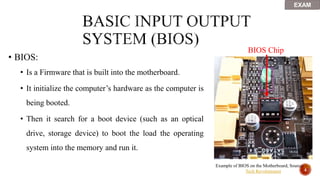
The document discusses BIOS, UEFI, POST and the CMOS chip. It provides the following key points:
- BIOS initializes hardware at startup and finds a boot device, while UEFI is a newer standard that offers improvements over BIOS like a graphical interface.
- The POST tests hardware for errors before booting the OS. Passing yields a single beep while errors produce unique beep codes.
- Settings are stored in the CMOS chip, which needs a battery to retain them when off. The BIOS chip holds the low-level software.