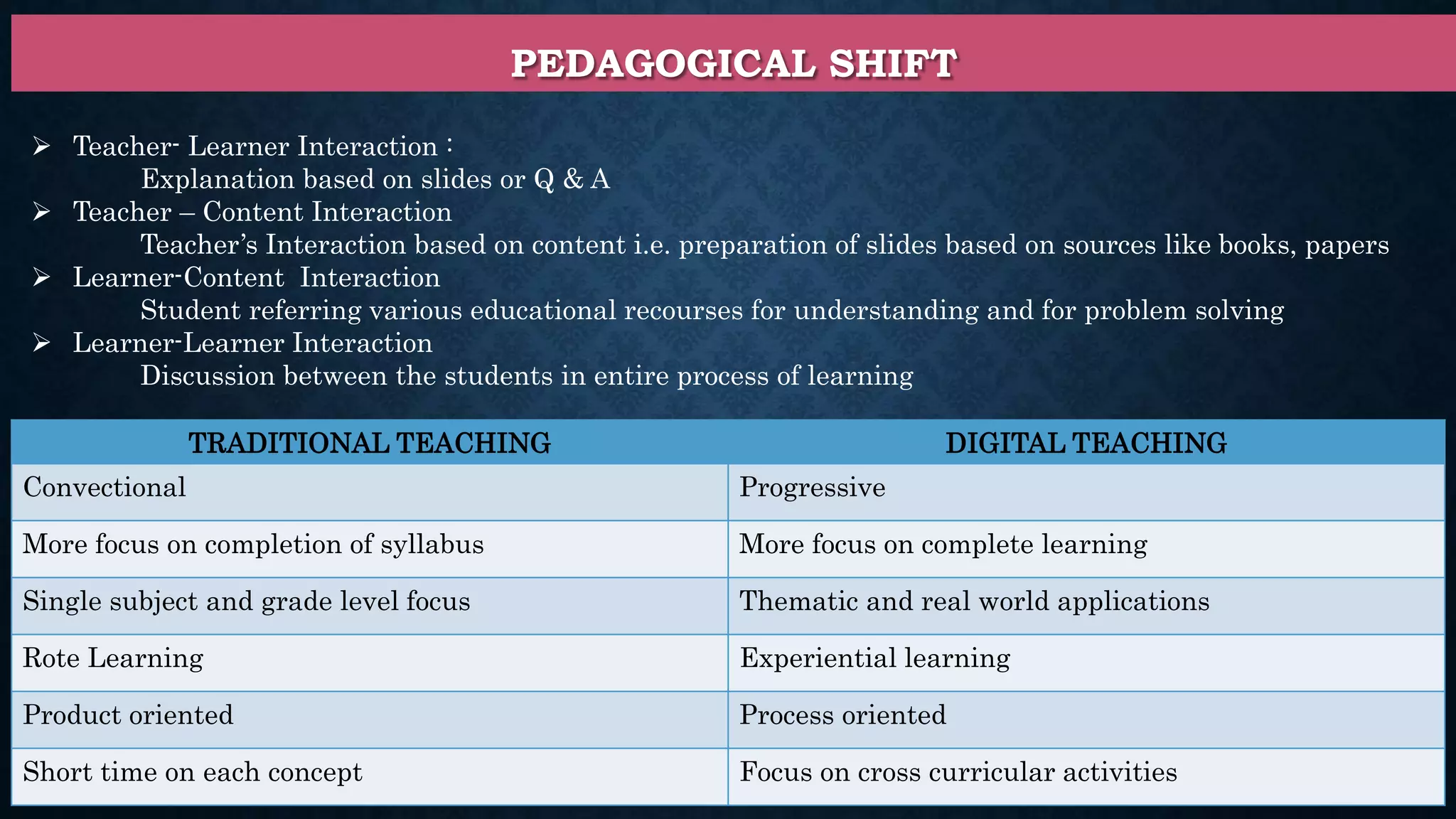
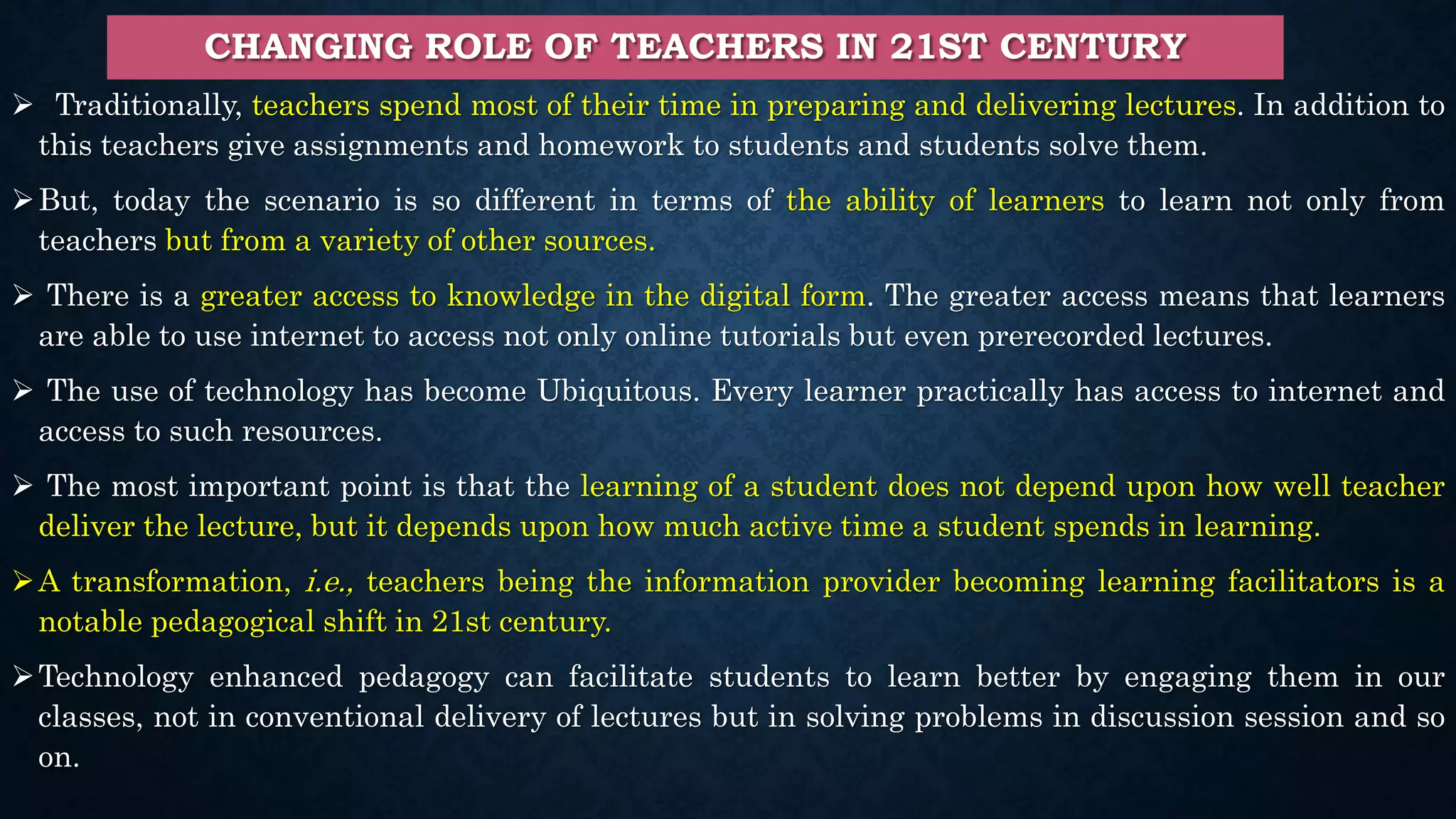
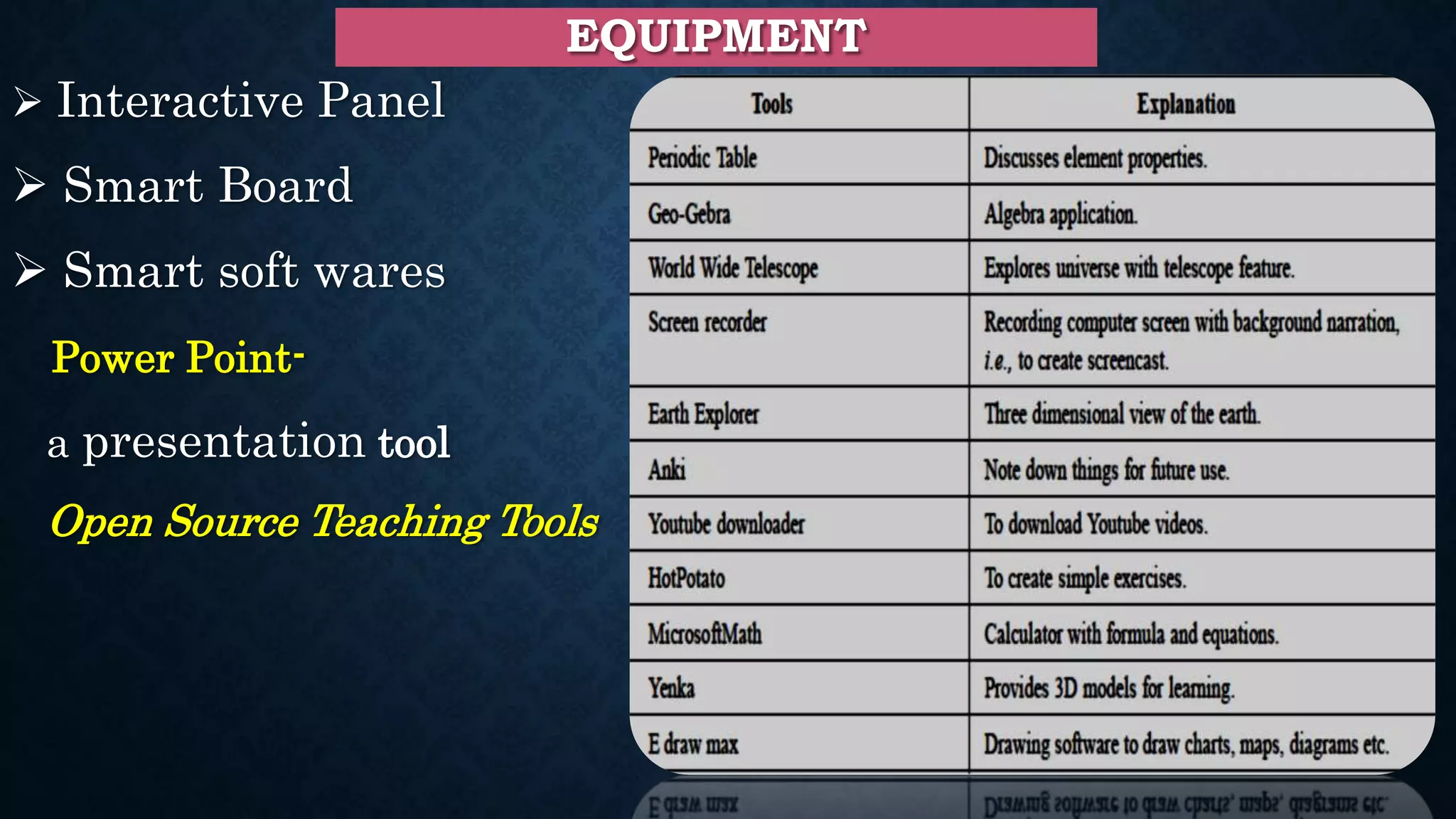
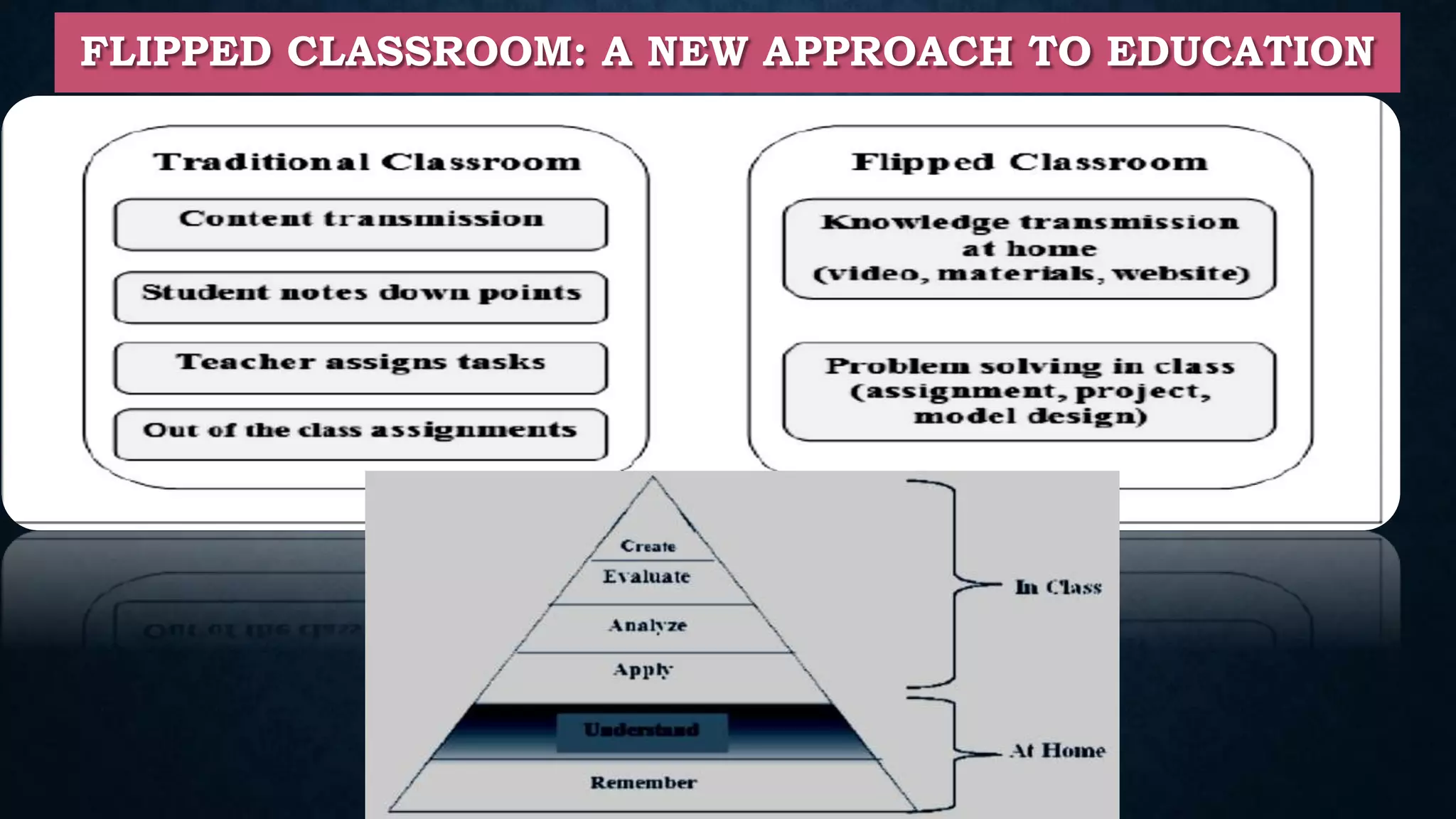
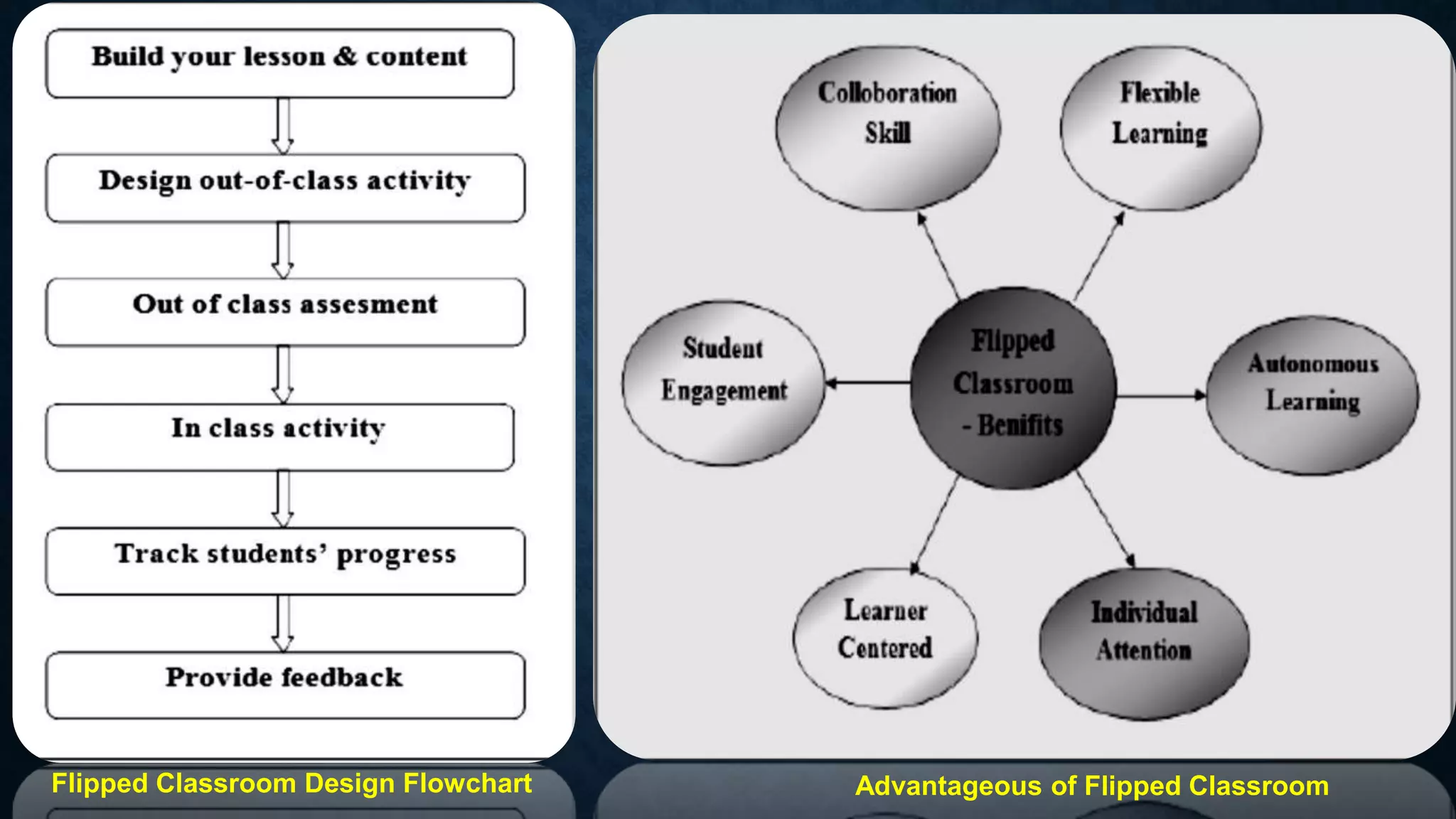
This document discusses digital teaching and the shift from traditional to modern pedagogical approaches. It outlines key differences between traditional and digital teaching such as a focus on complete learning over syllabus completion and experiential versus rote learning. The changing role of teachers as facilitators rather than only information providers is also covered. Features of digital teaching like enhanced interaction and flexibility are presented. Learning management systems and tools like Moodle that support online learning are also summarized.