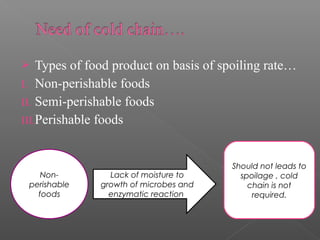
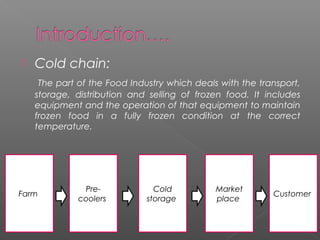
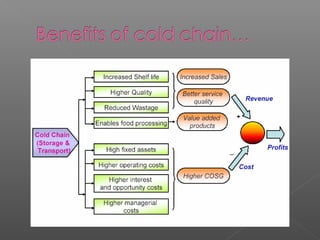
Cold chain management involves maintaining the proper temperature and humidity conditions for food products as they move through the supply chain from farm to customer. Perishable foods in particular require cold chain to slow microbial growth and enzymatic reactions that cause spoilage. The cold chain system includes equipment like pre-coolers and cold storage to keep foods frozen or refrigerated at the optimal temperatures during transport, storage, and distribution to preserve quality and extend shelf life. Proper packaging also acts as a barrier against contaminants and moisture that could lead to deterioration.