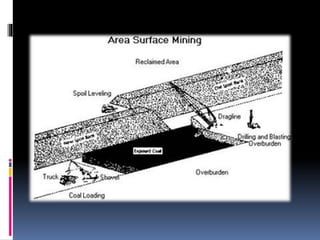
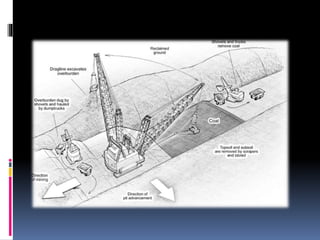
Coal and petroleum are non-renewable energy sources formed from ancient organic materials, with coal primarily consisting of carbon and petroleum made from decomposed sea creatures. Both resources have numerous applications, including electricity generation, fuel production, and the manufacturing of chemicals and plastics, but their extraction and use pose significant environmental hazards such as pollution and health risks. The document emphasizes the need for more efficient use of these resources and the development of cheaper energy technologies.