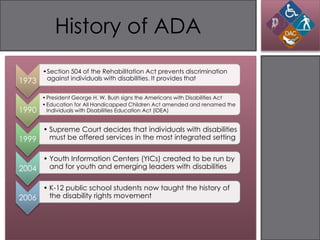
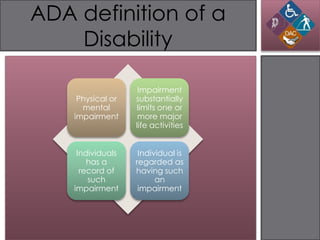
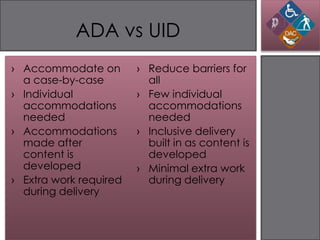
The document discusses the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) and its implications for information design. It provides background on the ADA and disabilities affecting learners. When designing instructional messages, universal design principles should be employed to accommodate all students' needs as required by the ADA, such as including text alternatives for images and ensuring readable font size and color contrast. Examples demonstrate violations of ADA guidelines and best practices for inclusive design.