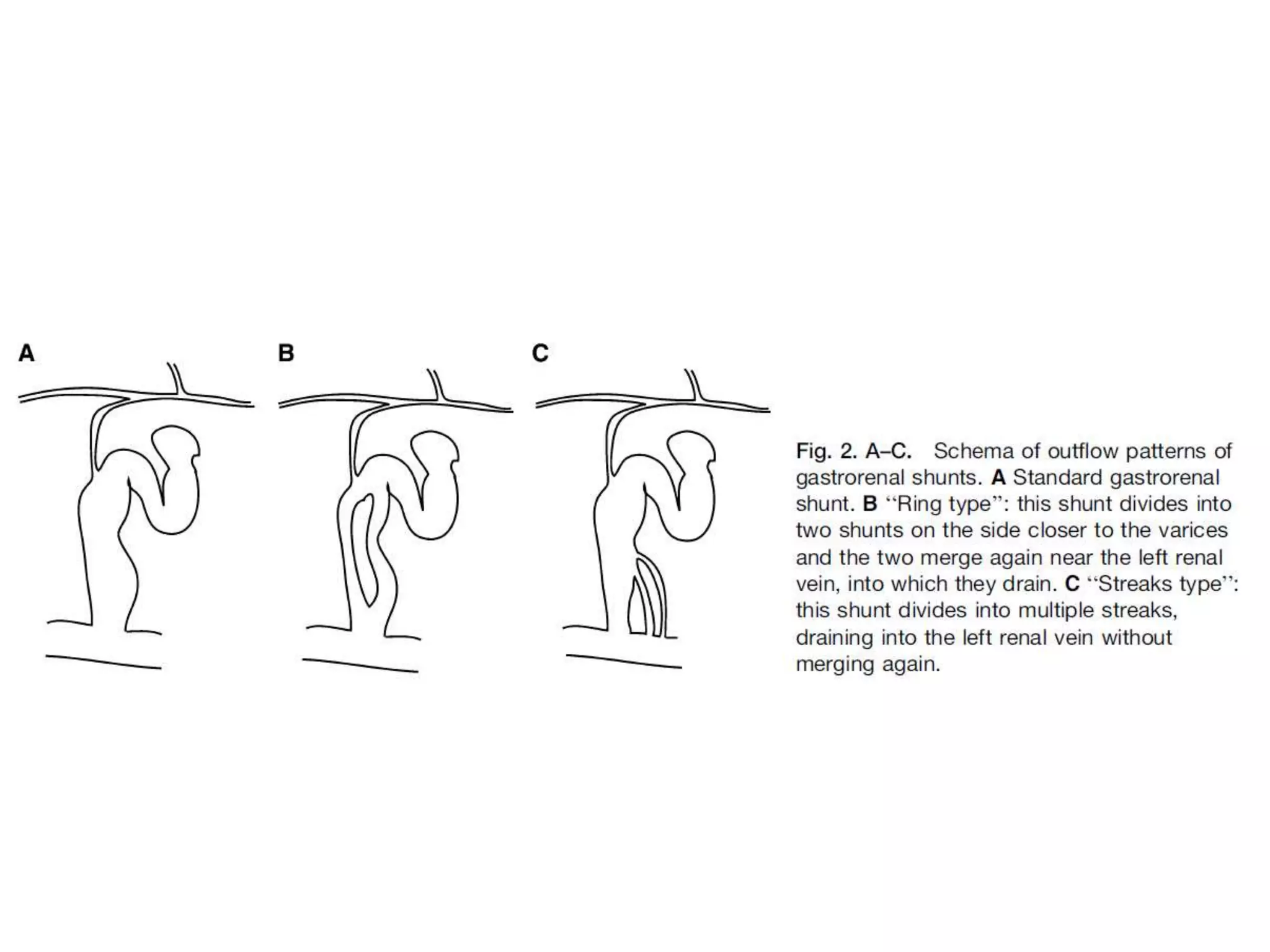
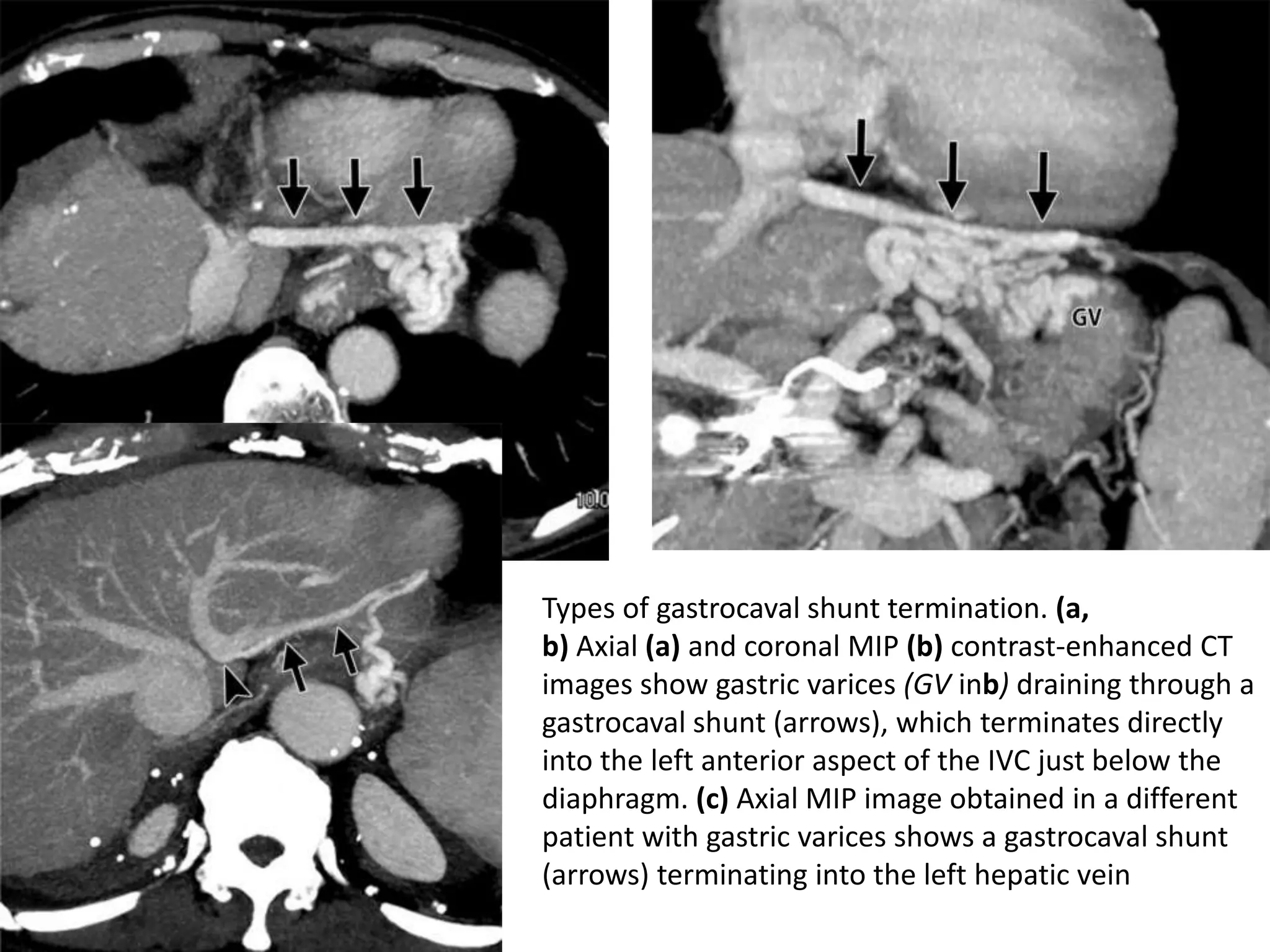
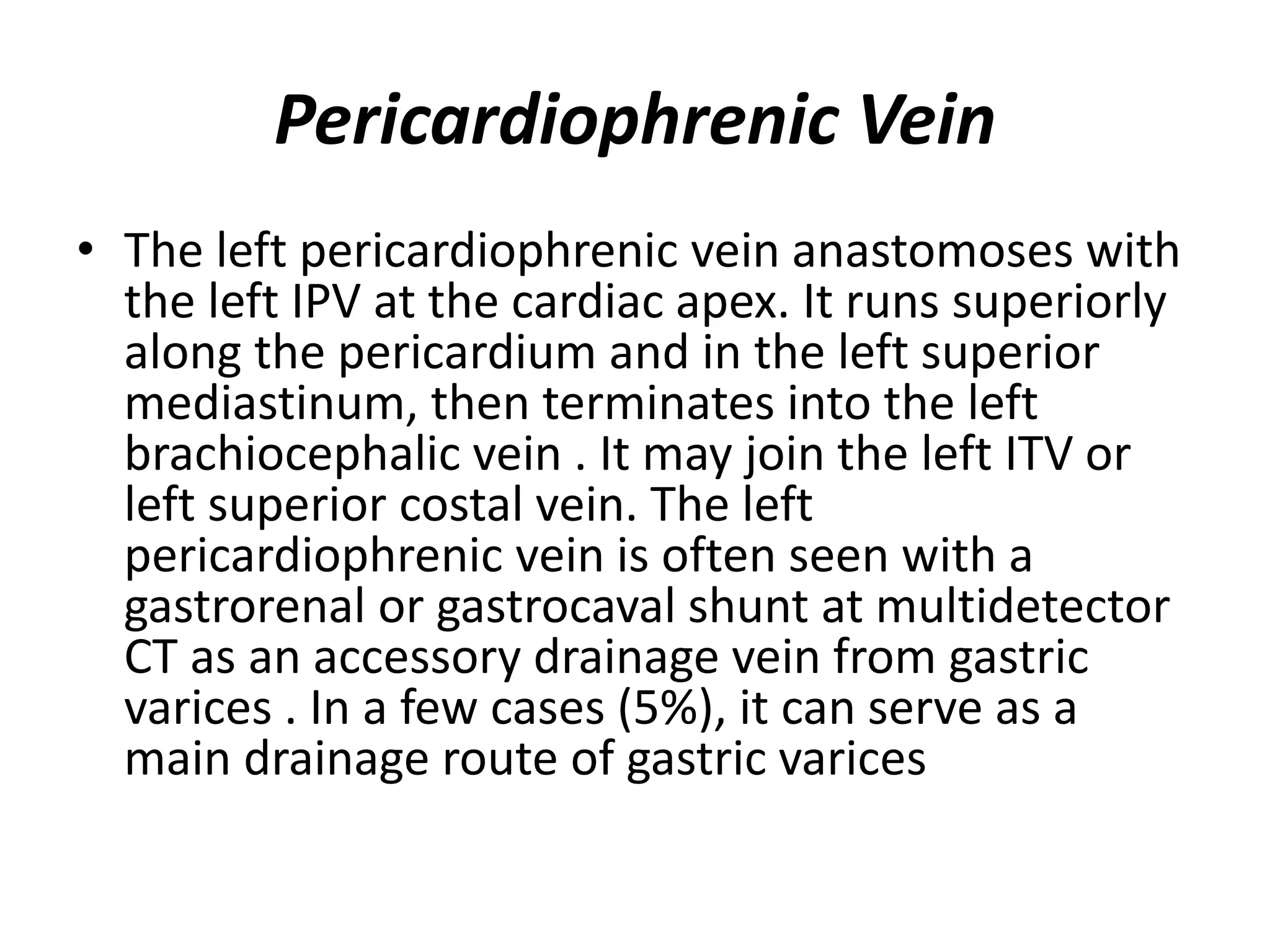
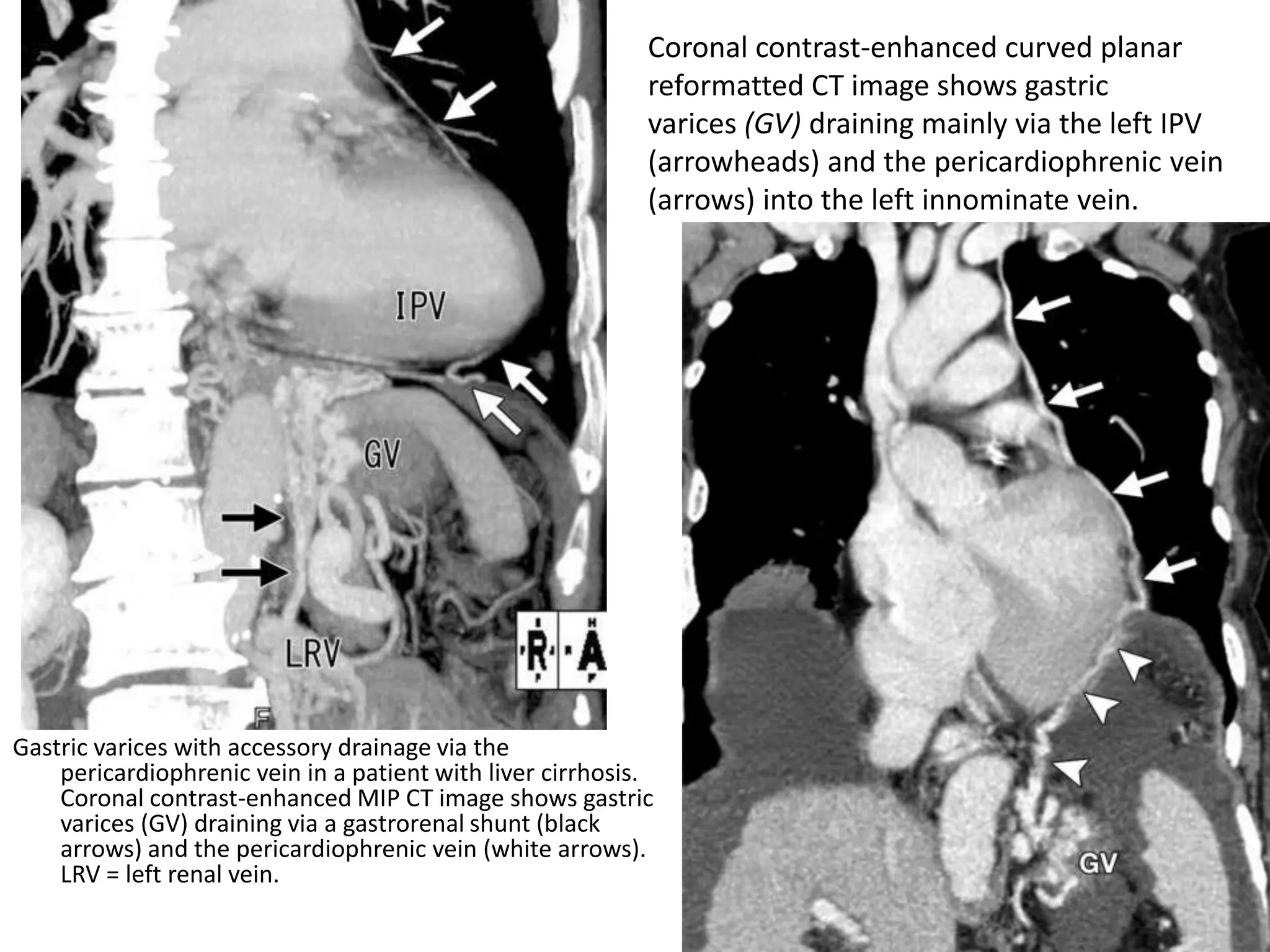
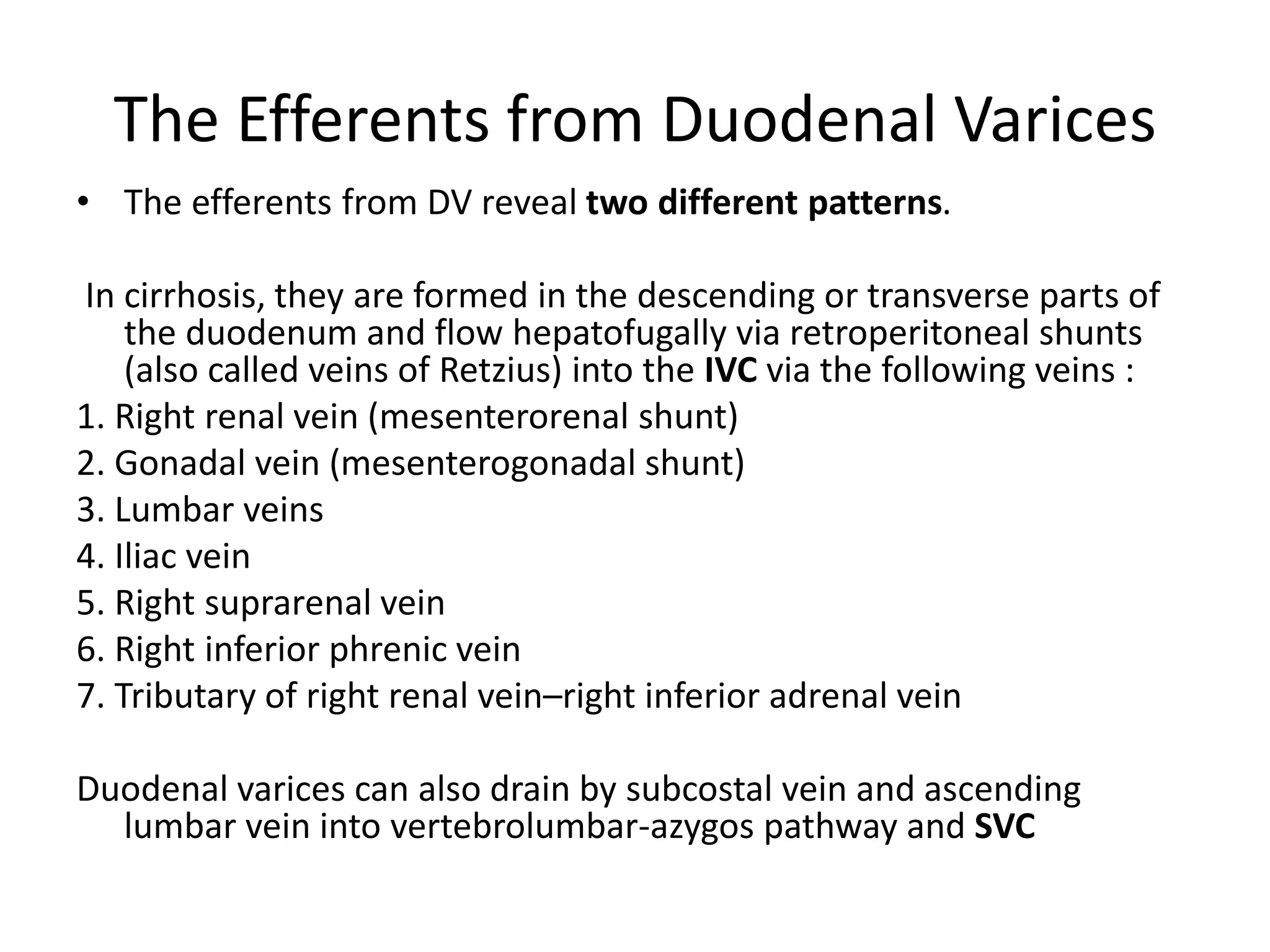
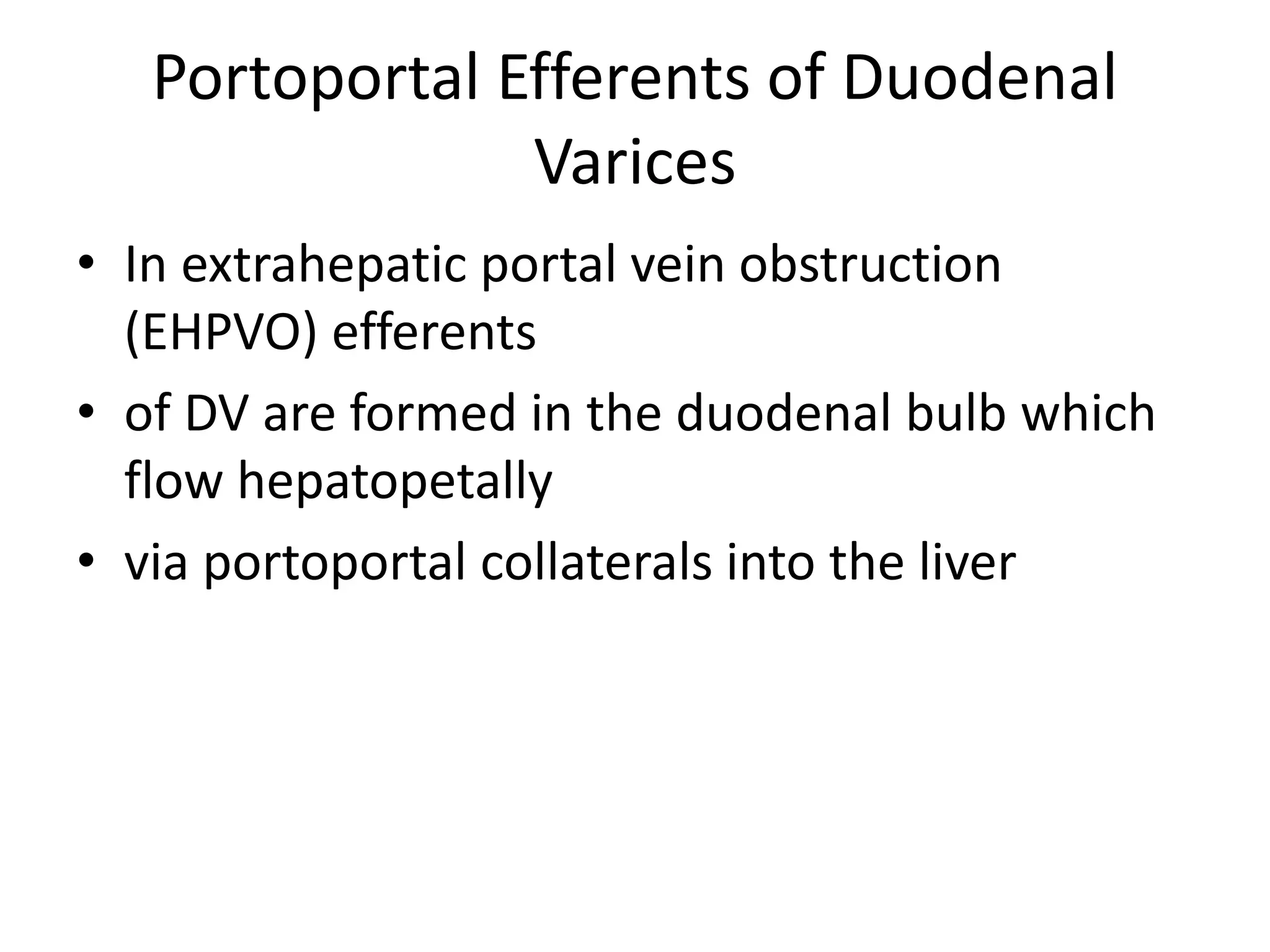
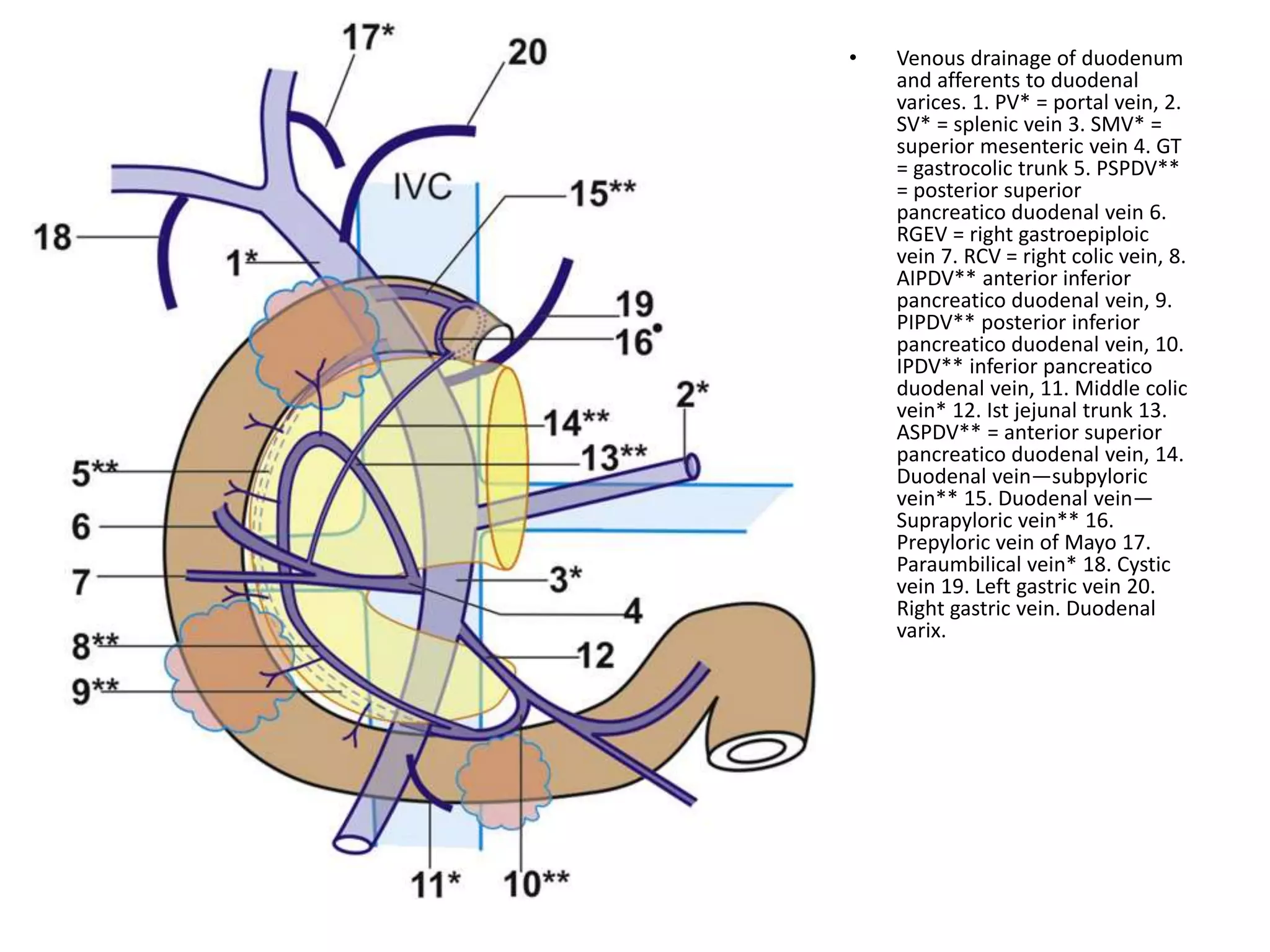
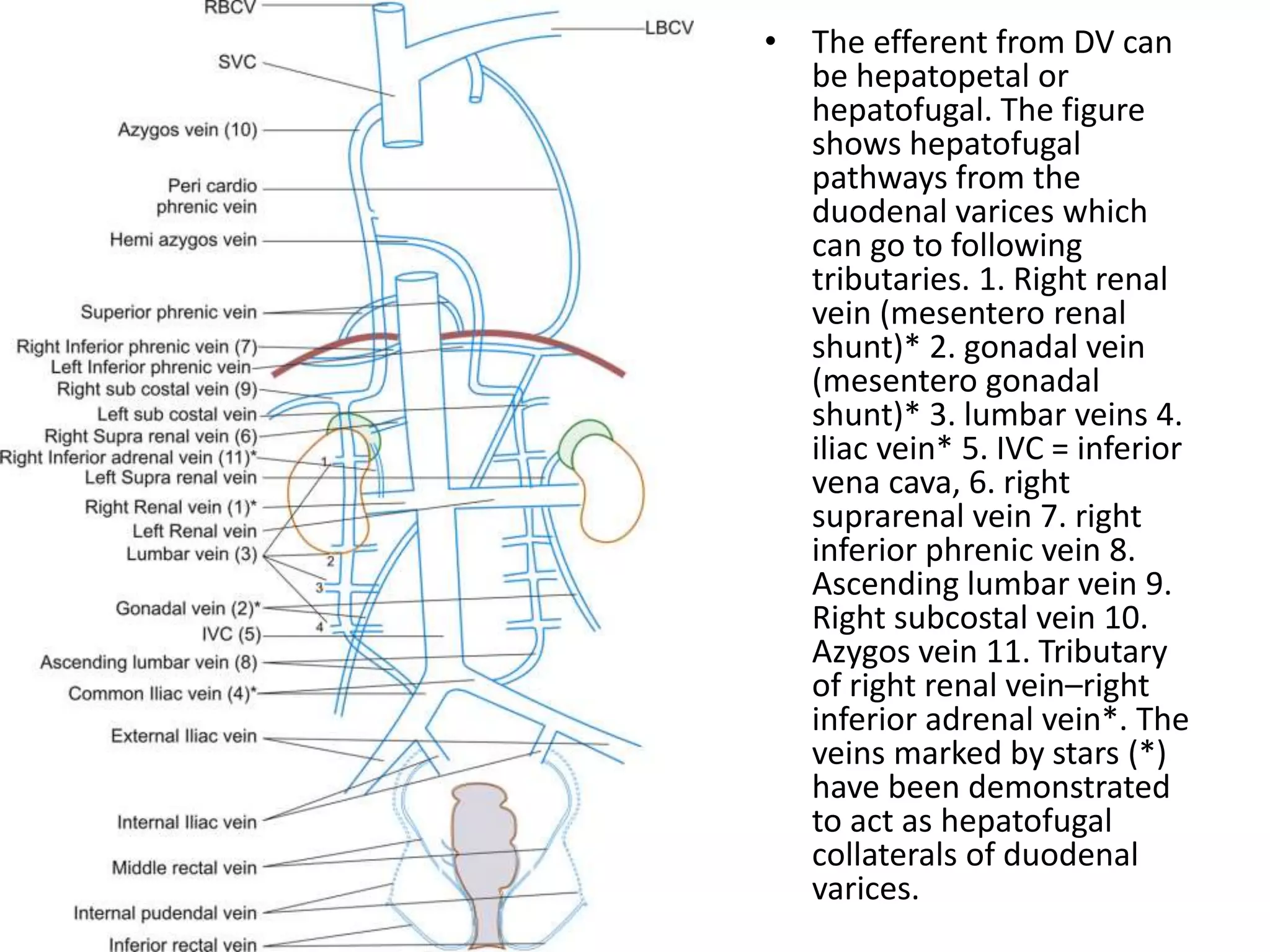
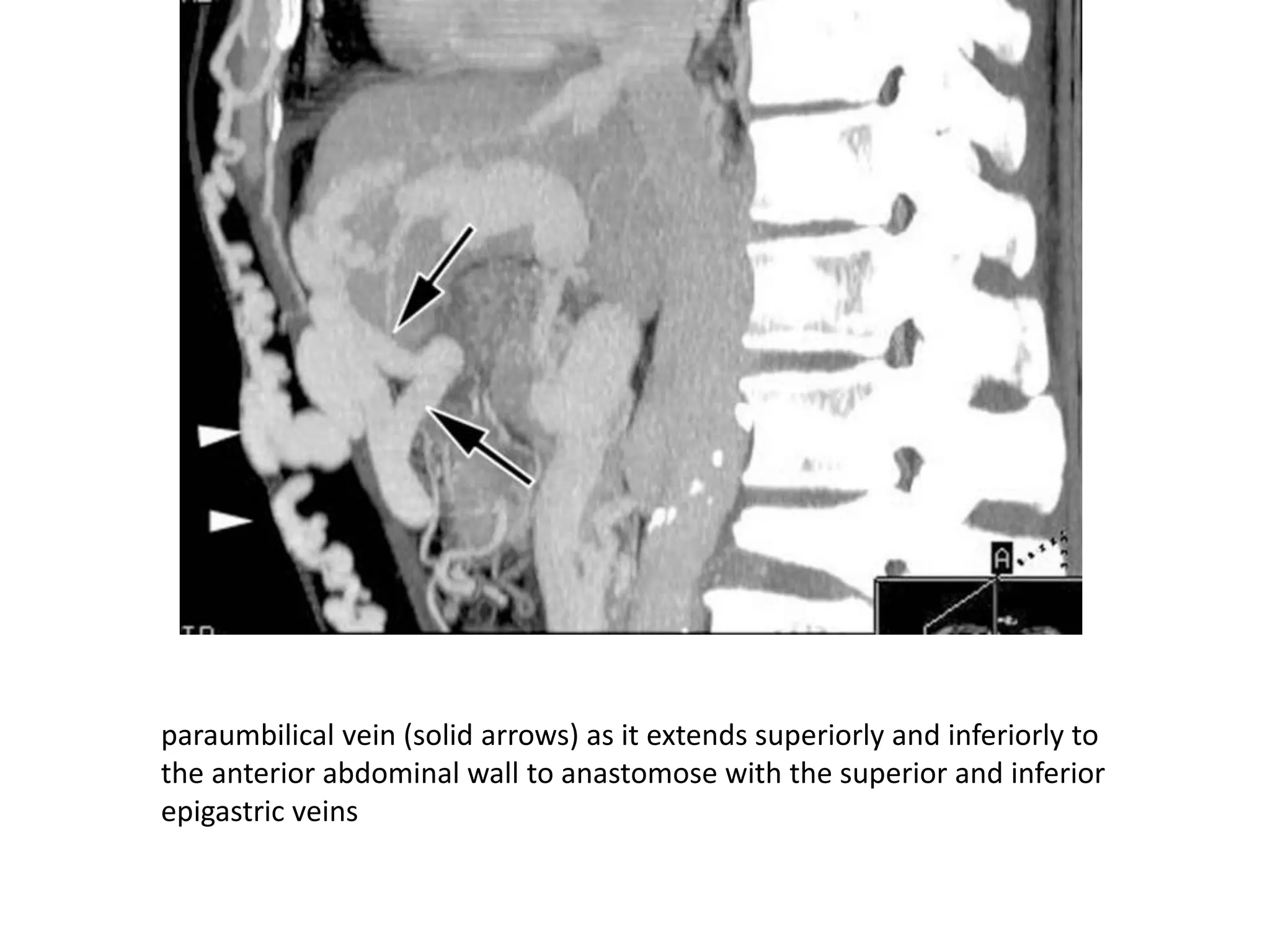
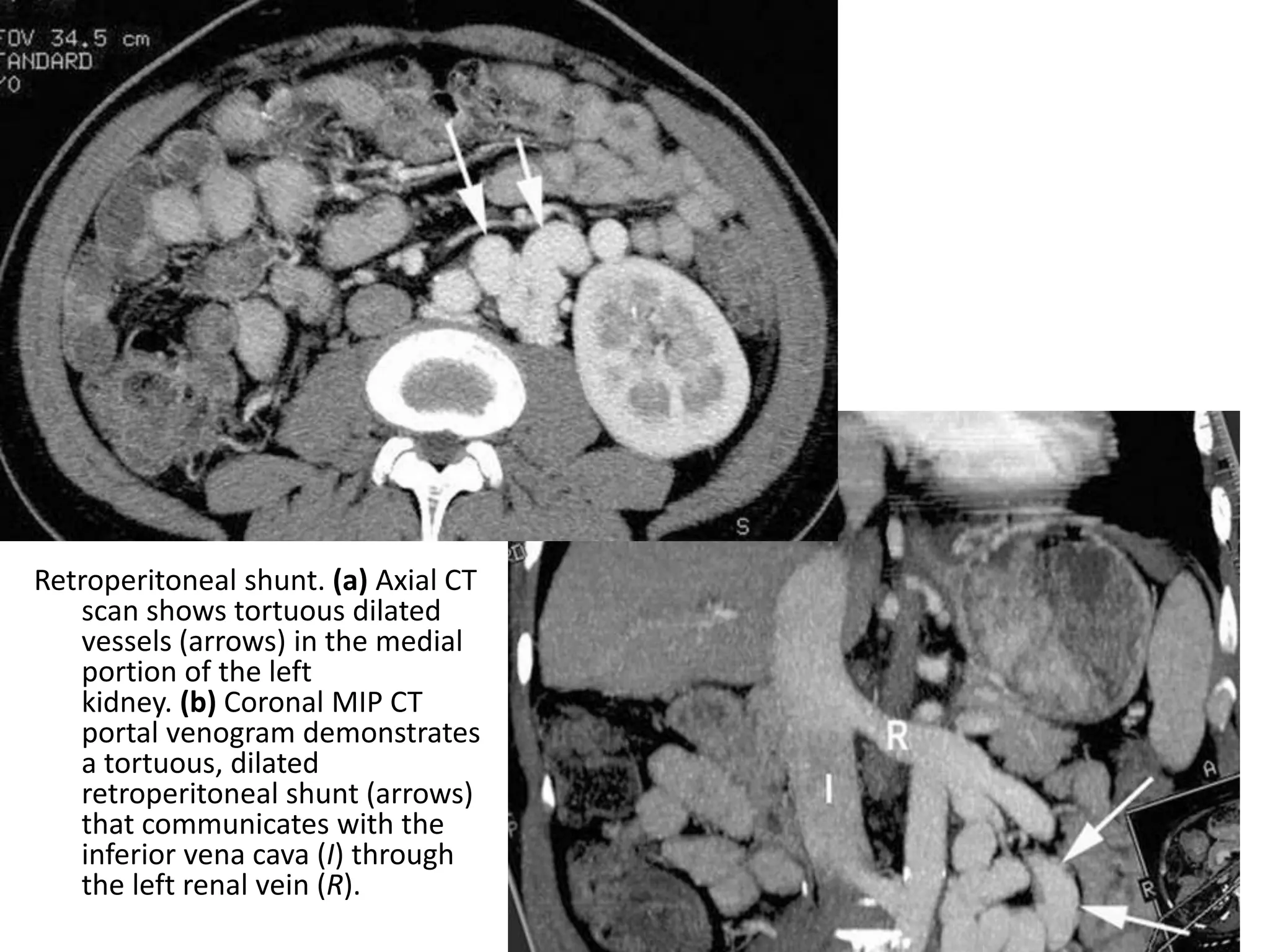
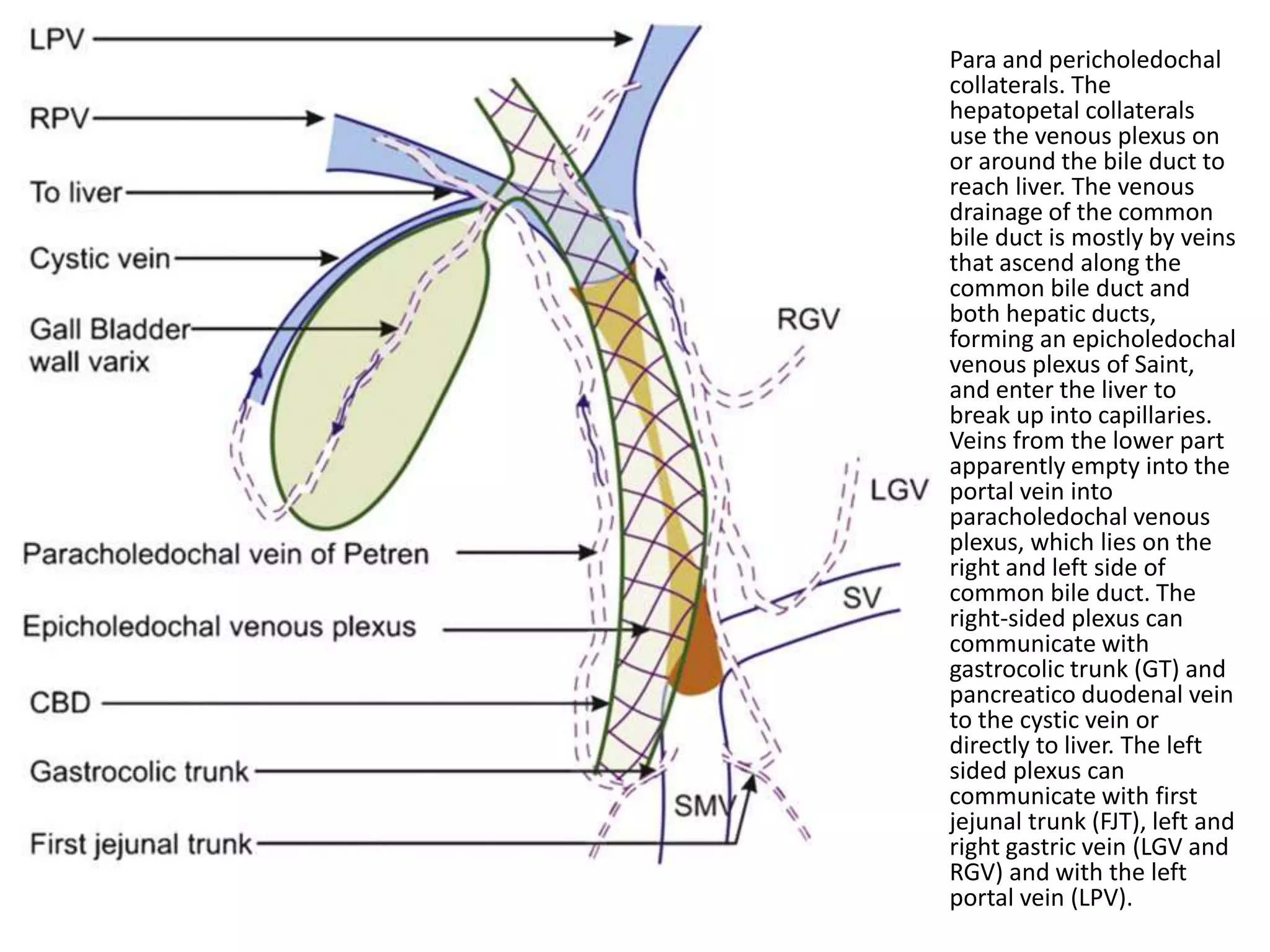
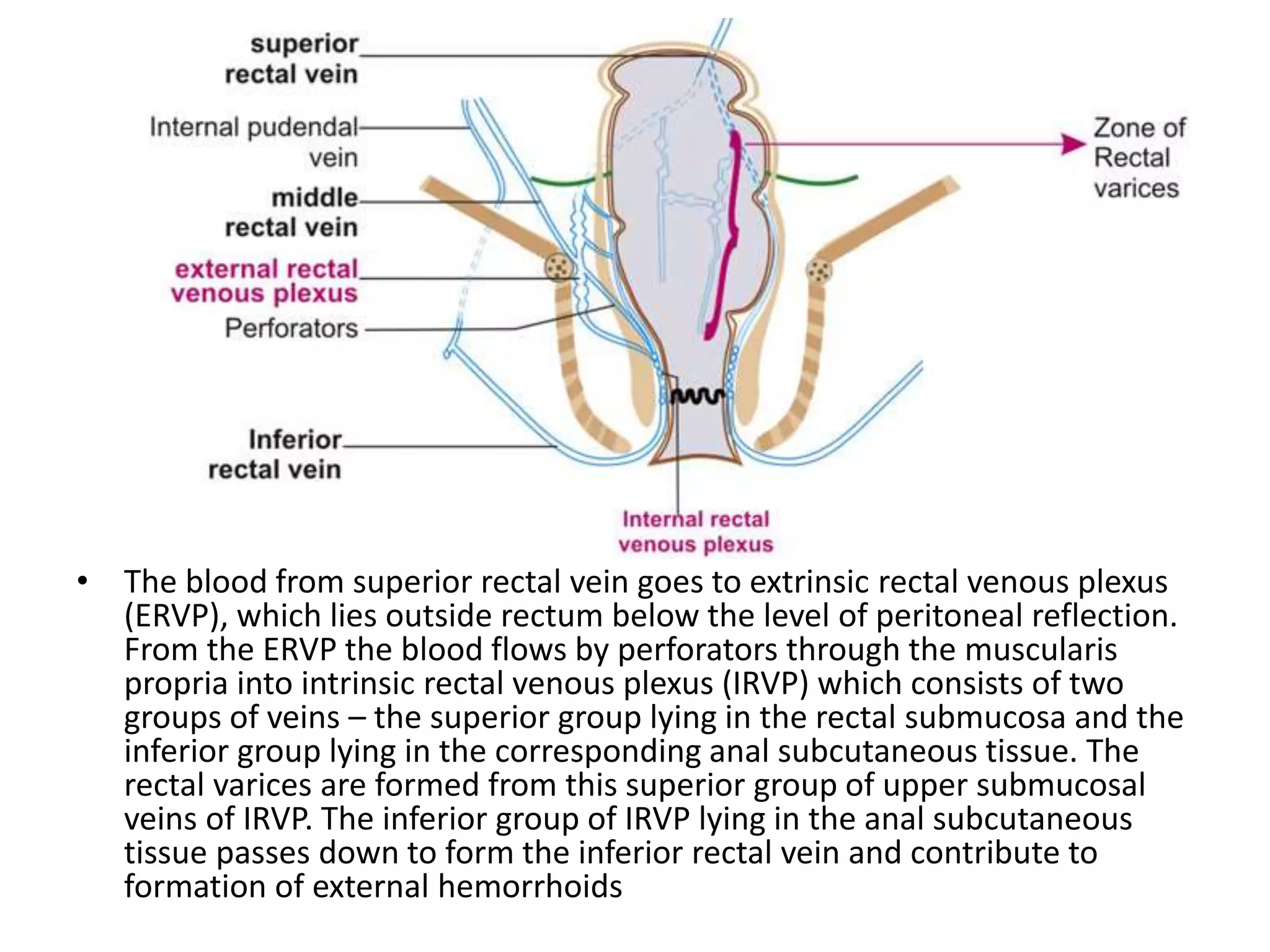
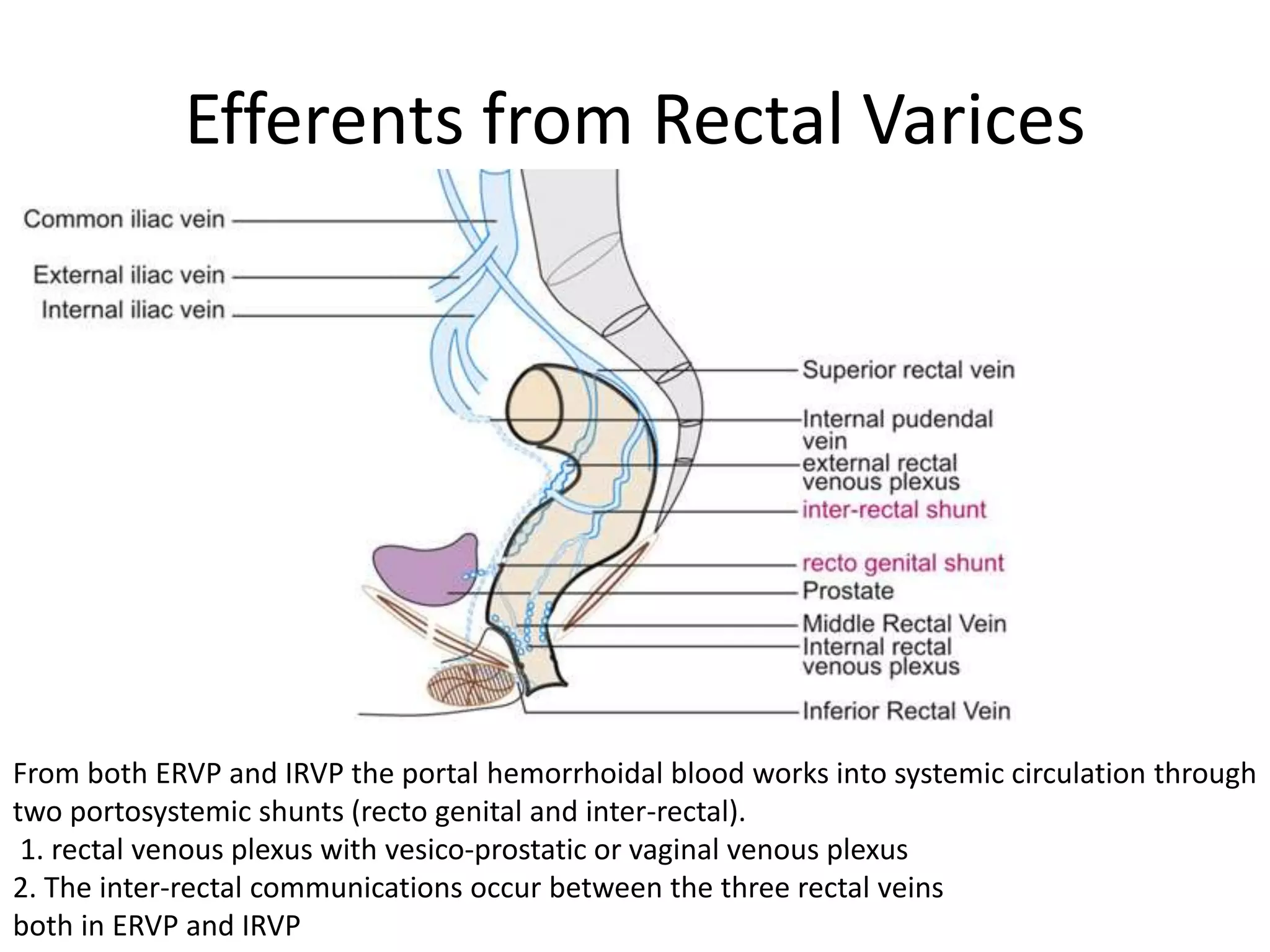
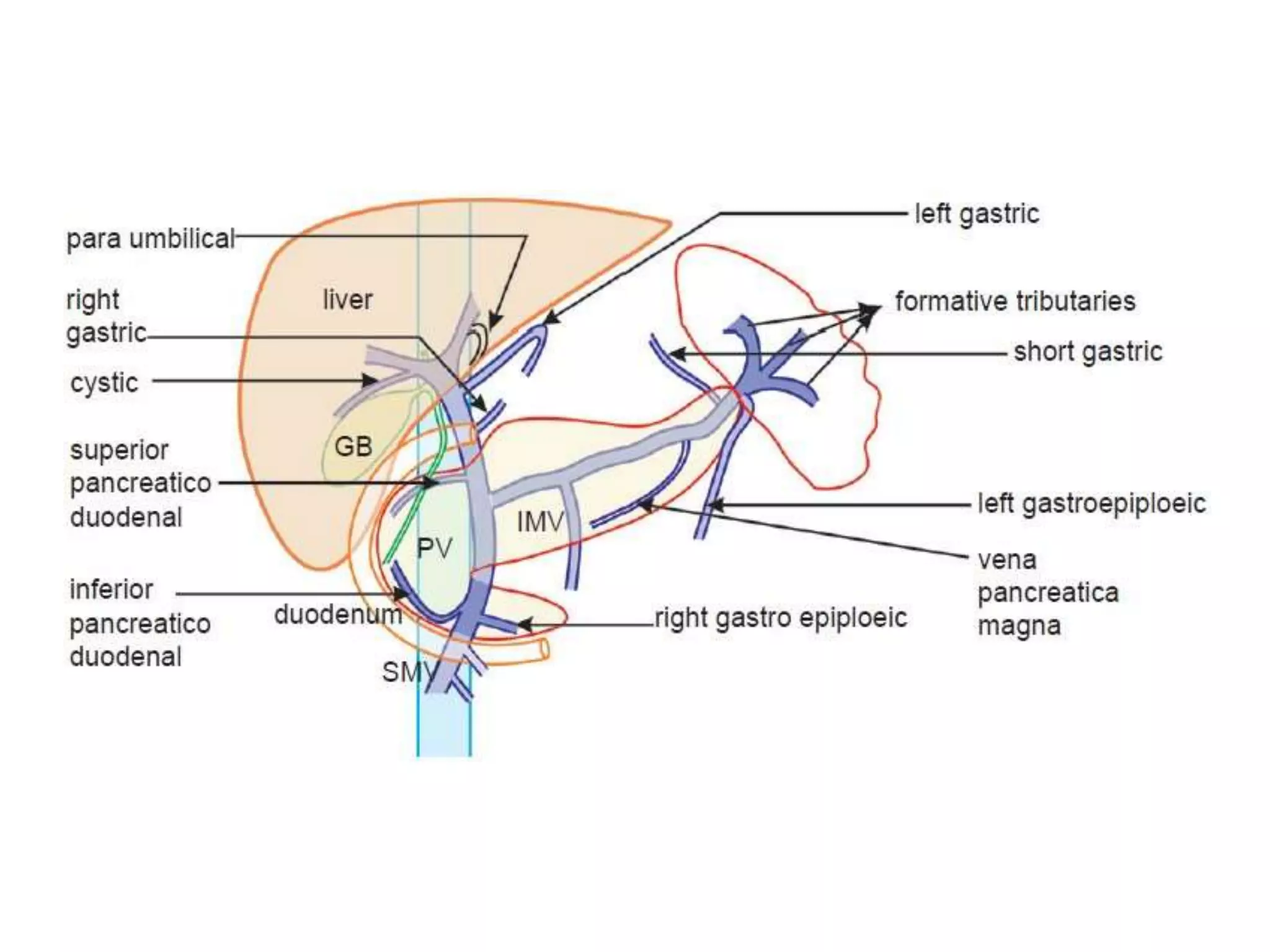
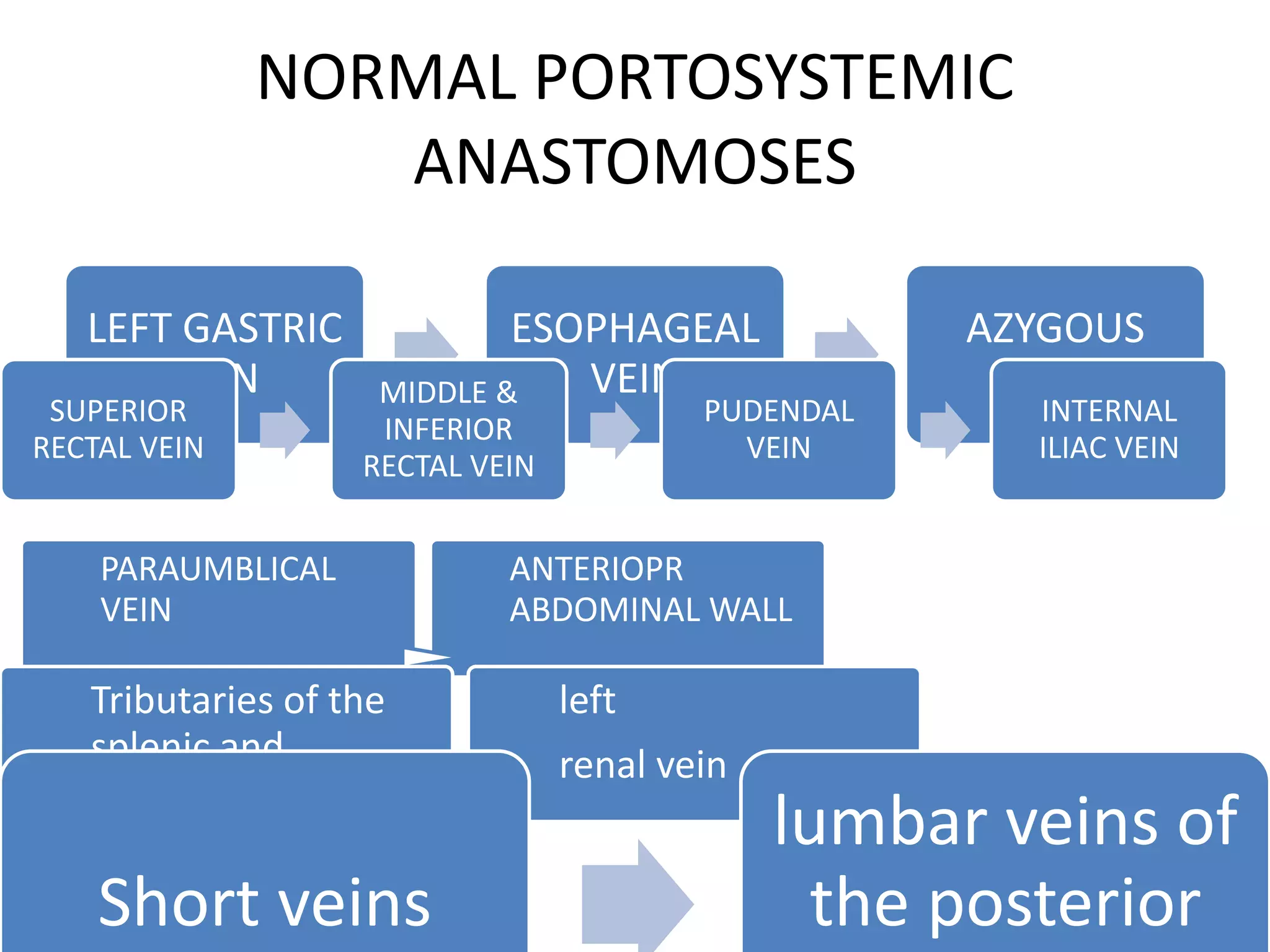
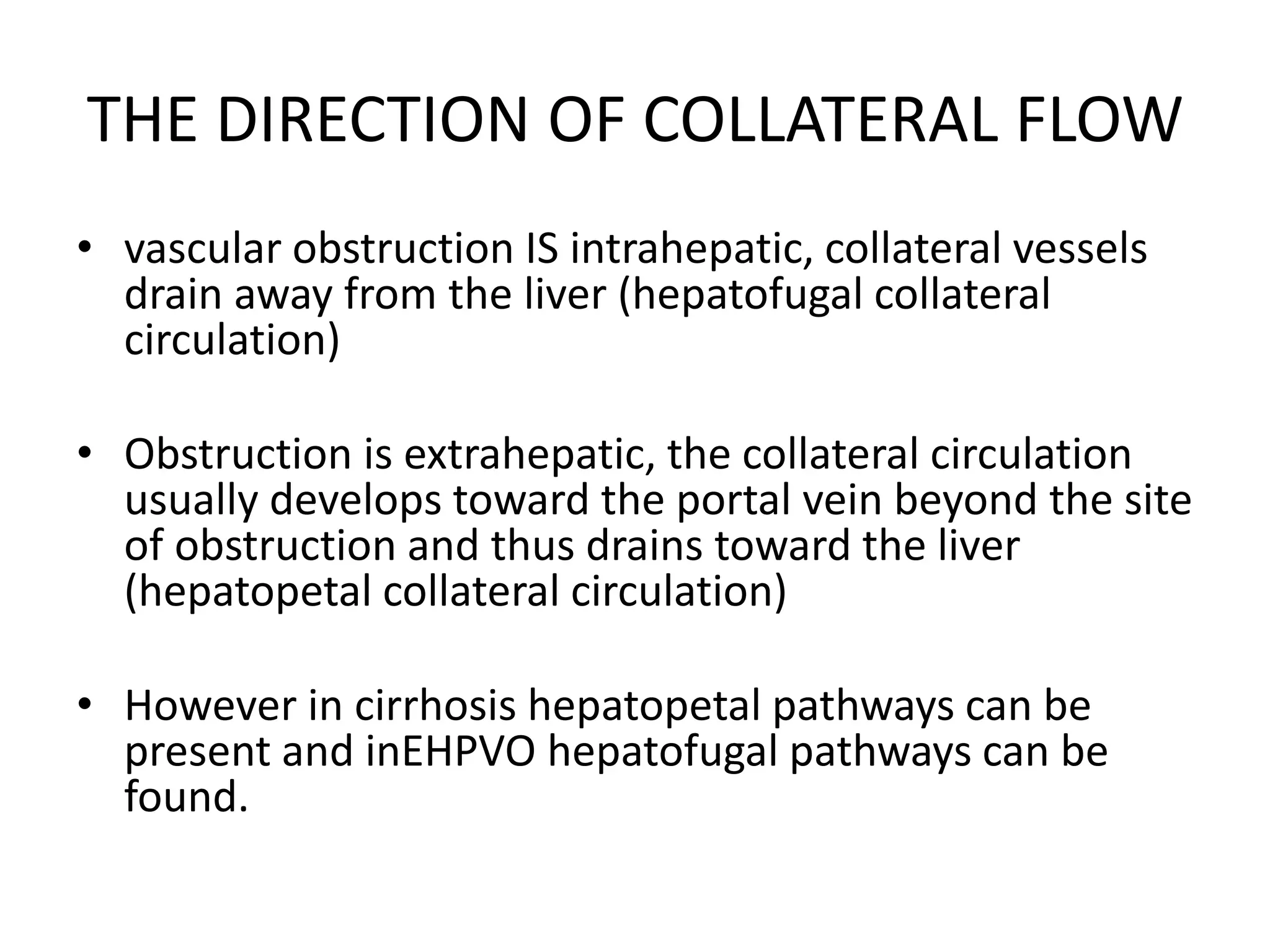
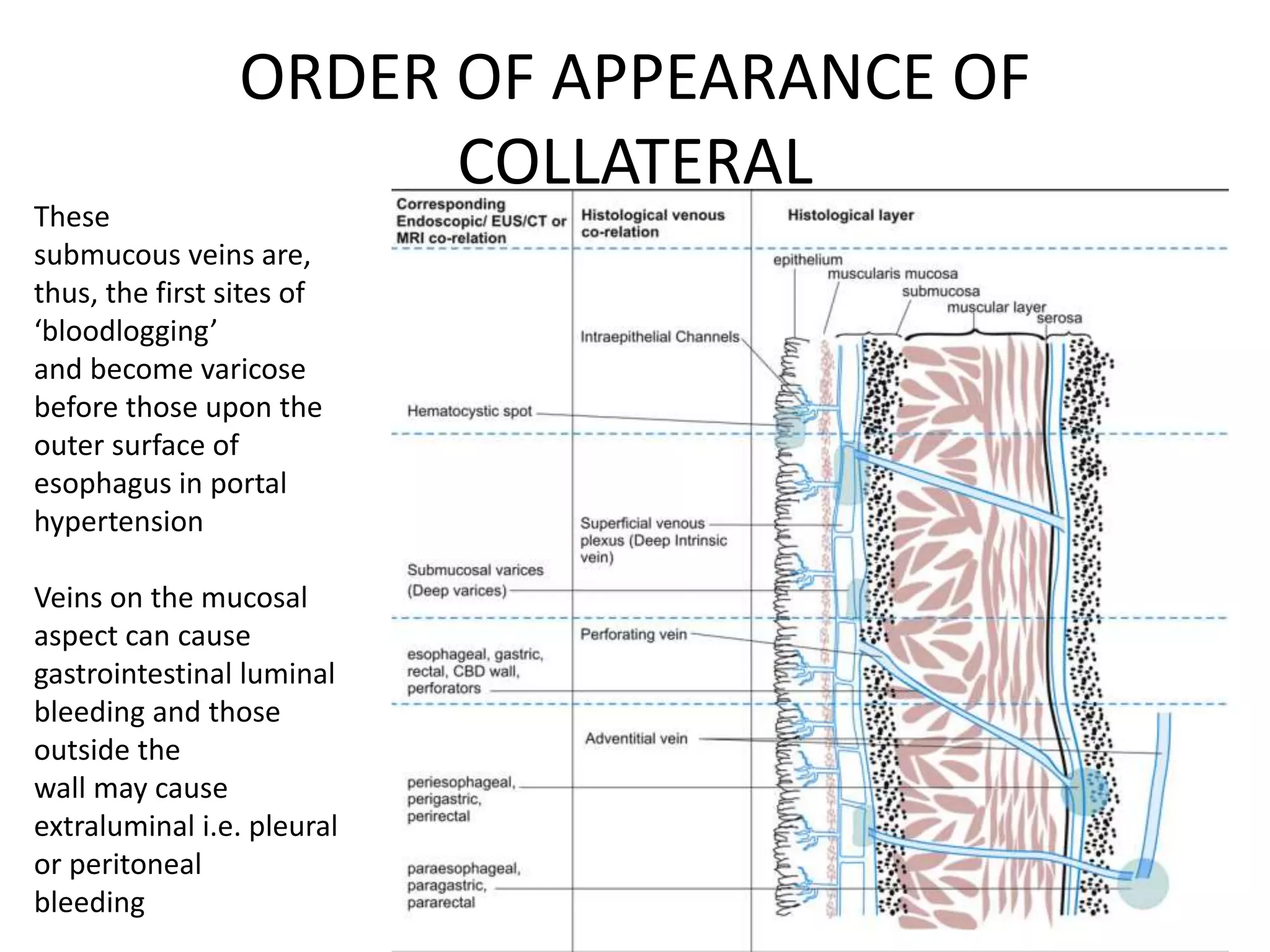
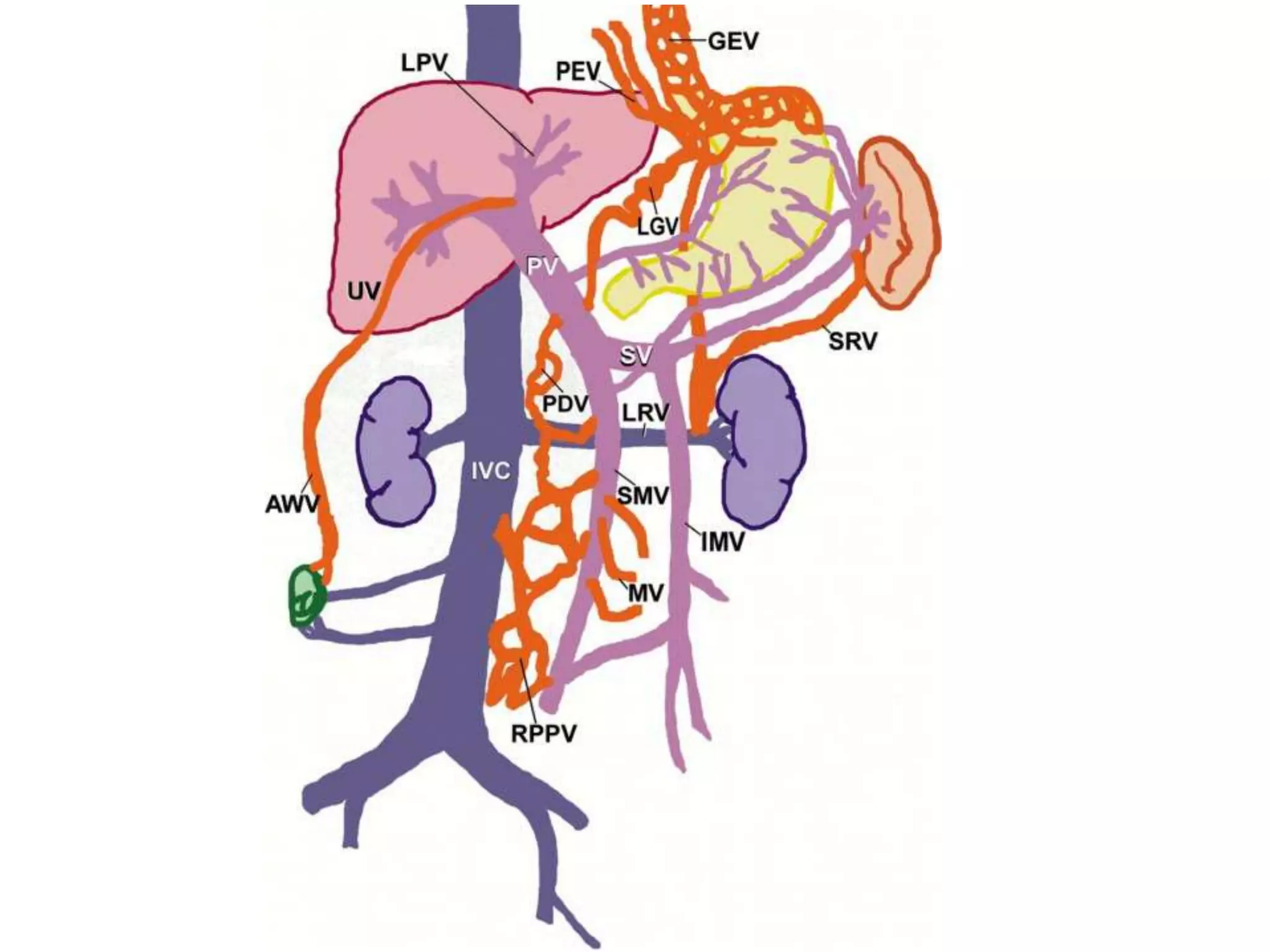
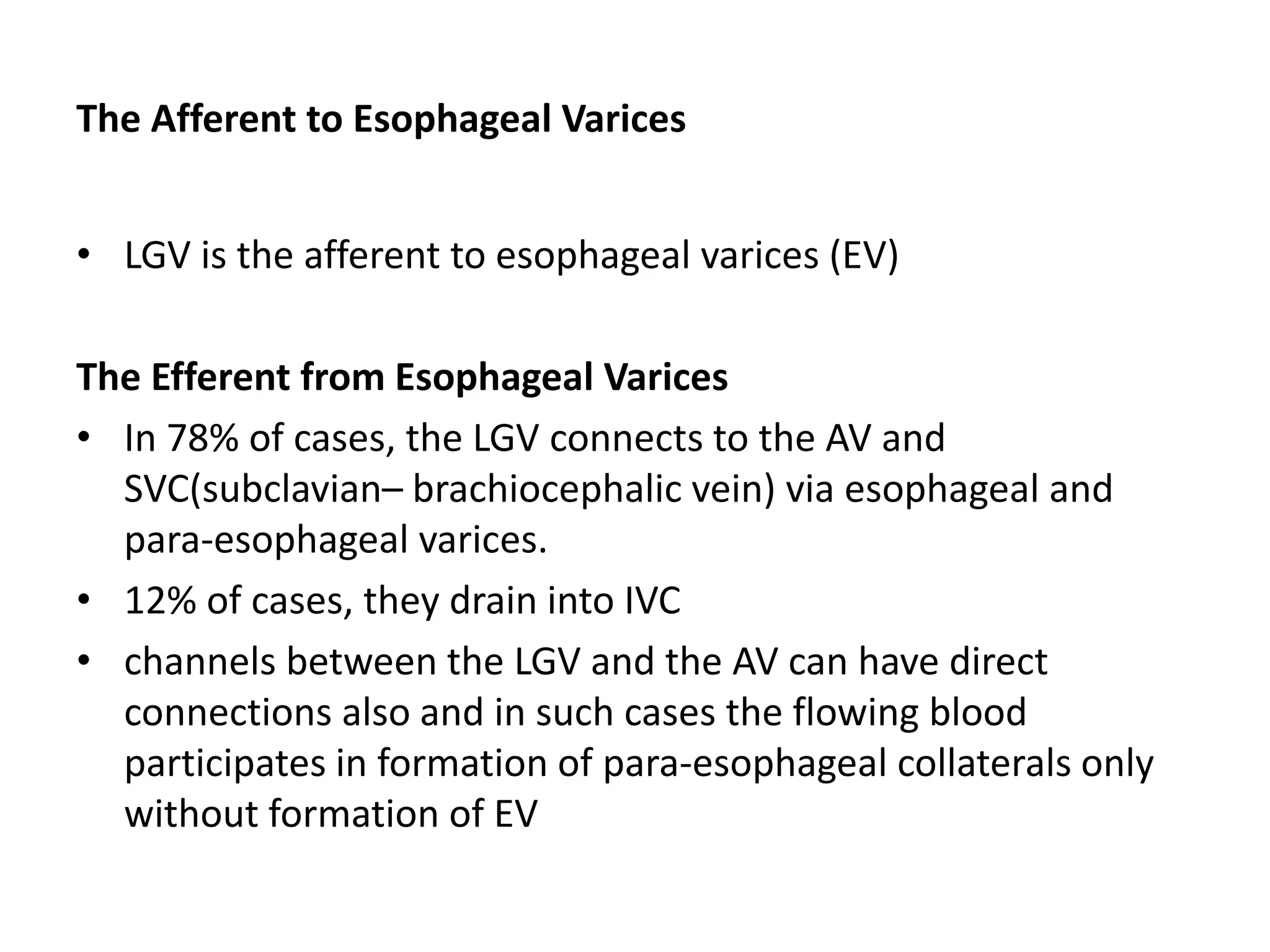
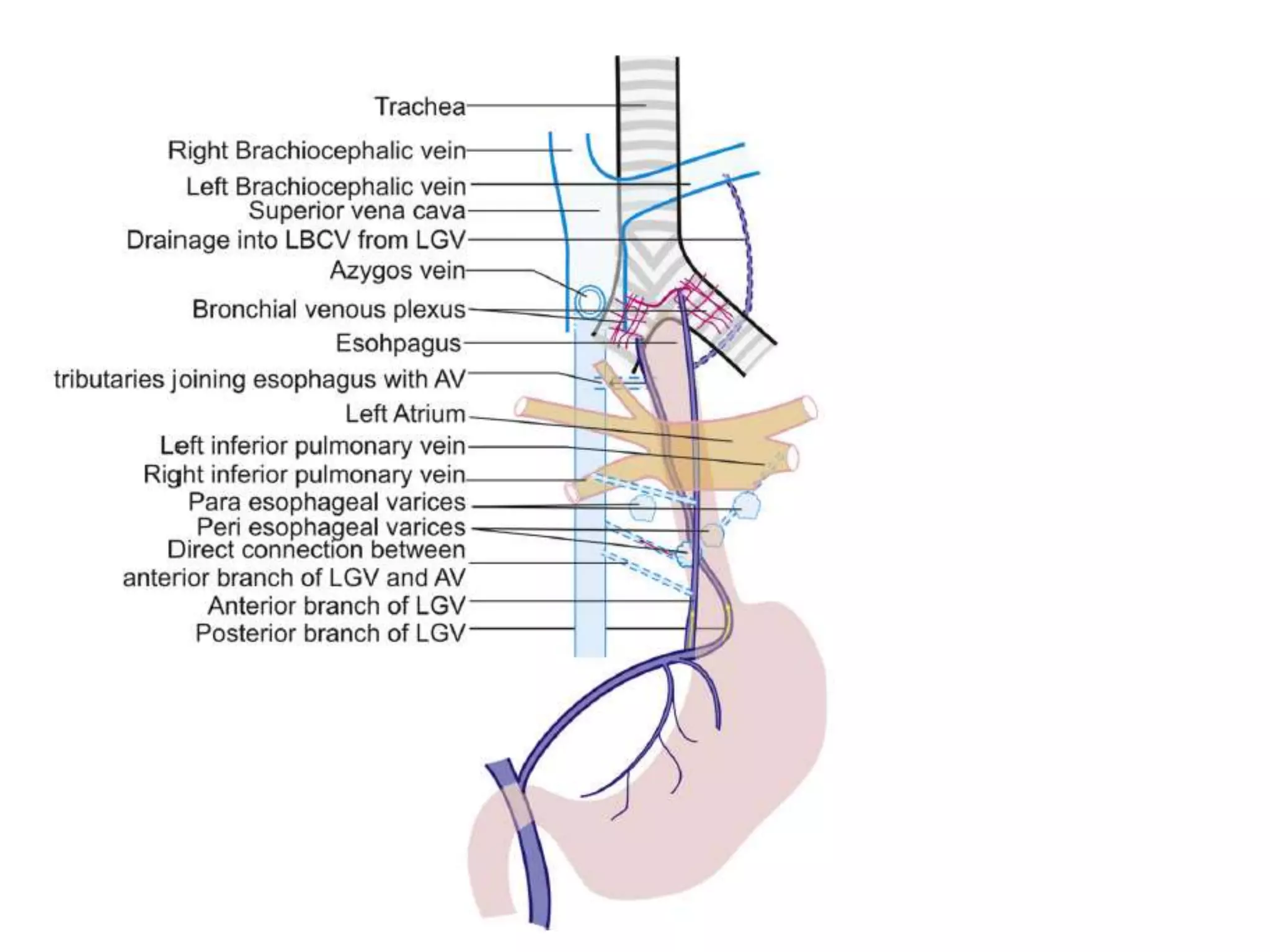
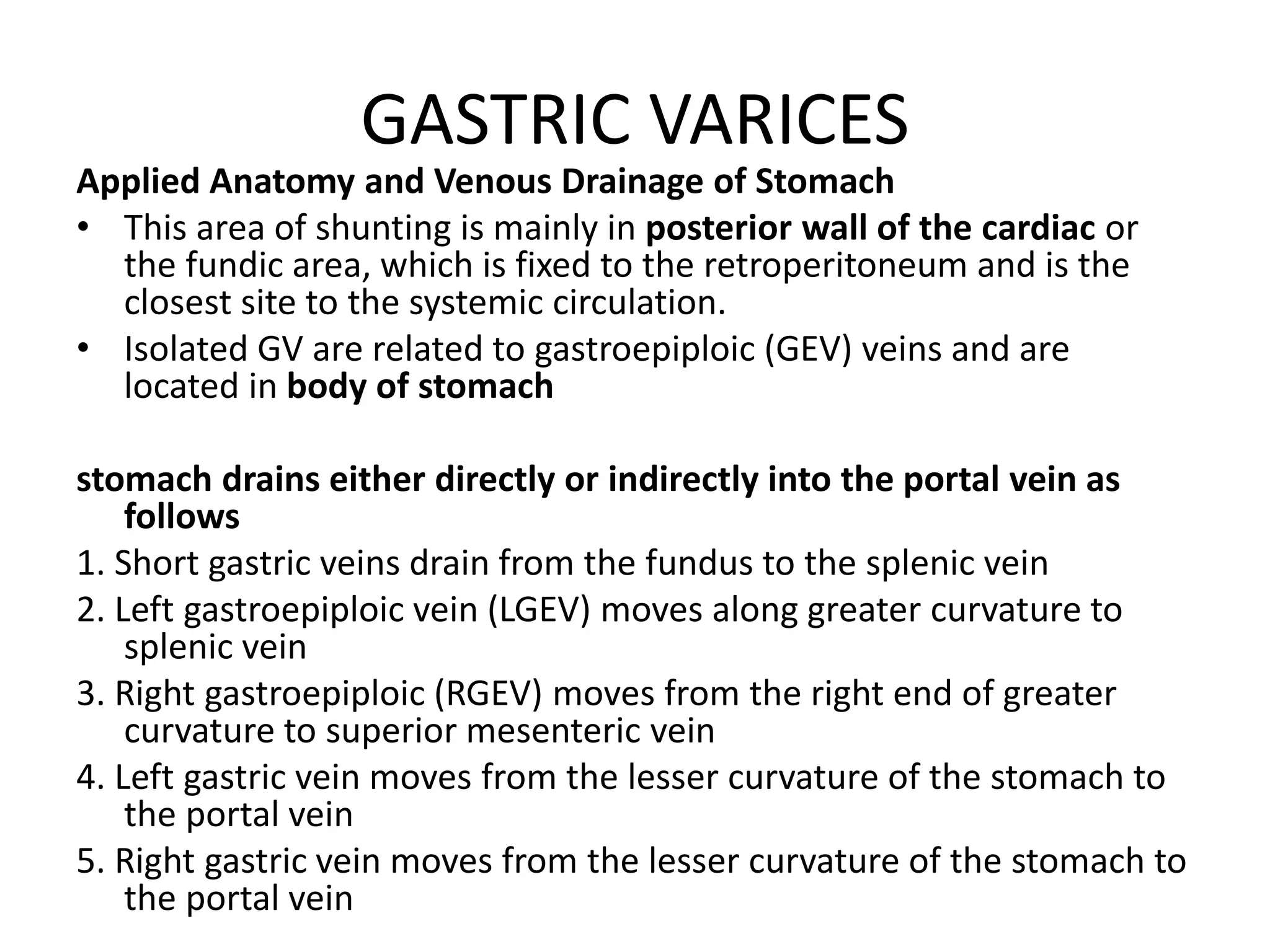
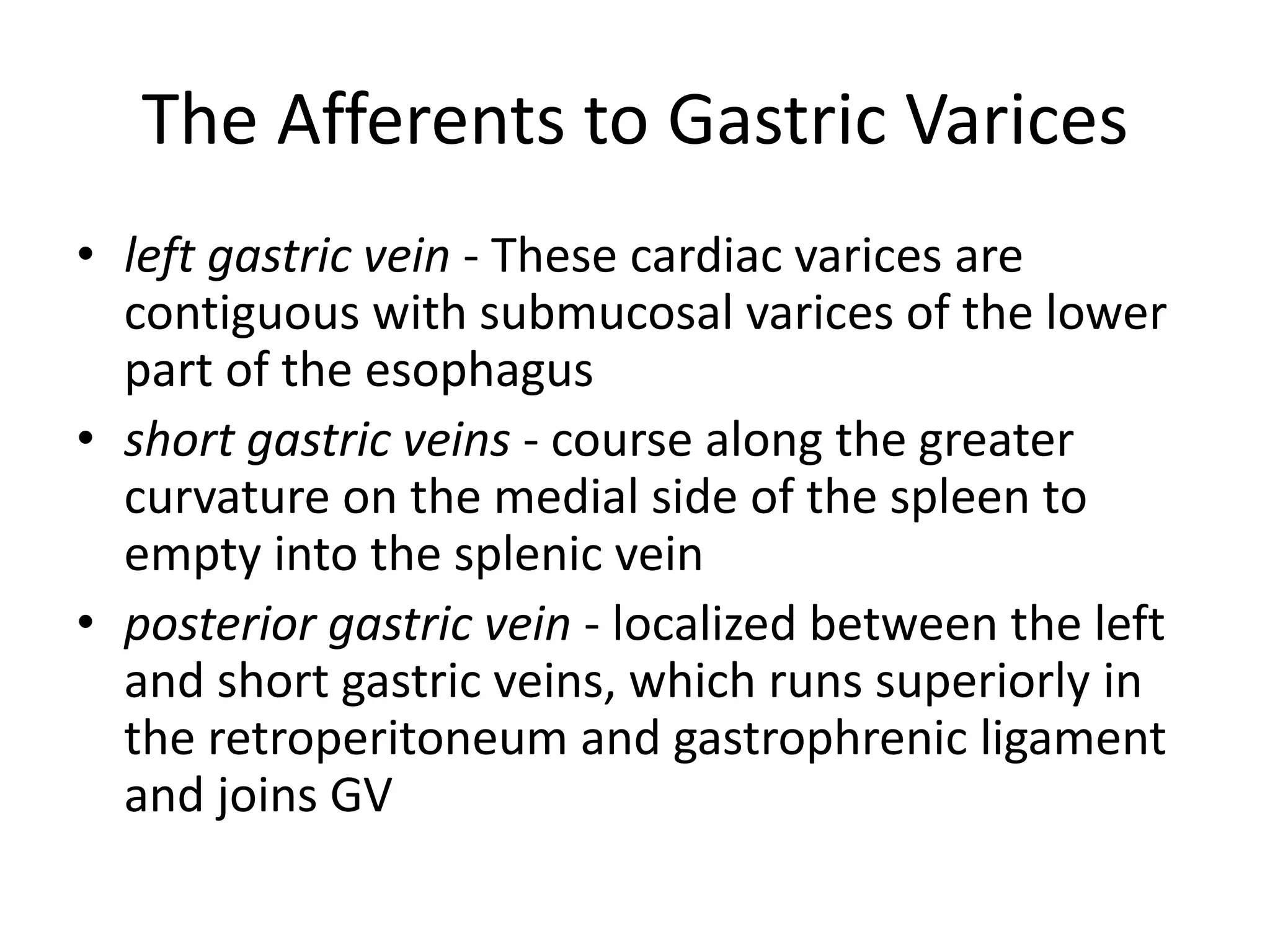
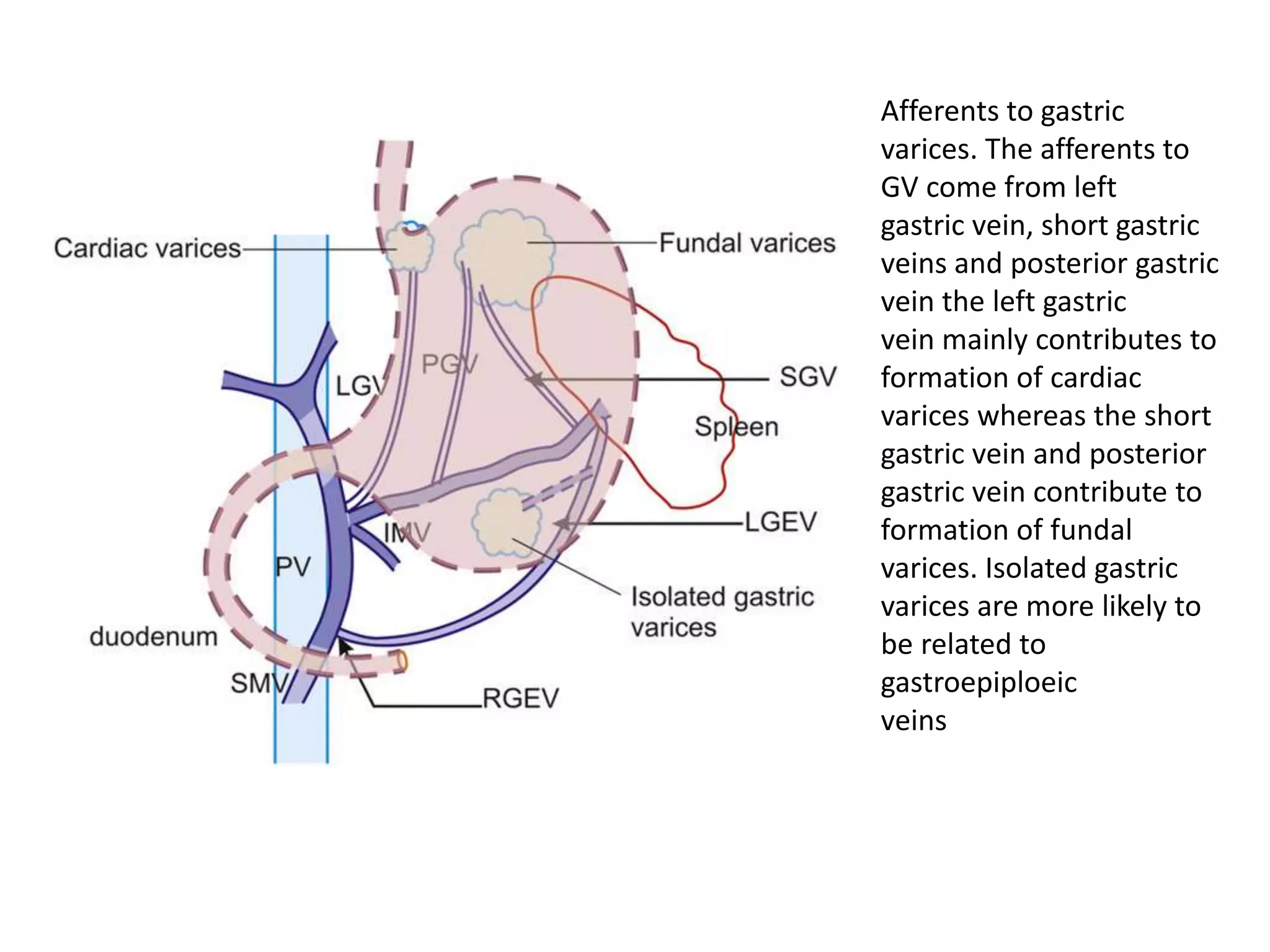
This document discusses collateral pathways in portal hypertension. It describes various veins that enlarge to drain blood away from the portal system and into the systemic circulation when portal pressures are elevated. These include esophageal varices, gastric varices, splenorenal shunts, paraumbilical veins, and retroperitoneal varices. The document explains the anatomy and venous drainage patterns of these various collateral pathways and how they develop as alternatives for blood flow.








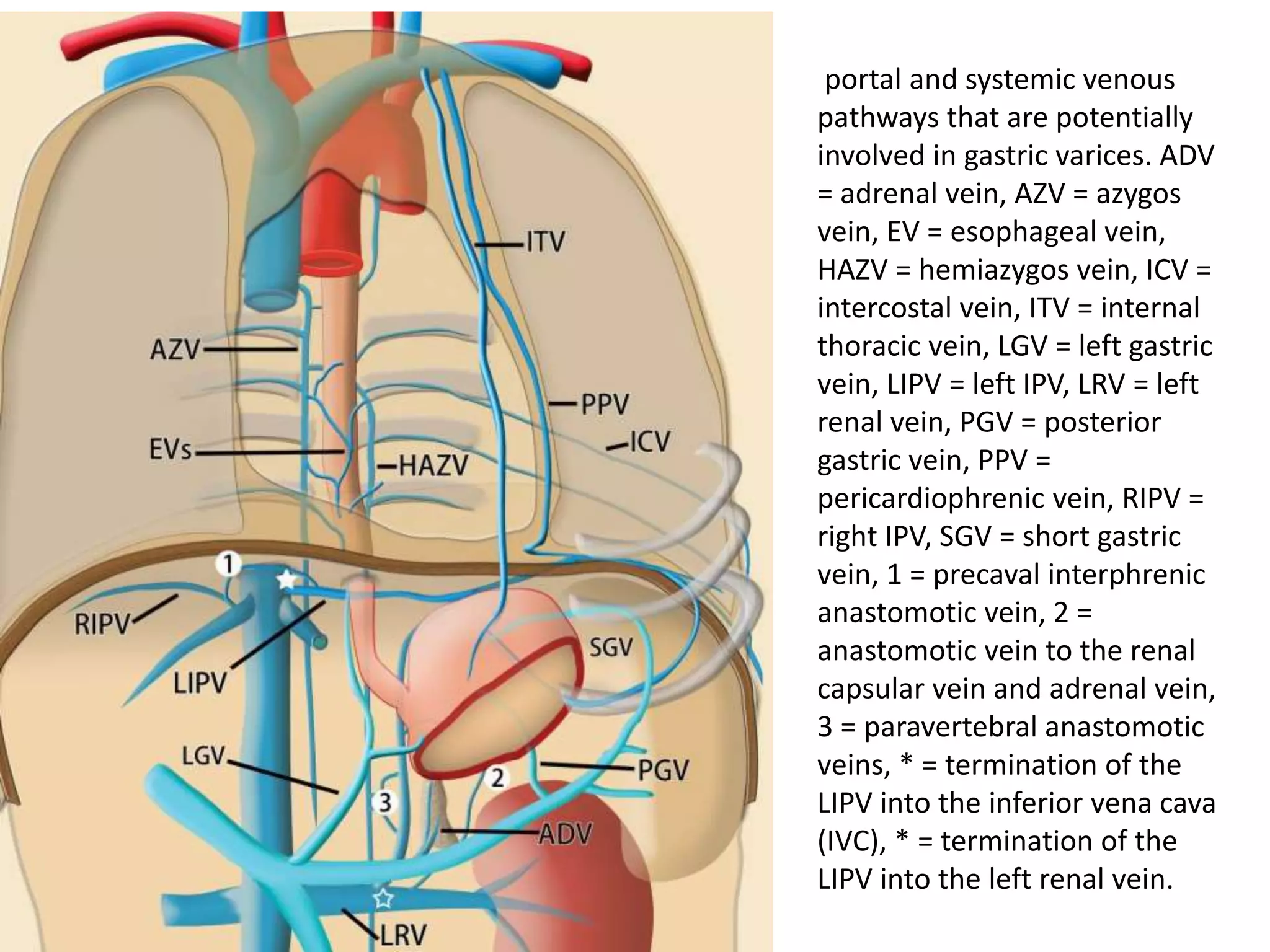

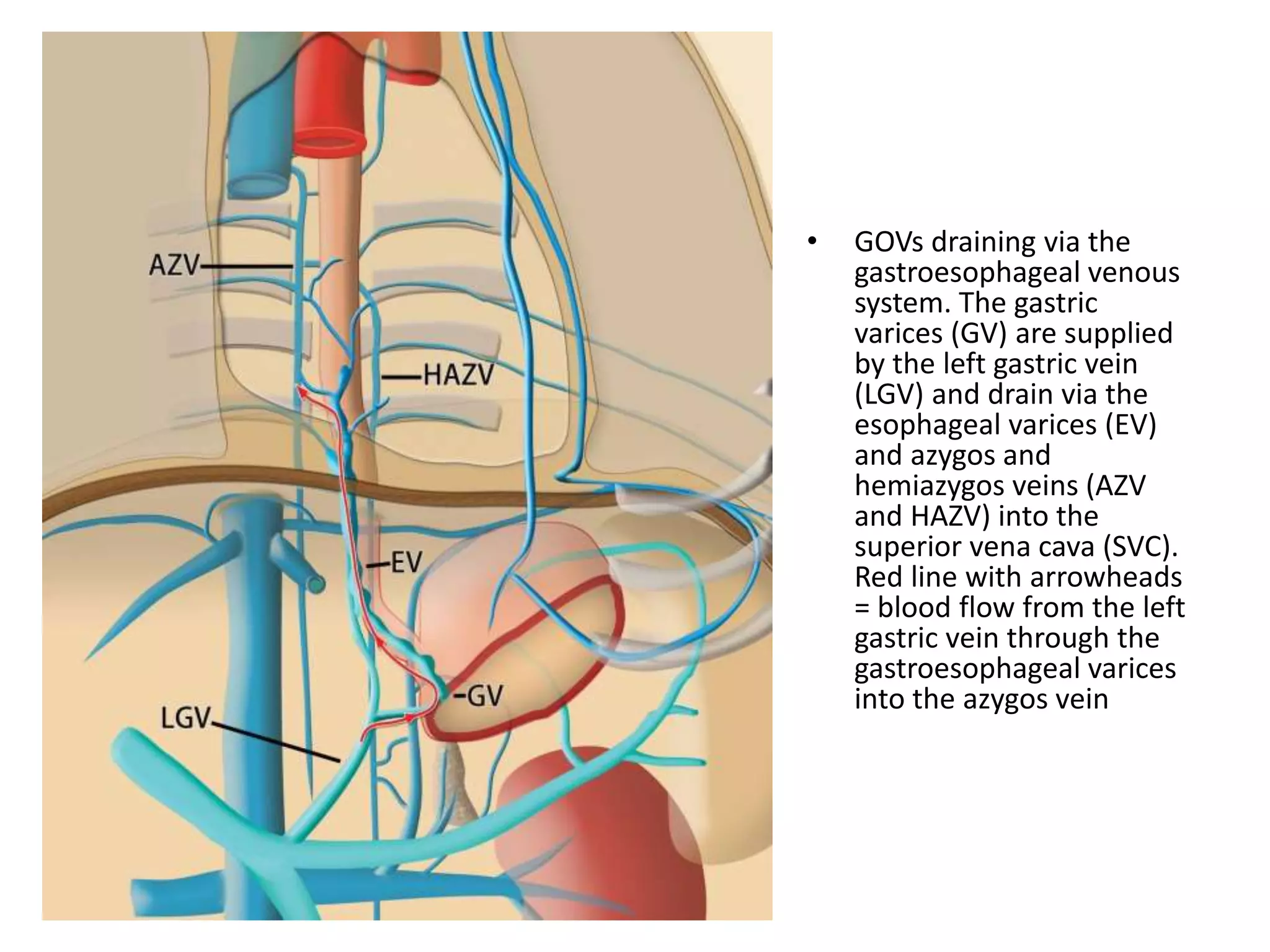
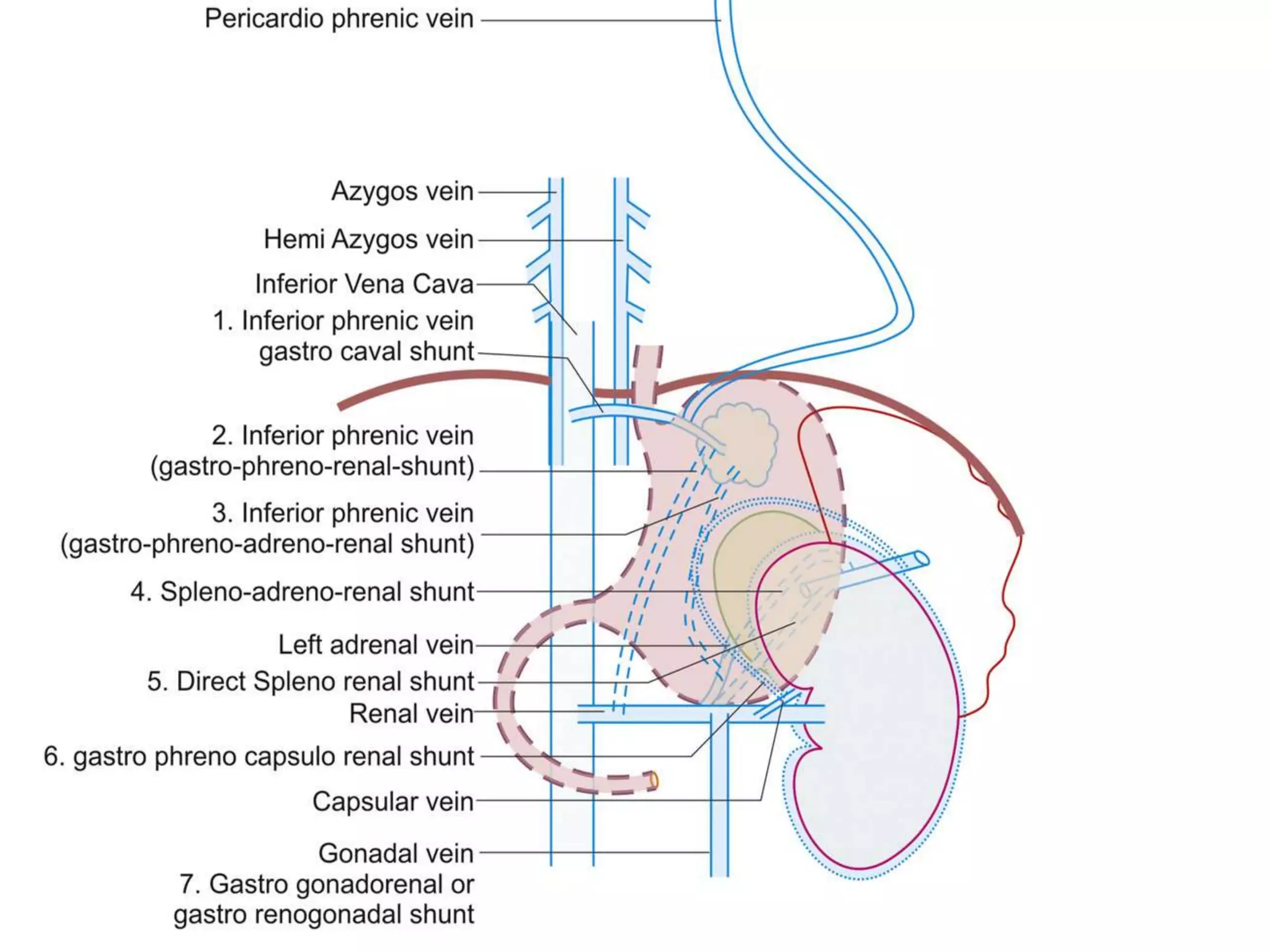
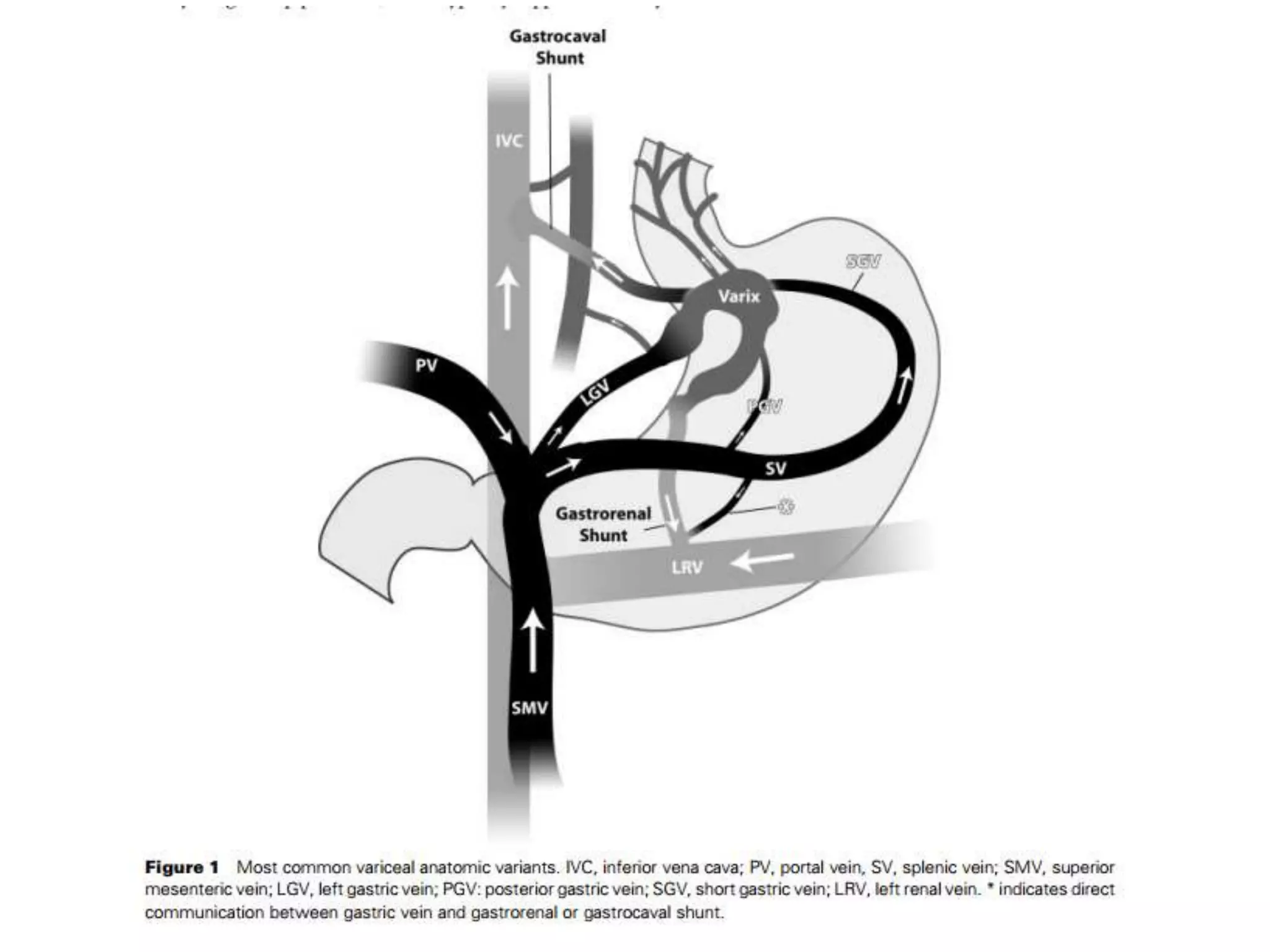
![• IGVs draining via the
gastrophrenic venous
system. Gastric varices
(GV) are supplied by the
posterior gastric vein
(PGV) and the short
gastric vein (SGV), which
drain via the IPV into
the left renal vein (LRV)
(forming a gastrorenal
shunt [GRS]) or IVC
(gastrocaval shunt
[GCS]). Red lines with
arrowheads = blood
flow from the posterior
and short gastric veins
through the gastric
varices into the
gastrorenal and
gastrocaval shunts. PPV
= pericardiophrenic
vein.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/collateralpathwaysinportalhypertension-150929083841-lva1-app6891/75/Collateral-pathways-in-portal-hypertension-23-2048.jpg)