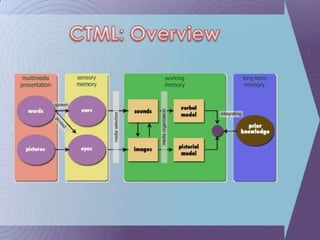
The document discusses the cognitive theory of multimedia learning. It states that according to this theory, people learn better from words and images than from words alone. The theory is based on the assumptions that people process visual and verbal information differently, have limited working memory capacity, and actively process information. Effective multimedia instruction follows principles such as coherence, redundancy, spatial contiguity, temporal contiguity, and modality to help learners select, organize and integrate information into long-term memory.