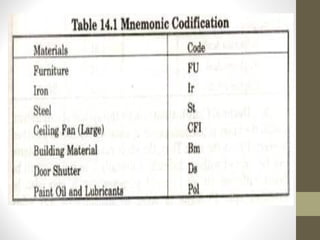
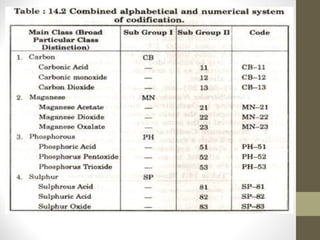
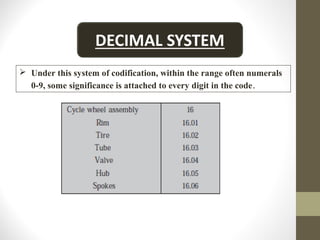
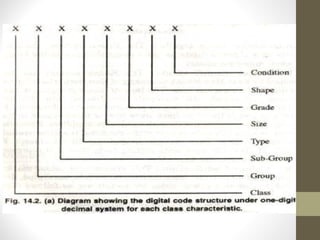
This document discusses codification systems for organizing materials in industries. It defines codification as representing equipment, materials, tools, and other items with abbreviated codes using letters, numbers, colors, or symbols. The objectives of codification are accurate identification, standardization, prevention of duplication, efficient purchasing, and computerization. Common codification methods described include alphabetical, numerical, mnemonic, combined alphabetical-numerical, decimal, British, Kodak, and color coding systems. Benefits of codification include accurate identification, simplified purchasing and inventory processes, and enabling computerization.