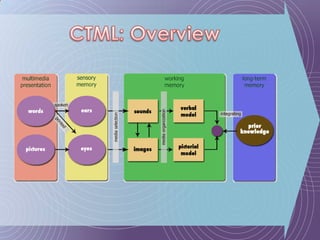
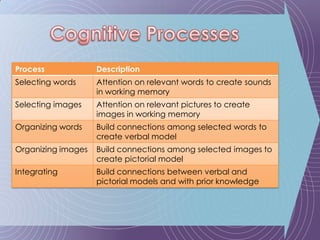
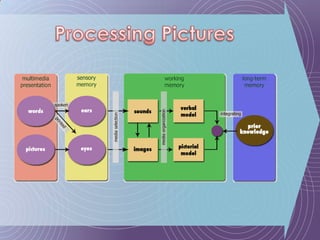
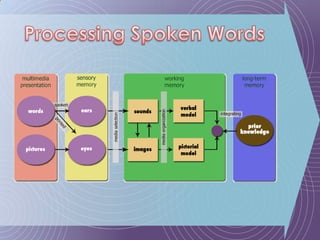
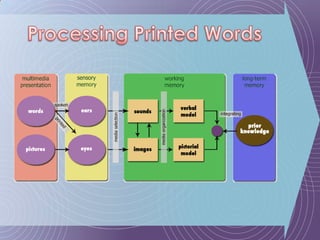
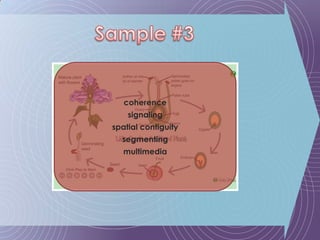
The document discusses the Cognitive Theory of Multimedia Learning (CTML). It provides an overview of CTML and lists some of its major researchers like Richard Mayer and Roxana Moreno. It also mentions some significant studies conducted within the CTML framework and lists basic principles of CTML such as split-attention and modality effects as well as more advanced principles involving things like guided discovery, worked examples, and prior knowledge.