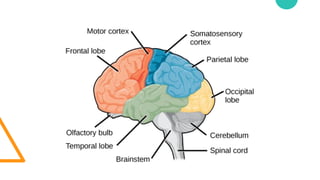
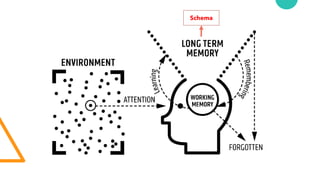
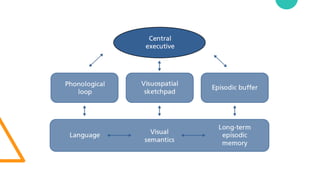
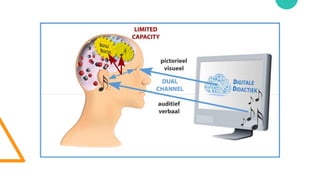
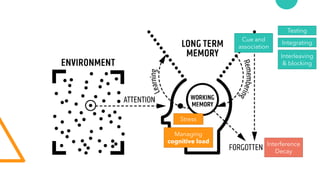
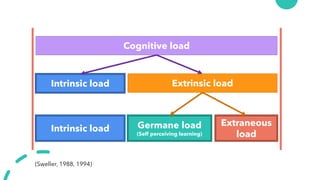
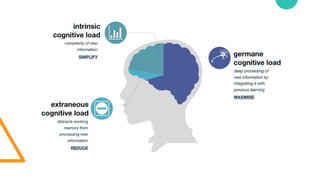
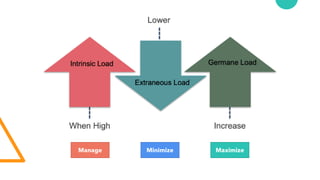
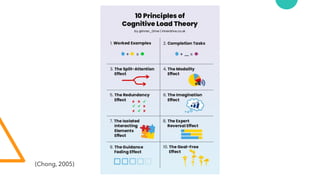
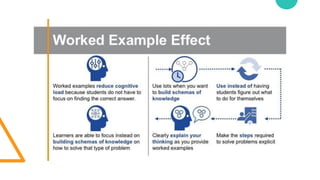
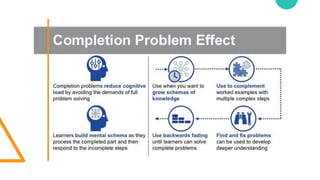
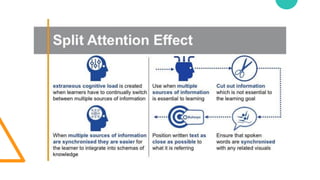
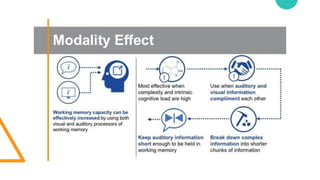
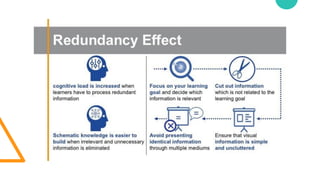
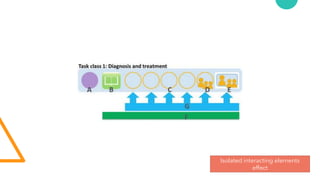
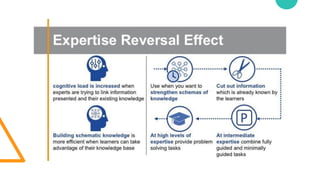
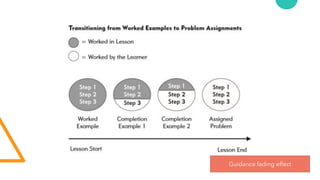
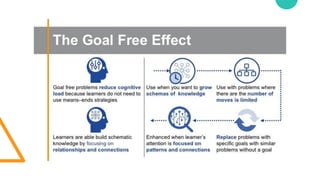
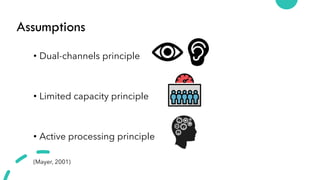
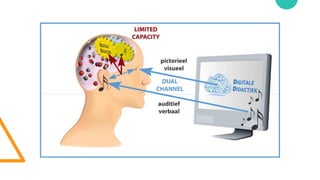
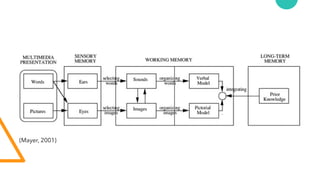
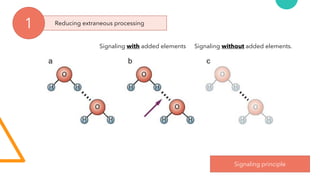
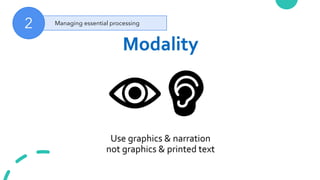
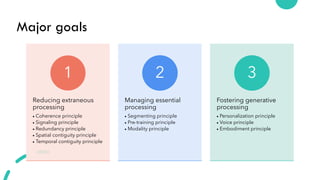
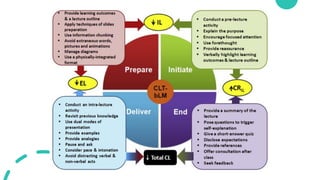
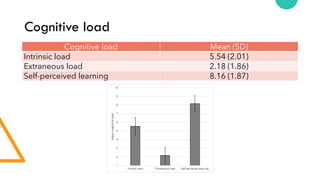
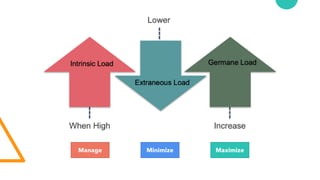
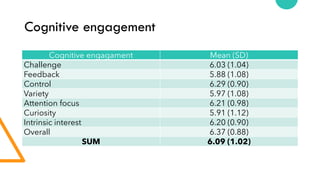
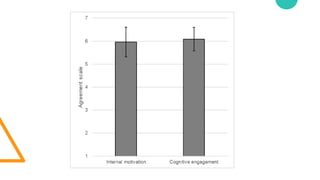
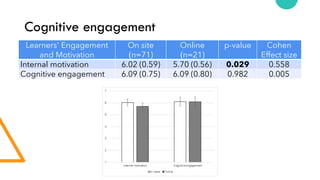
The document discusses Cognitive Load Theory (CLT) and its application in teaching. CLT is based on the science of learning and how the human cognitive system processes information. It posits that there are different types of cognitive load that affect learning. The Cognitive Theory of Multimedia Learning builds on CLT and provides principles for designing effective multimedia instruction. These theories inform a CLT-based lecture model that aims to reduce extraneous cognitive load and manage essential load. The author applies this model and finds it lowers extraneous load and increases intrinsic motivation and cognitive engagement compared to traditional lectures.