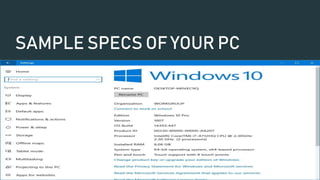
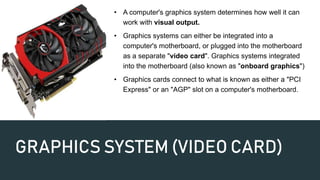
Computer system specifications describe the key components that determine a computer's performance, including the processor, RAM, graphics system, and hard drive. The processor speed and architecture, amount of RAM, graphics card capabilities, and hard drive speed and capacity all impact how well a computer can perform. The BIOS or UEFI firmware installed on the motherboard initializes these hardware components and allows the operating system to boot. Updating the BIOS/UEFI firmware can provide improvements and support for newer hardware.