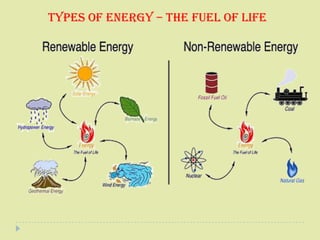
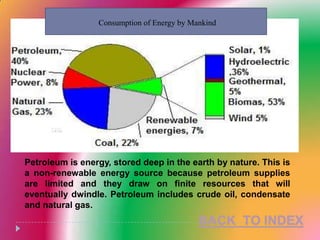
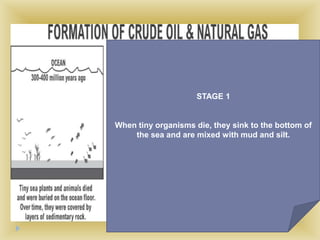
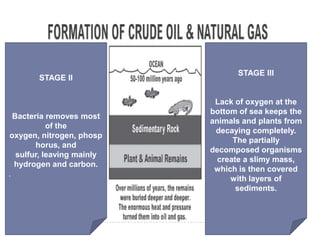
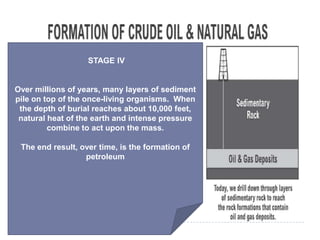
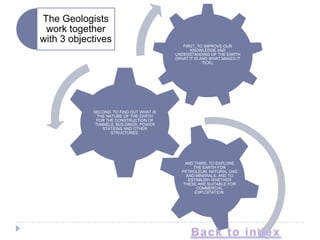
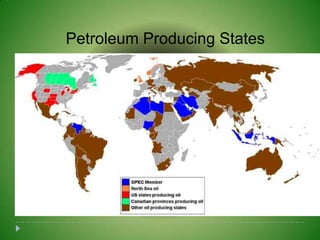
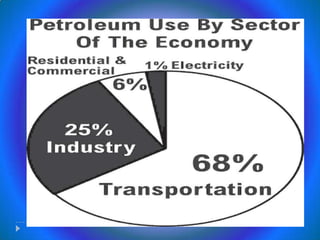
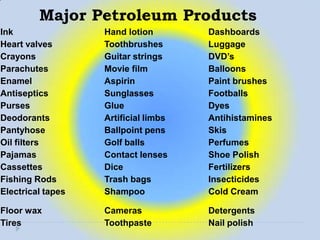
Petroleum is a non-renewable energy source formed from the remains of ancient organisms over millions of years. Geologists and geophysicists use their knowledge of rocks and earth science to locate potential underground petroleum deposits. Once extracted, crude oil is refined into useful petroleum products like gasoline, diesel, and jet fuel as well as many other products people use every day.