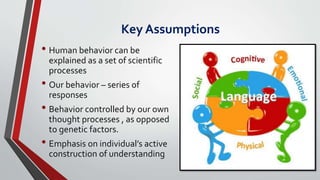
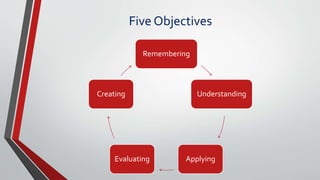
The document summarizes key aspects of the cognitive approach to language learning. It discusses how the cognitive approach views learning as a conscious and reasoned thinking process involving learning strategies. It outlines assumptions that behavior is controlled by thought processes. It compares the mind to a computer that encodes and stores information. It discusses the teacher's pivotal role and provides examples of cognitive learning activities and strategies. It also notes limitations of the cognitive approach's focus on logical mental processes over emotional and social aspects.