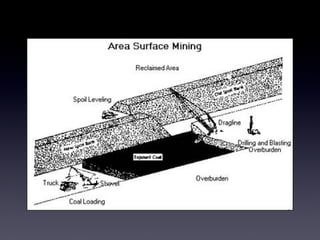
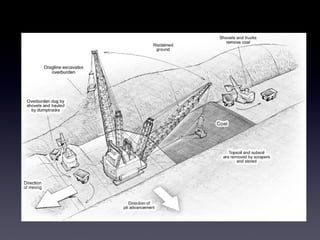
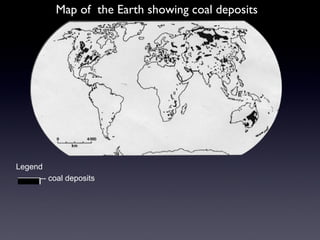
Coal and petroleum are non-renewable sources of energy that were formed from ancient plant and animal remains over millions of years. Coal is a combustible rock formed from fossilized vegetation and is mined through surface or underground methods. Petroleum is a flammable liquid found beneath the earth's surface that was produced from the remains of sea creatures. Both coal and petroleum are used as fuel sources but their extraction and use also poses environmental risks like pollution and oil spills.