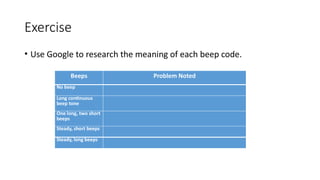
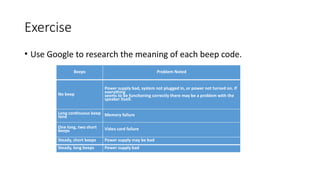
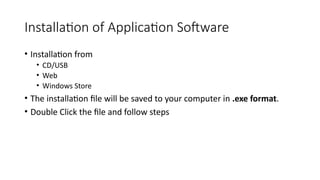
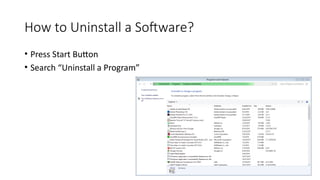
The document outlines an agenda for a lab focused on BIOS (Basic Input Output System), explaining how to access BIOS settings, change boot device priority, and establish BIOS security. It details the role of BIOS in initializing hardware and storing configurations in CMOS, as well as providing step-by-step instructions for accessing BIOS on various Windows operating systems. Additionally, it includes practical exercises related to BIOS navigation, boot sequence examination, and security setup.