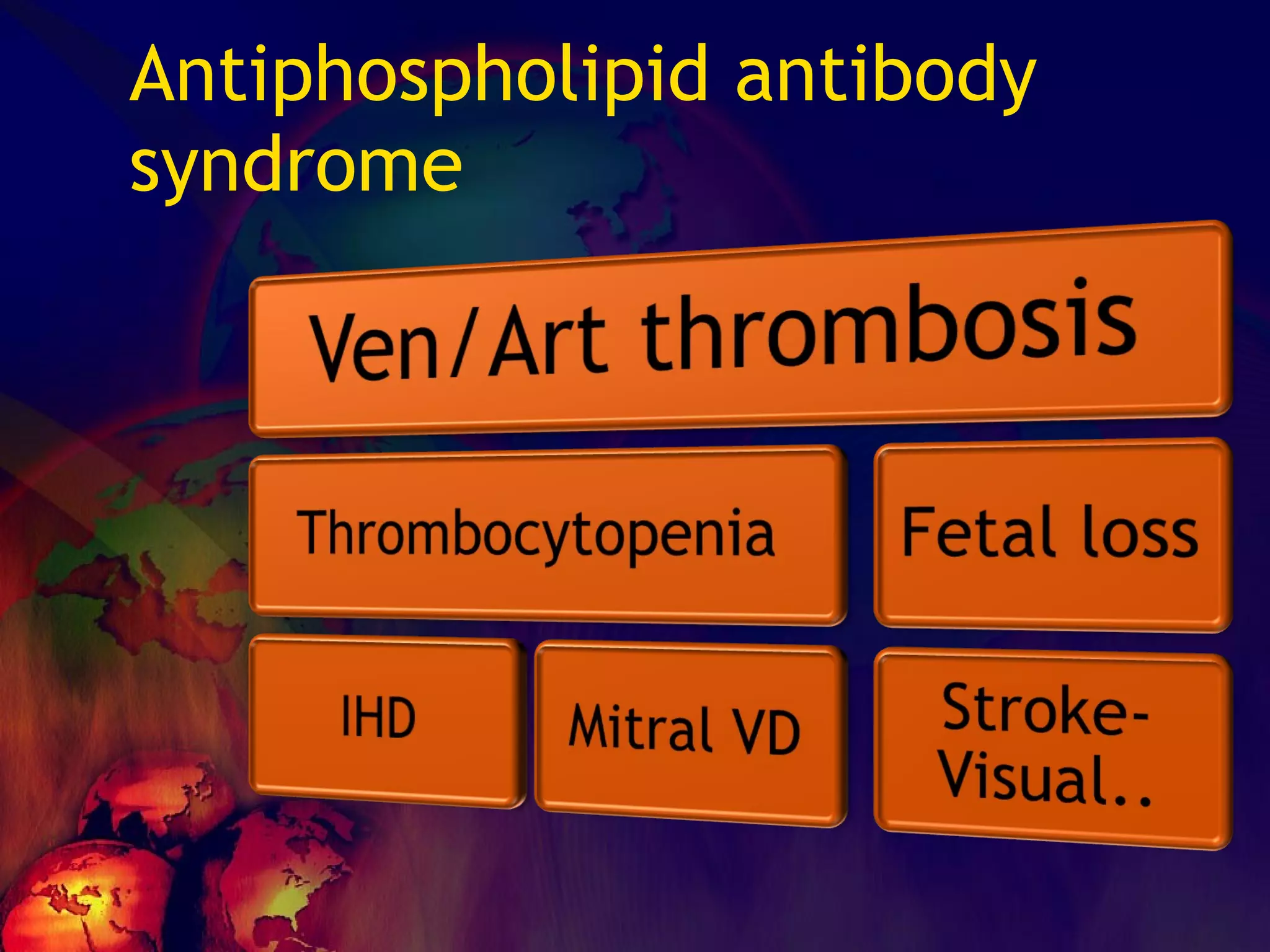
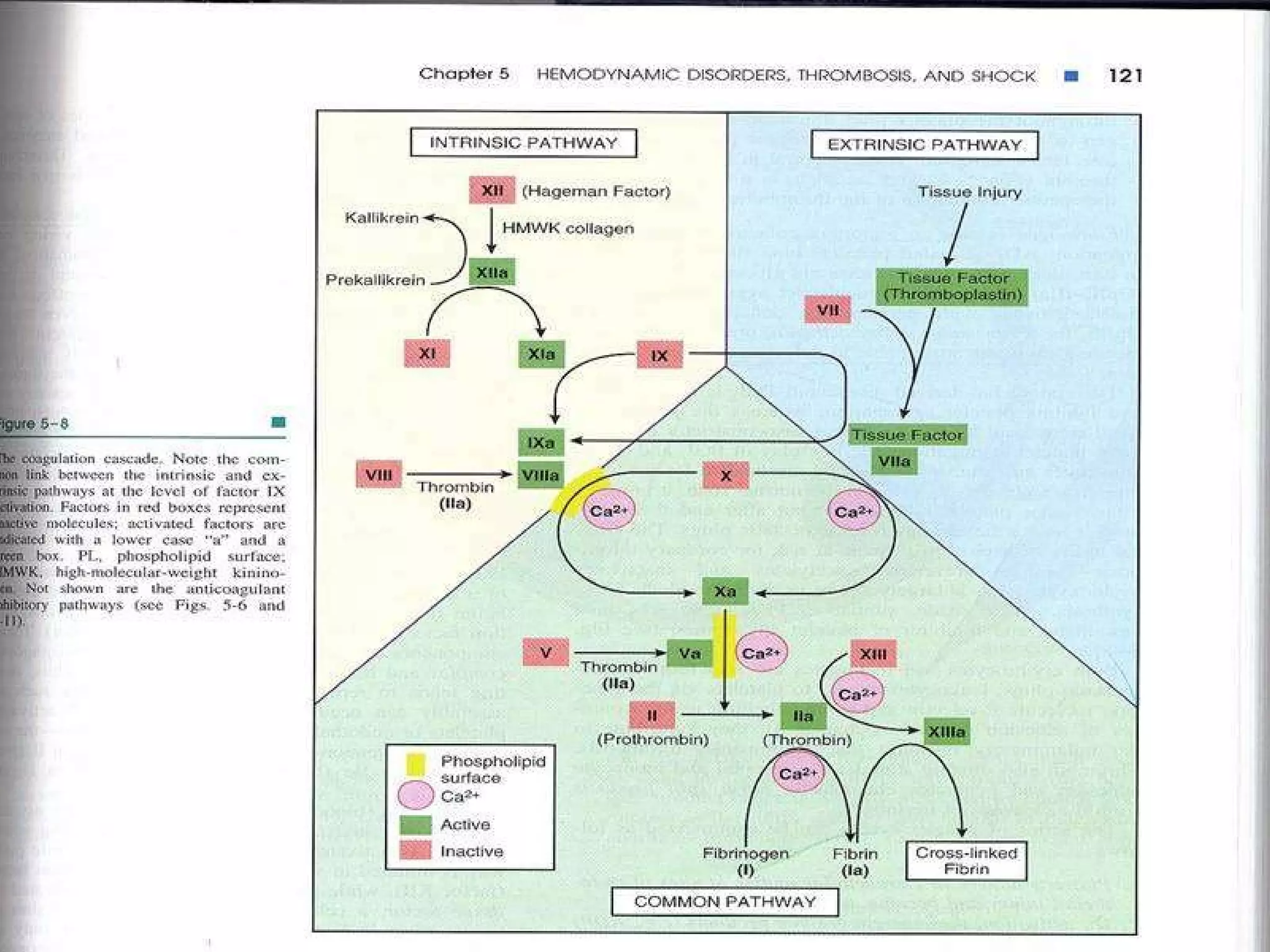
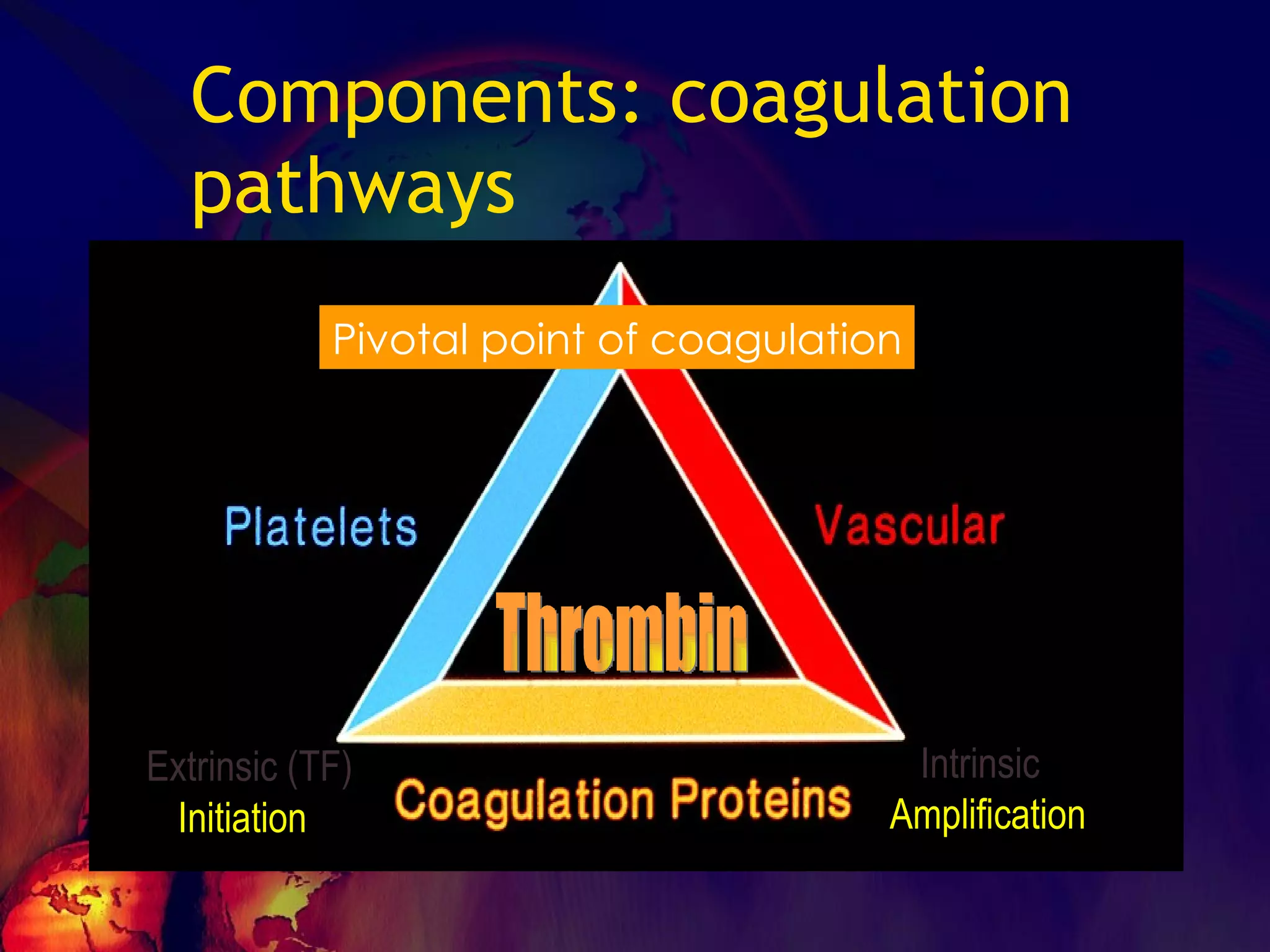
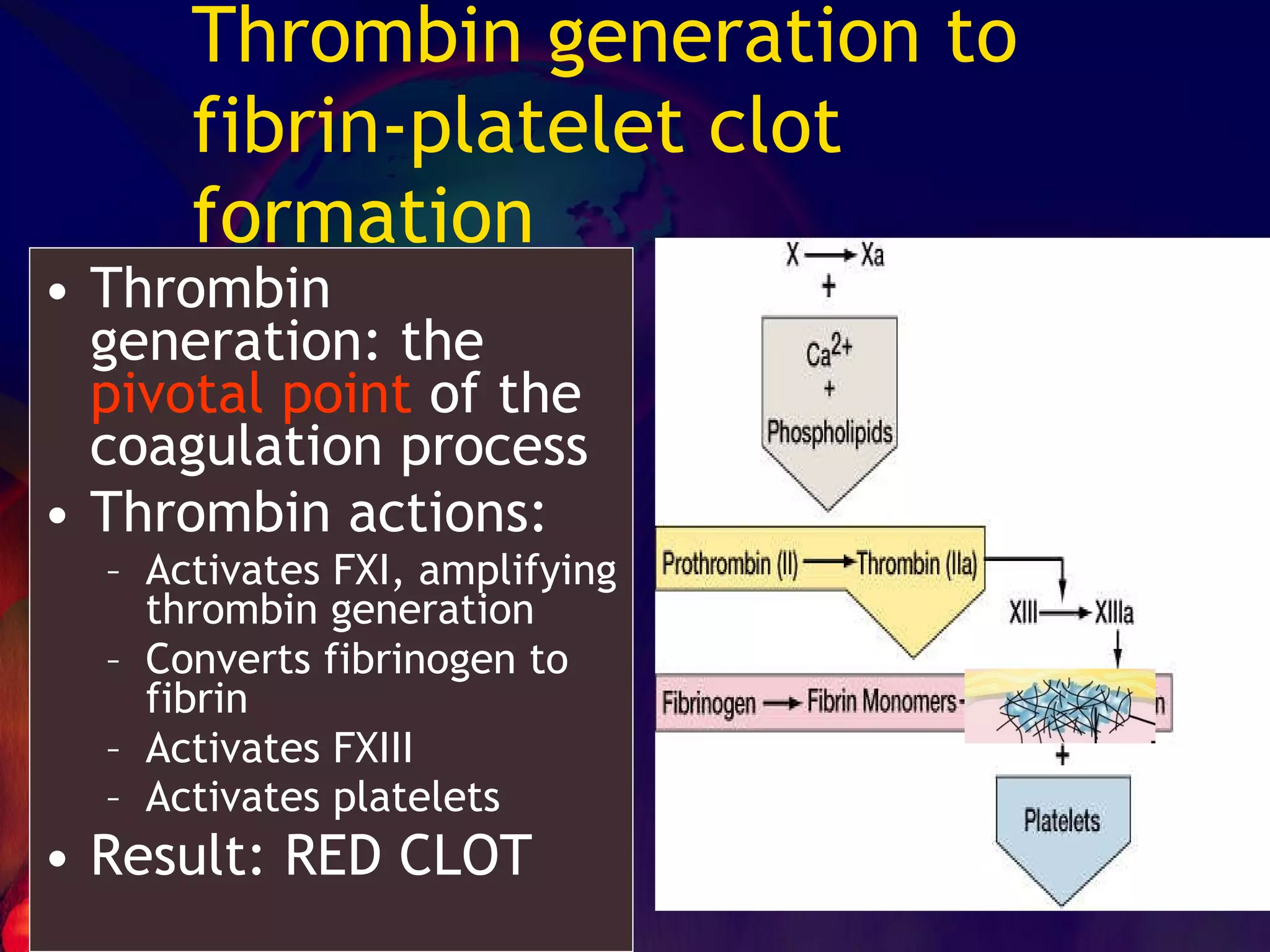
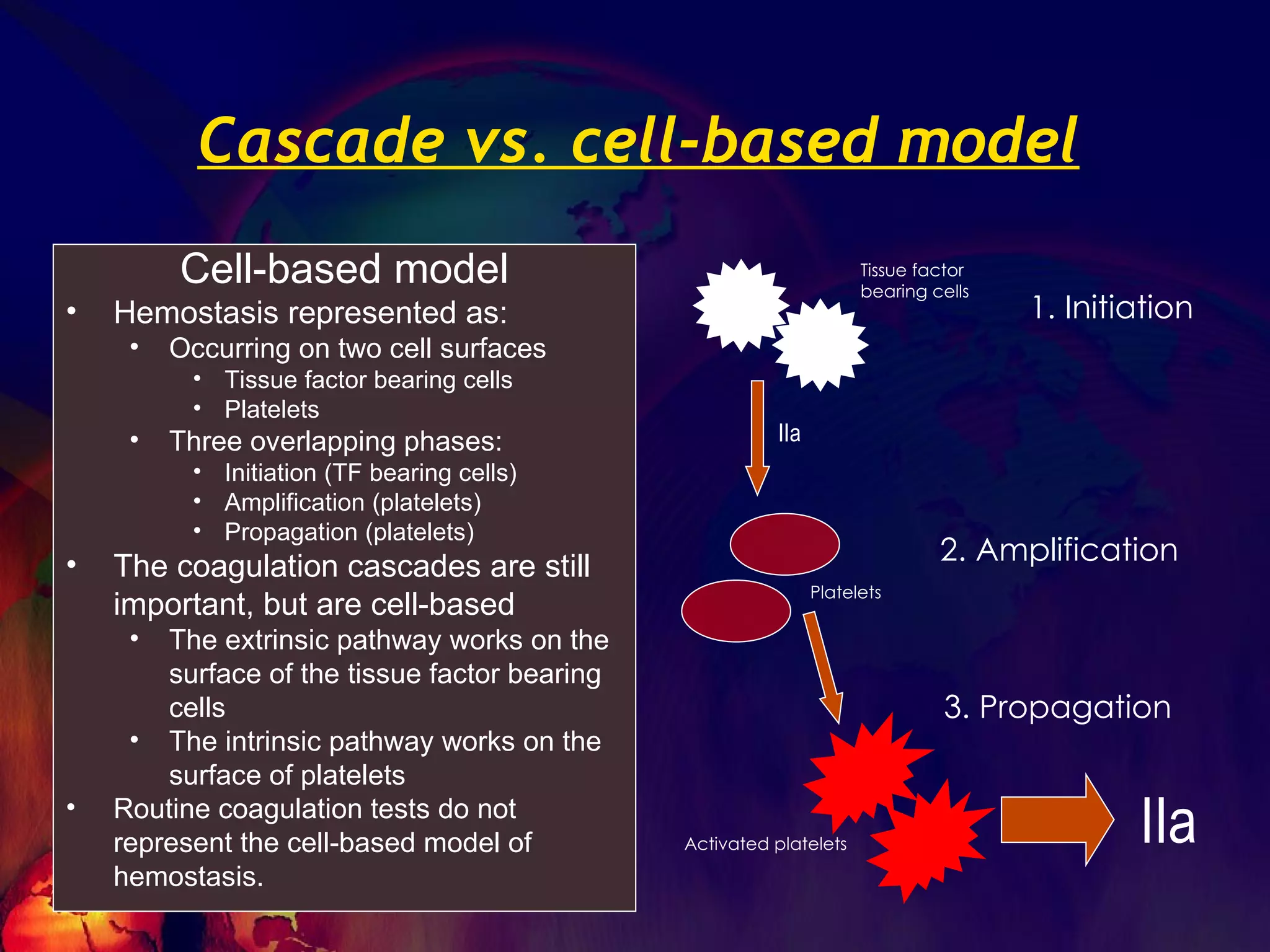
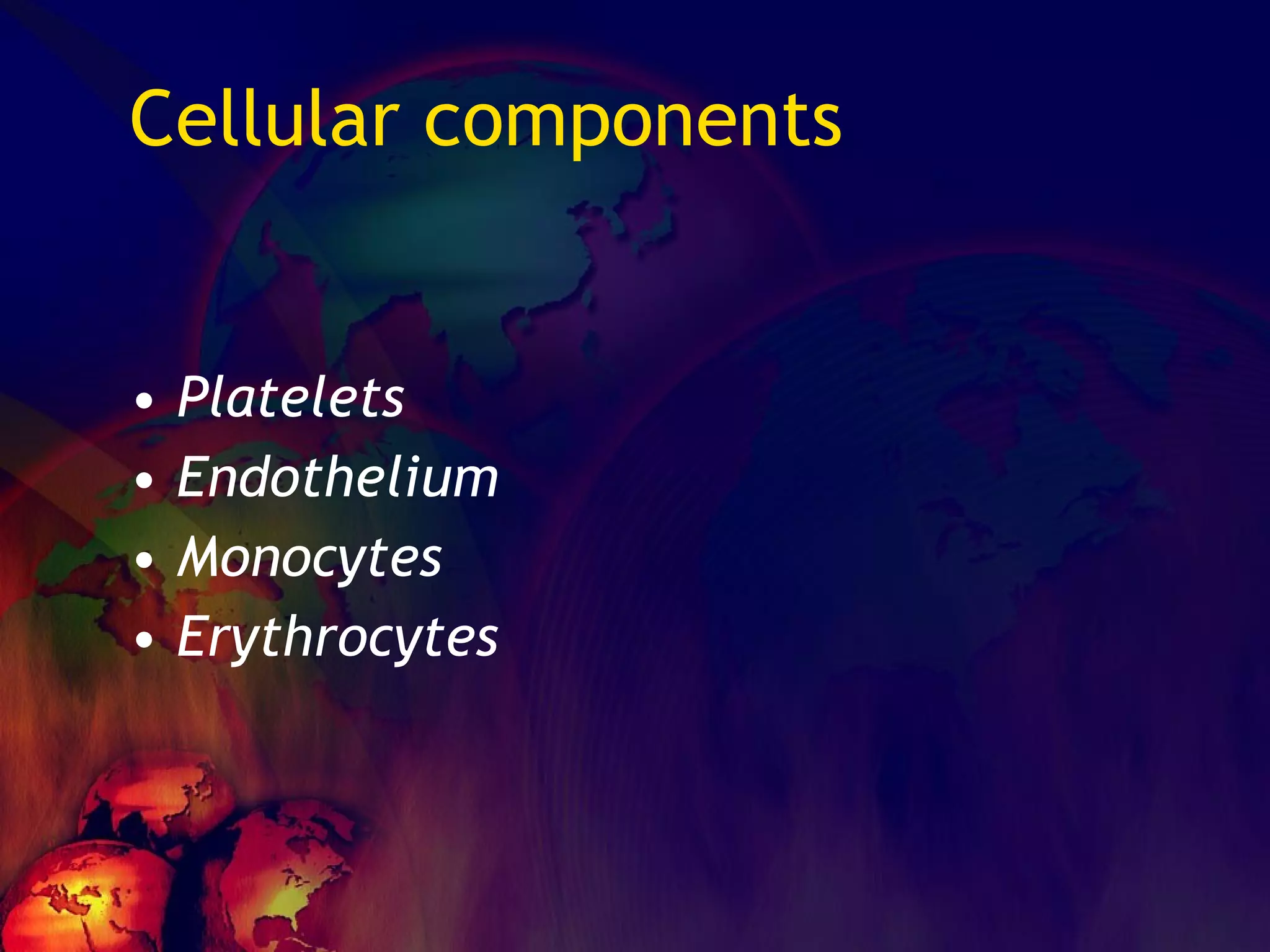
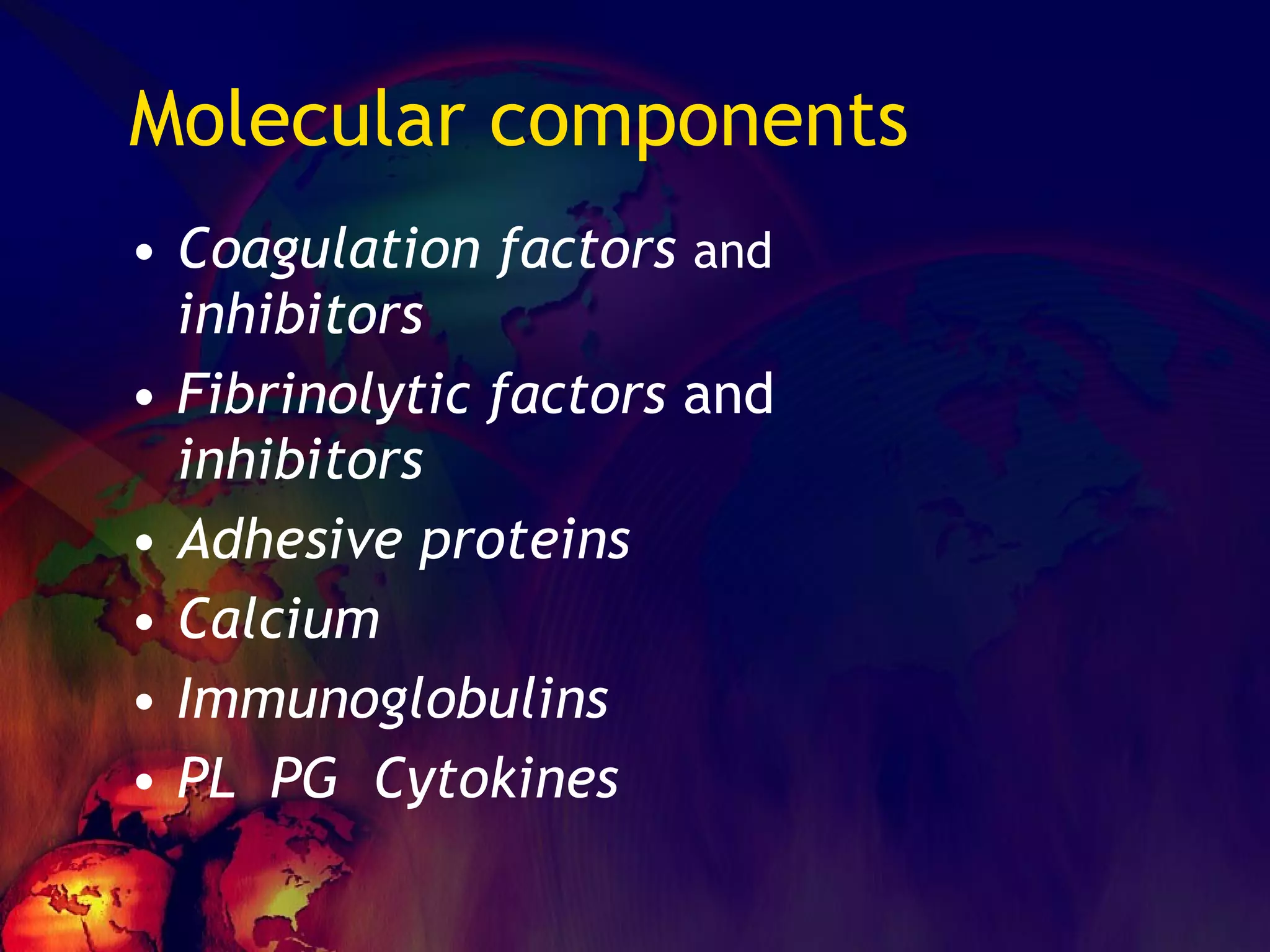
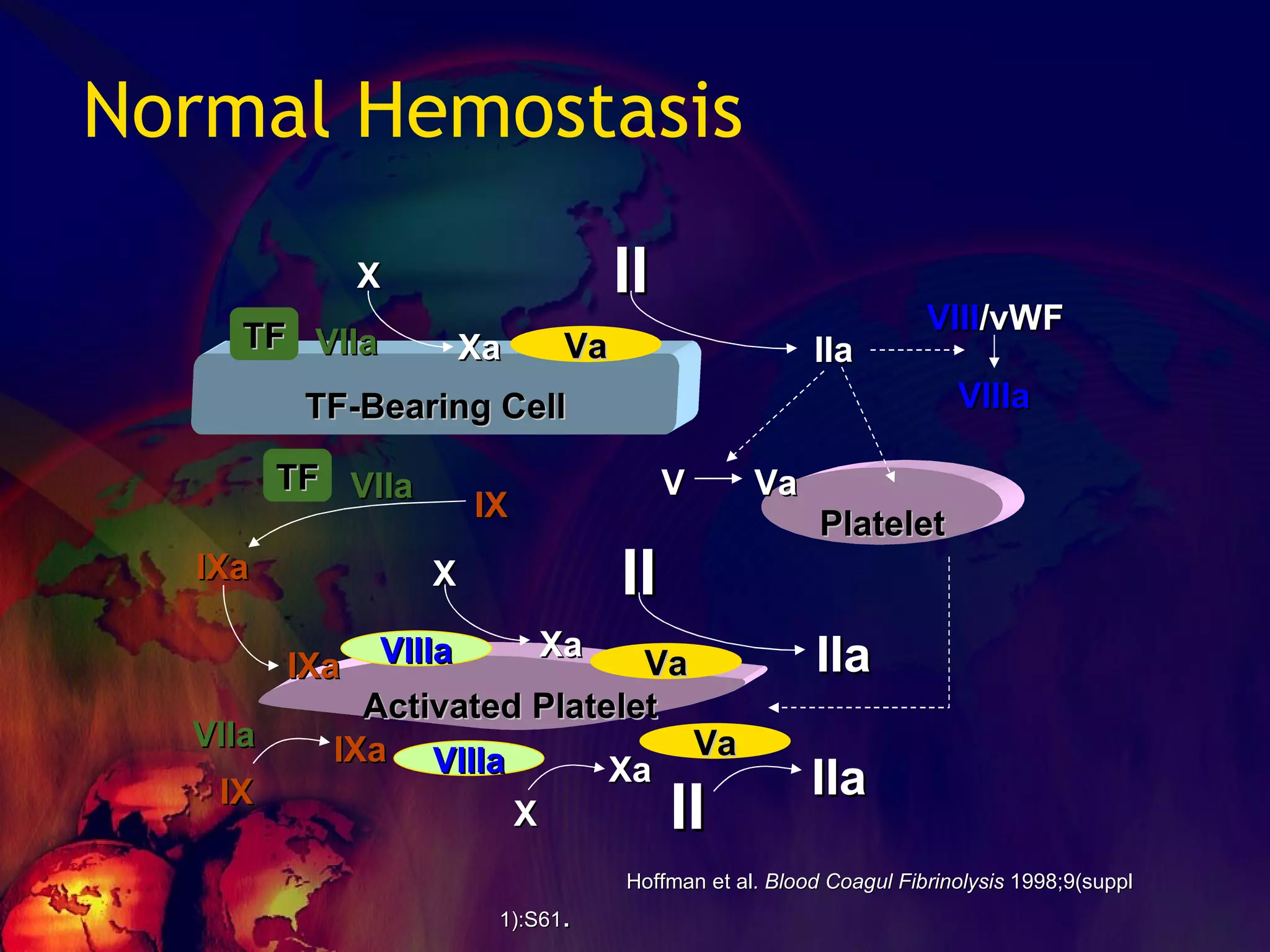
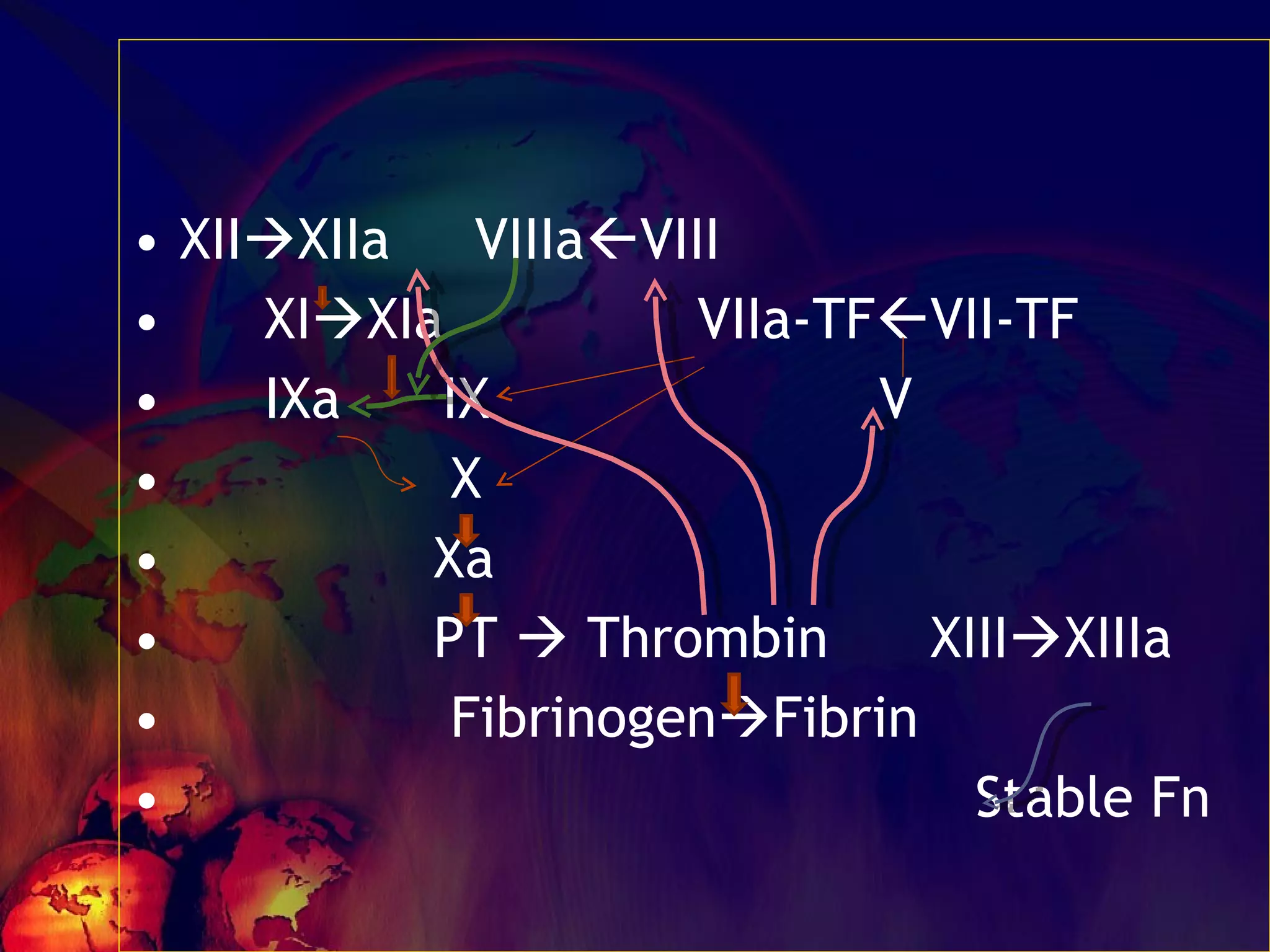
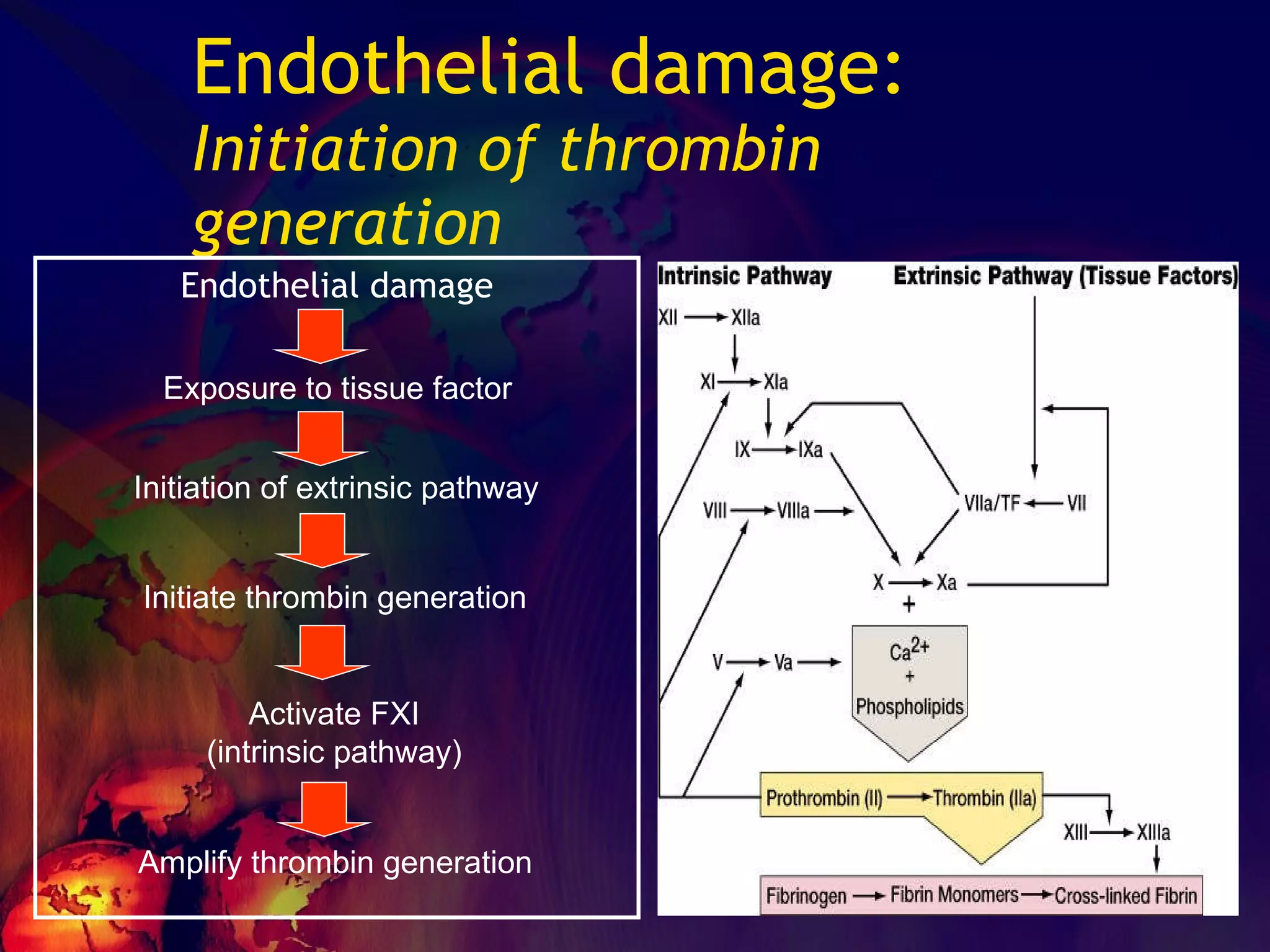
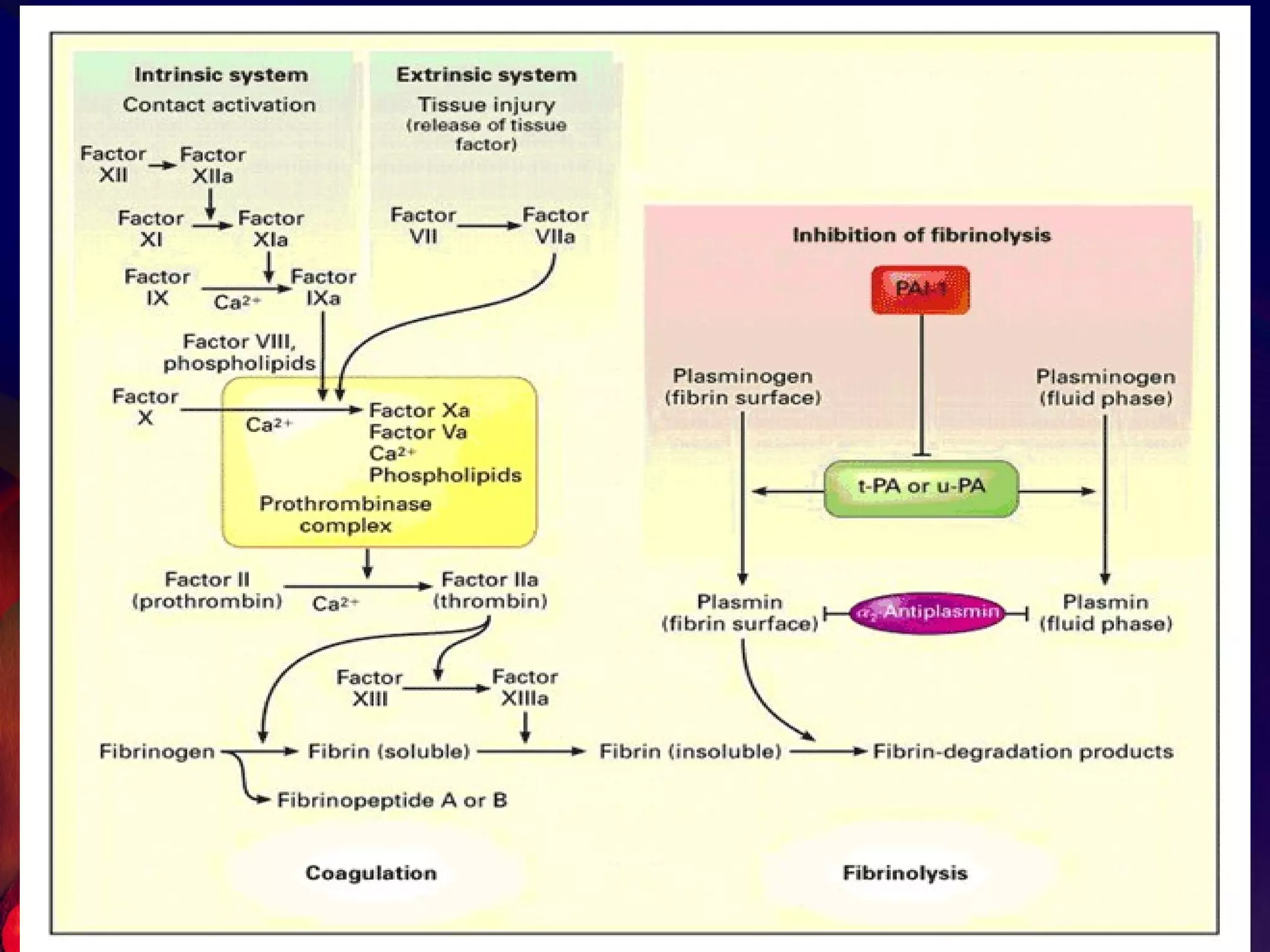
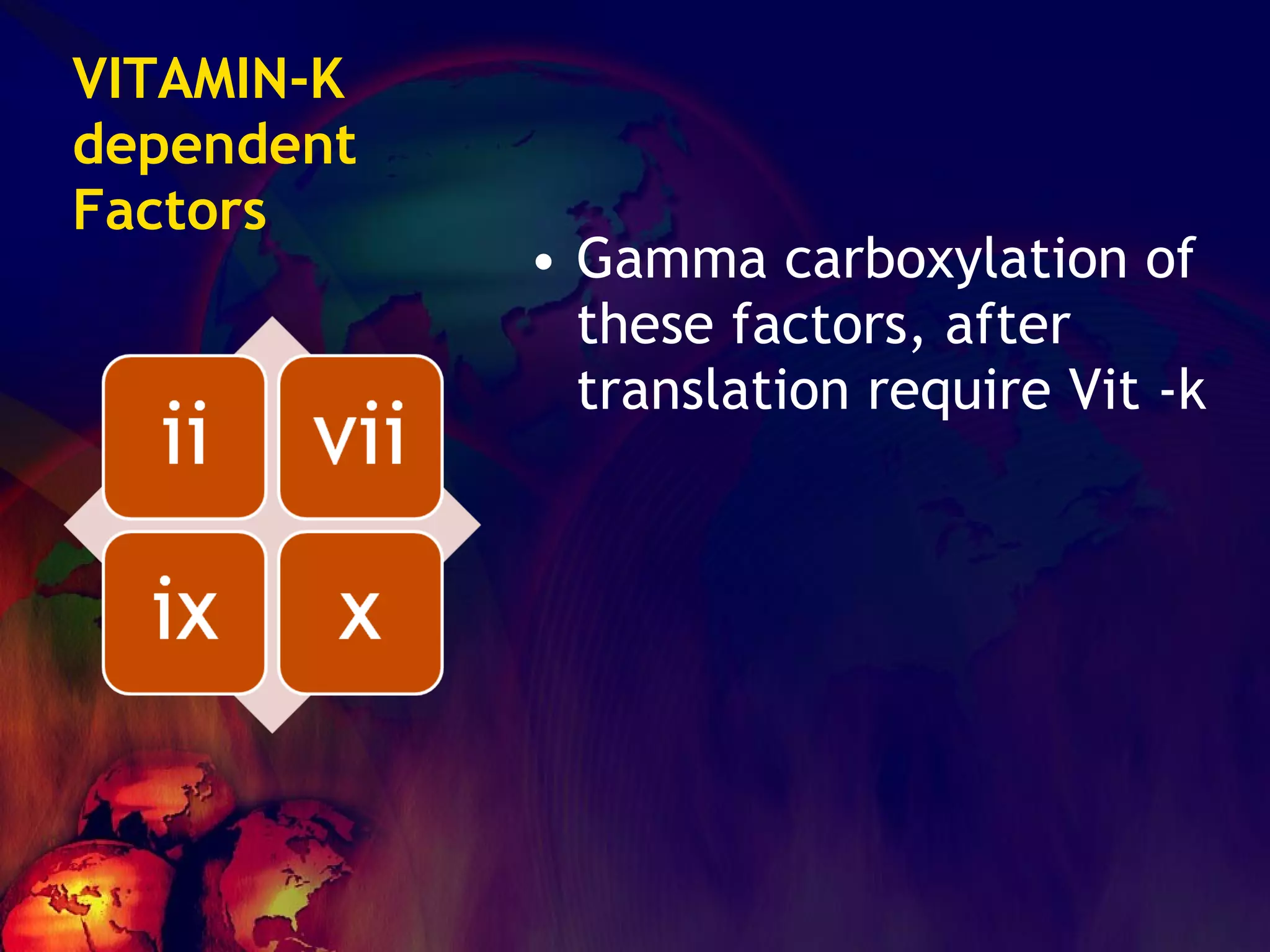
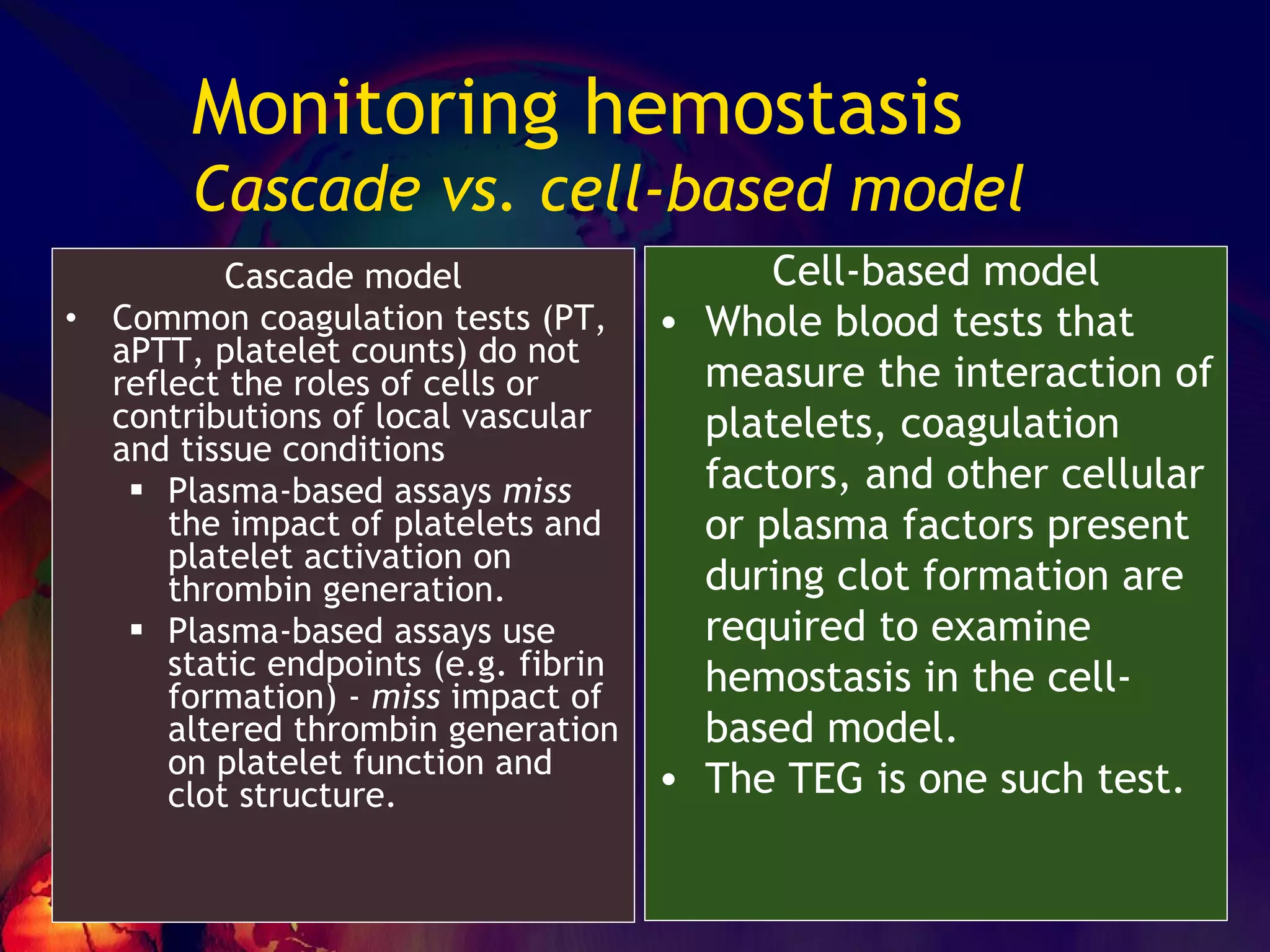
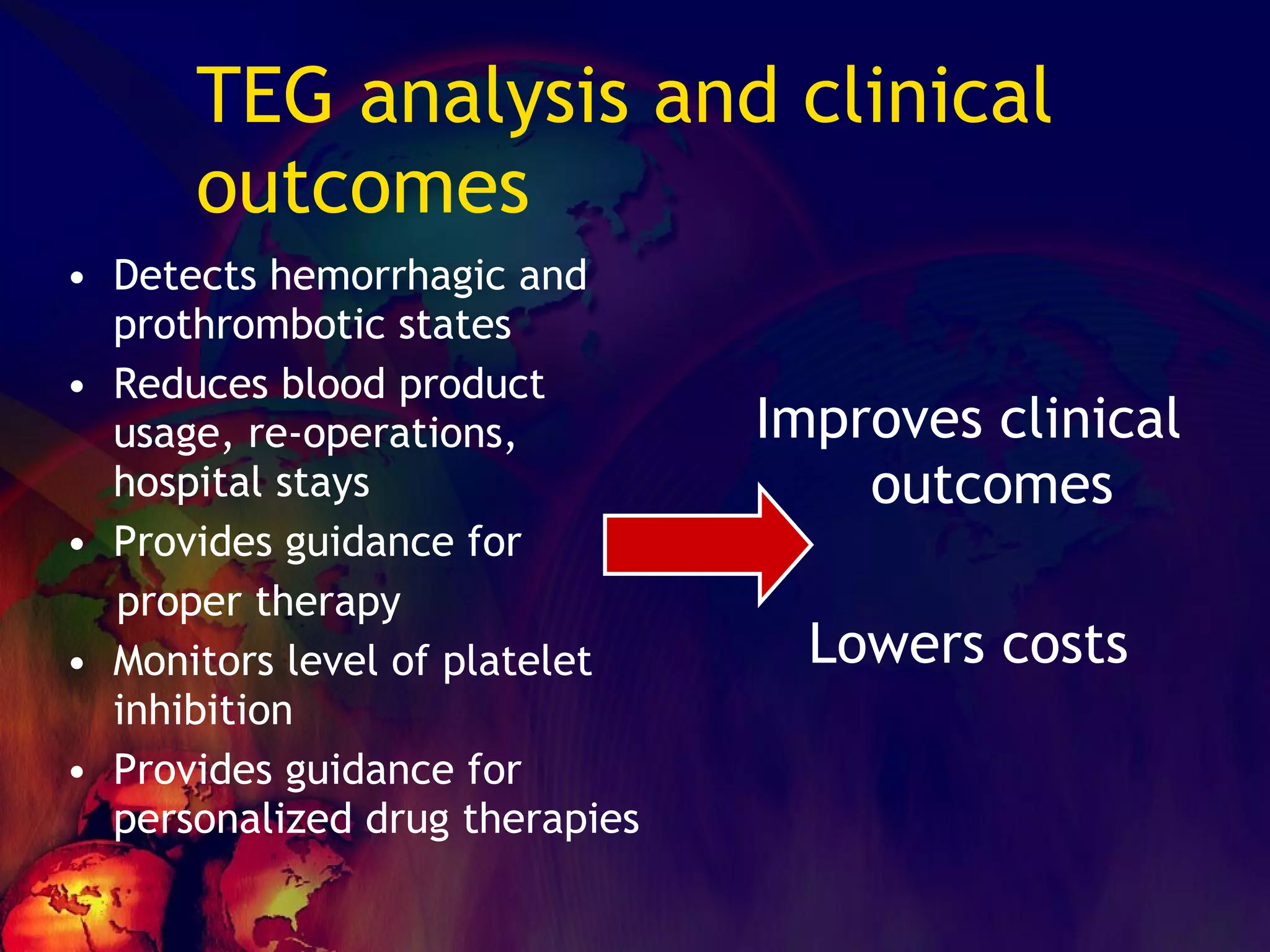
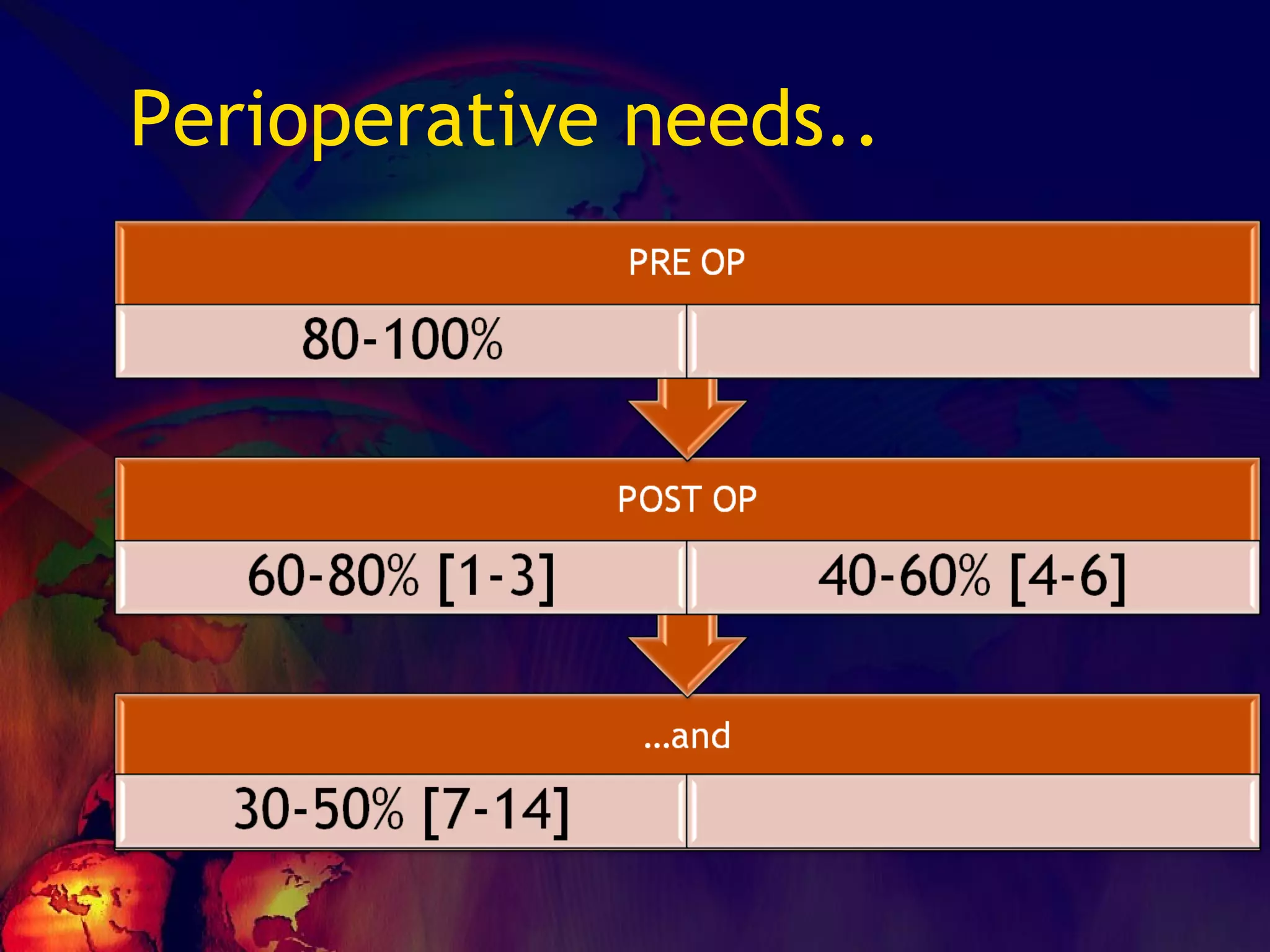
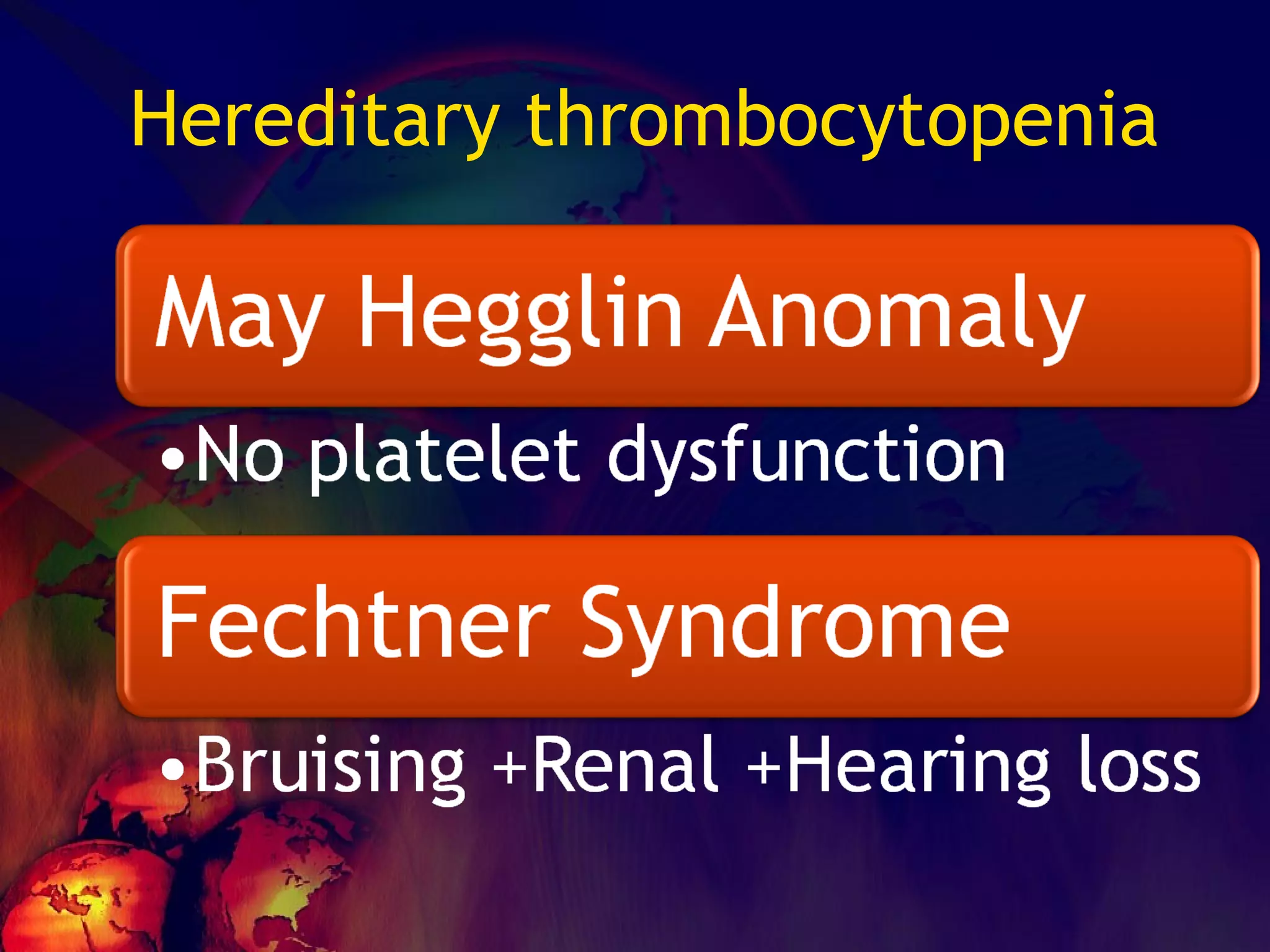
The document discusses coagulation disorders and their implications in anesthesia, detailing the components of hemostasis, including primary and secondary hemostasis processes. It emphasizes the roles of platelets, coagulation factors, and the importance of monitoring hemostasis through various laboratory tests. Additionally, it covers inherited bleeding disorders such as hemophilia, their treatment, and considerations for anesthesia management in patients with coagulation issues.


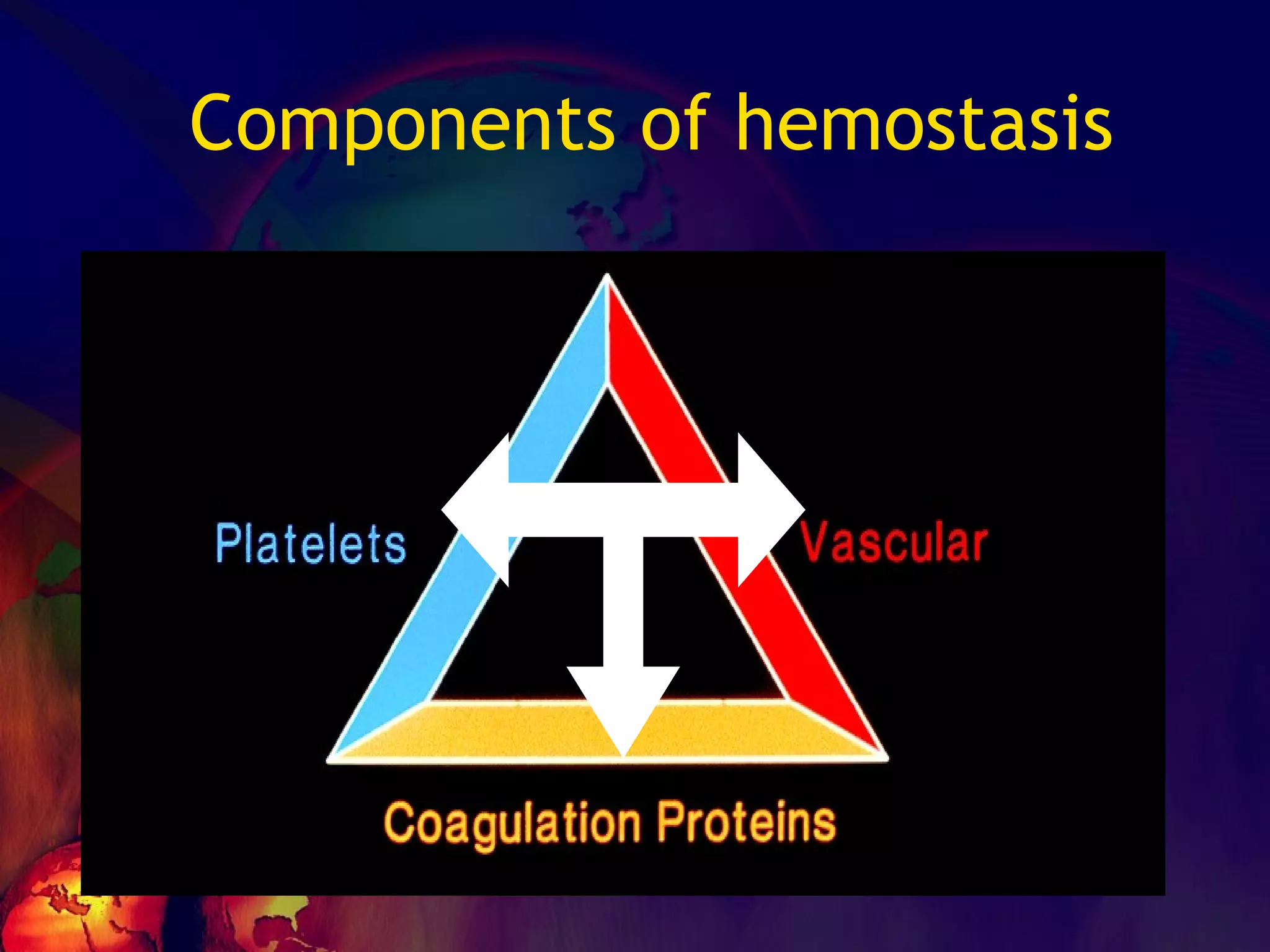
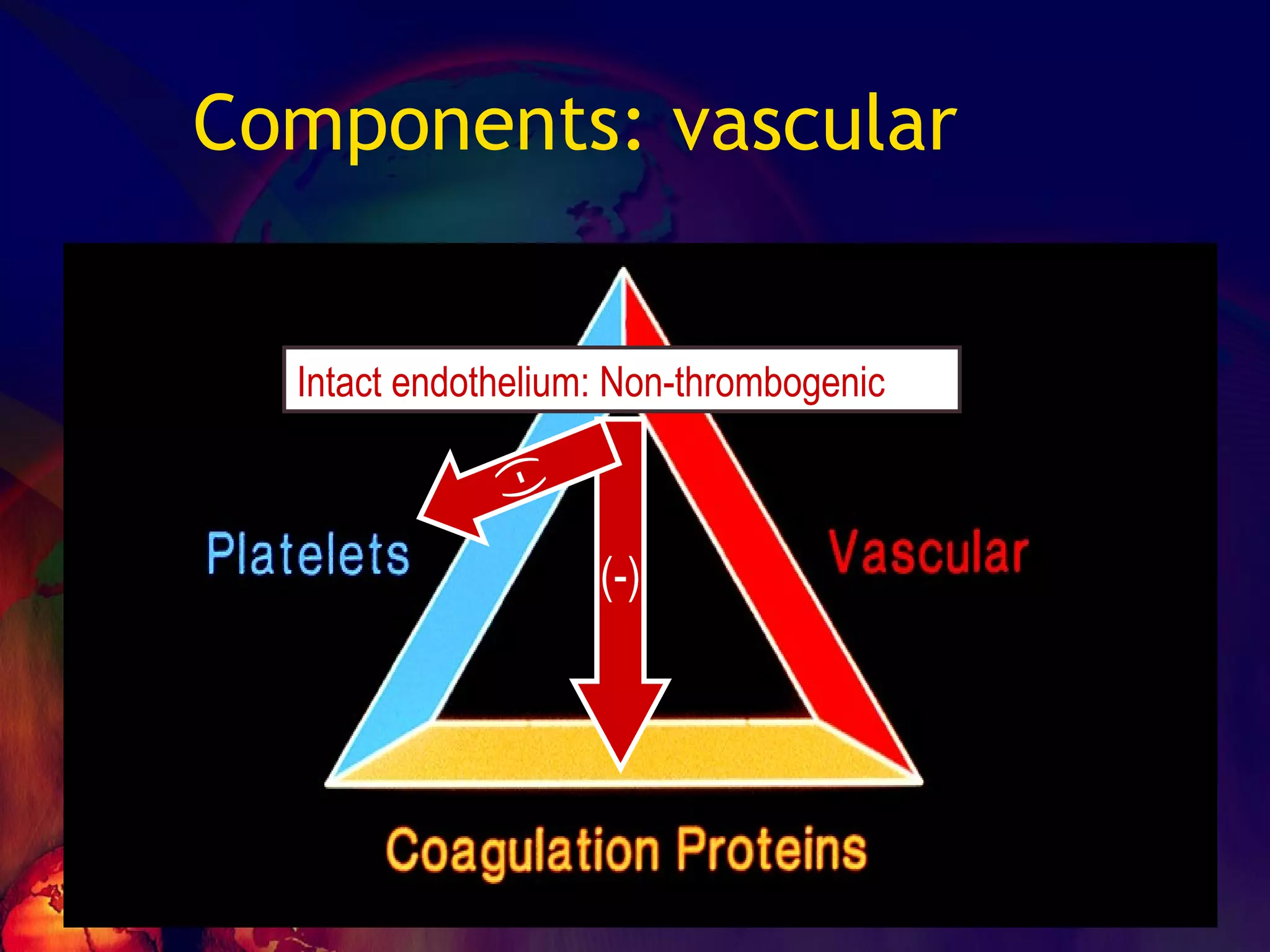
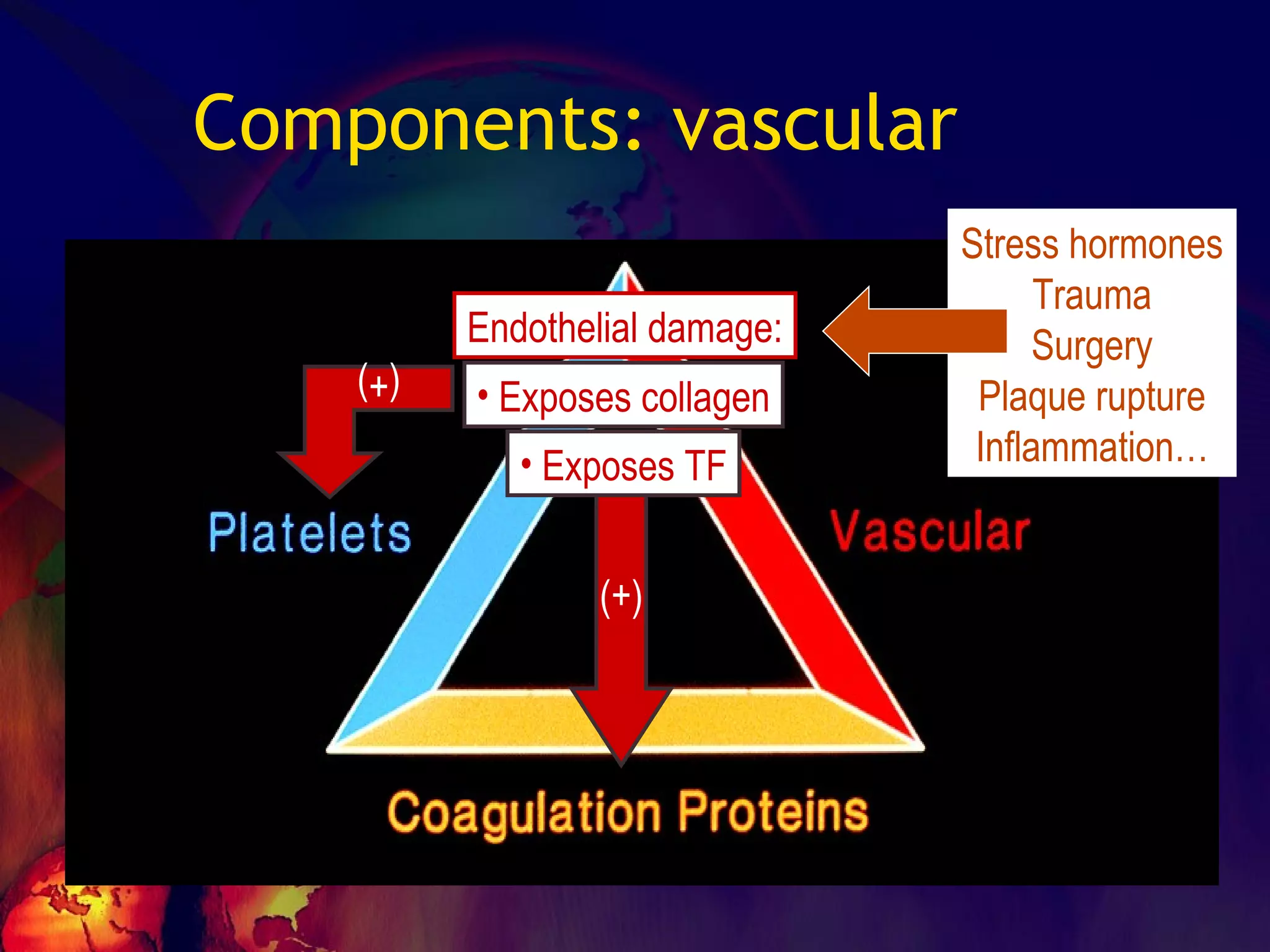

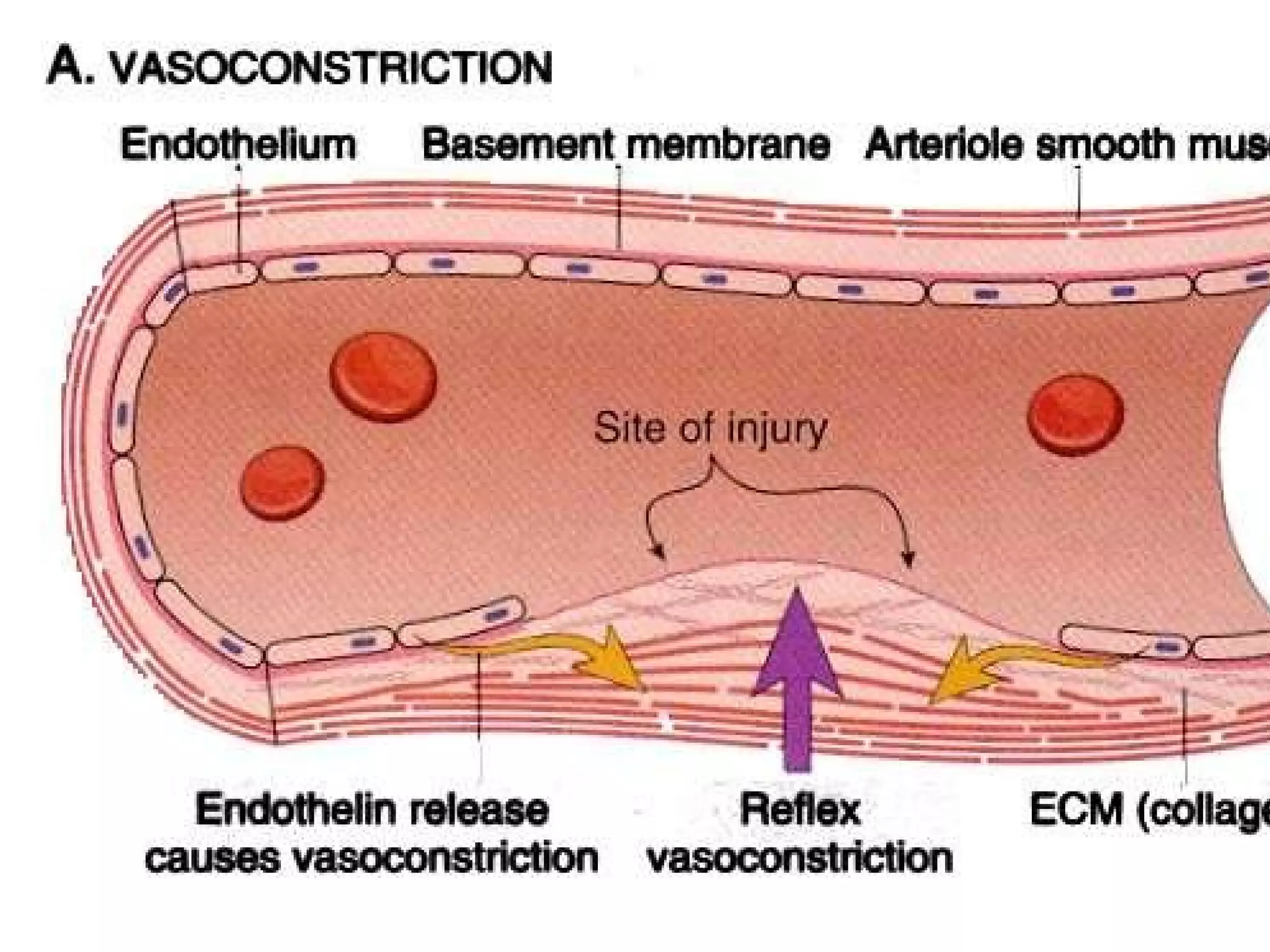

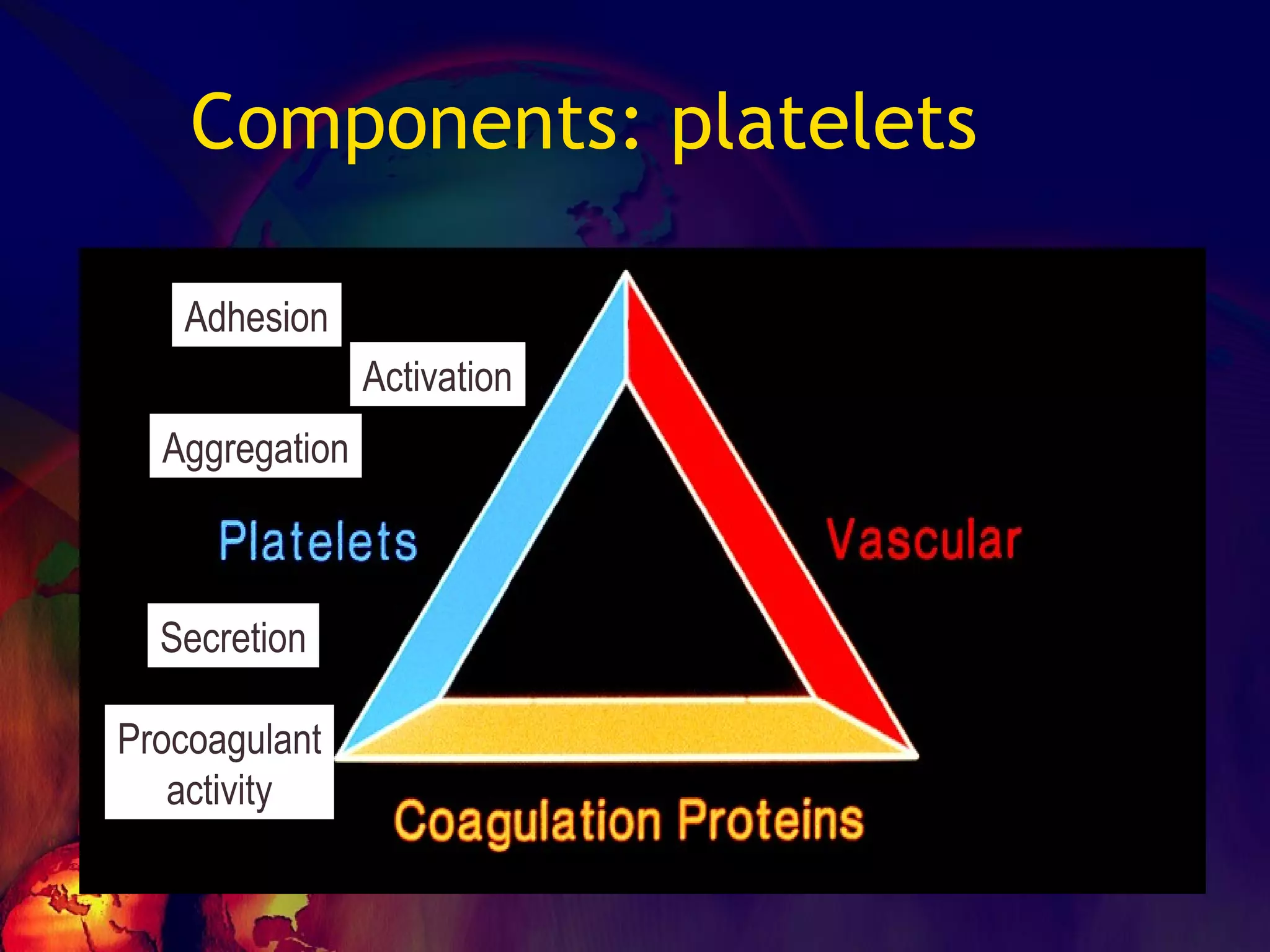
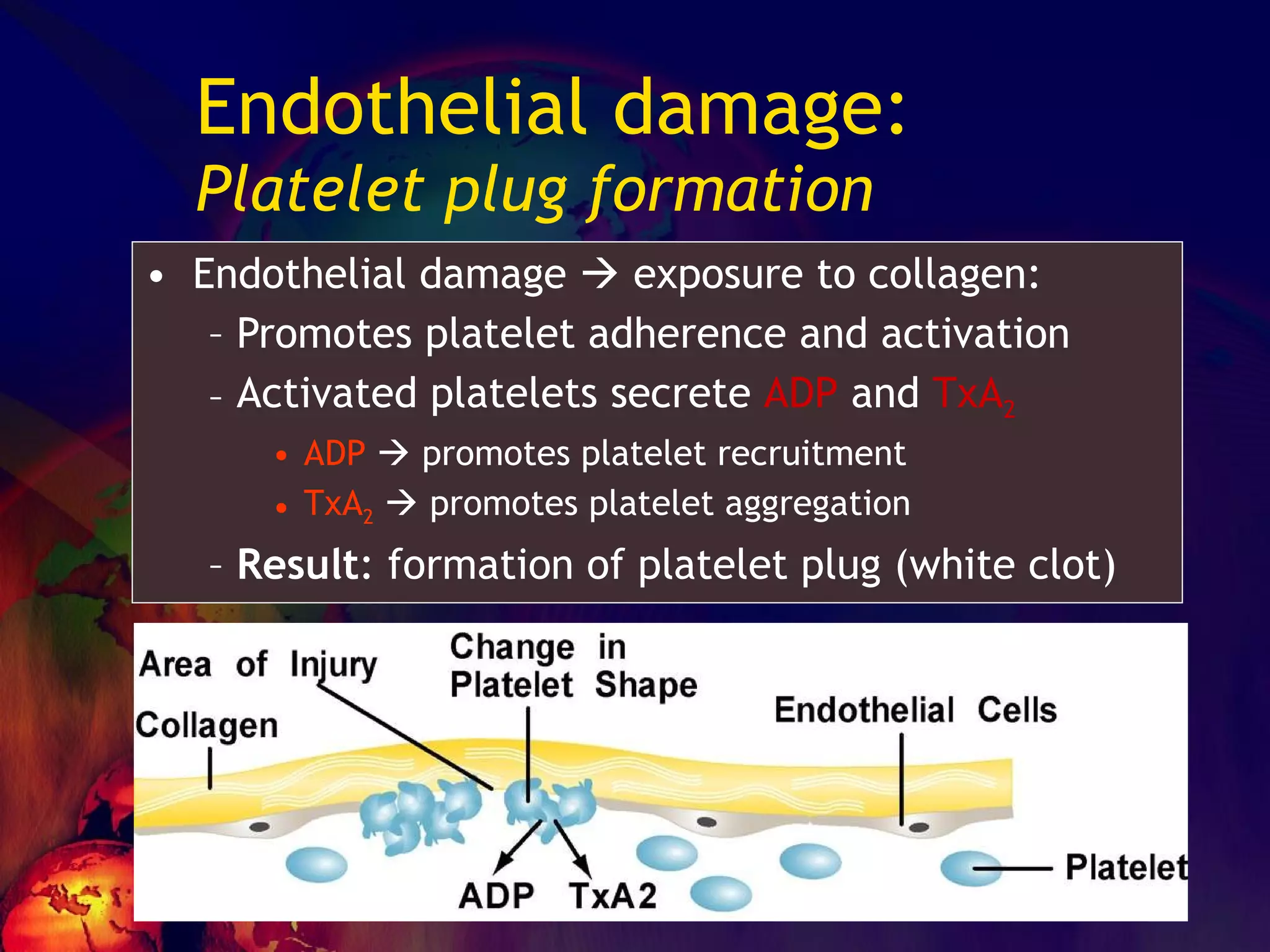
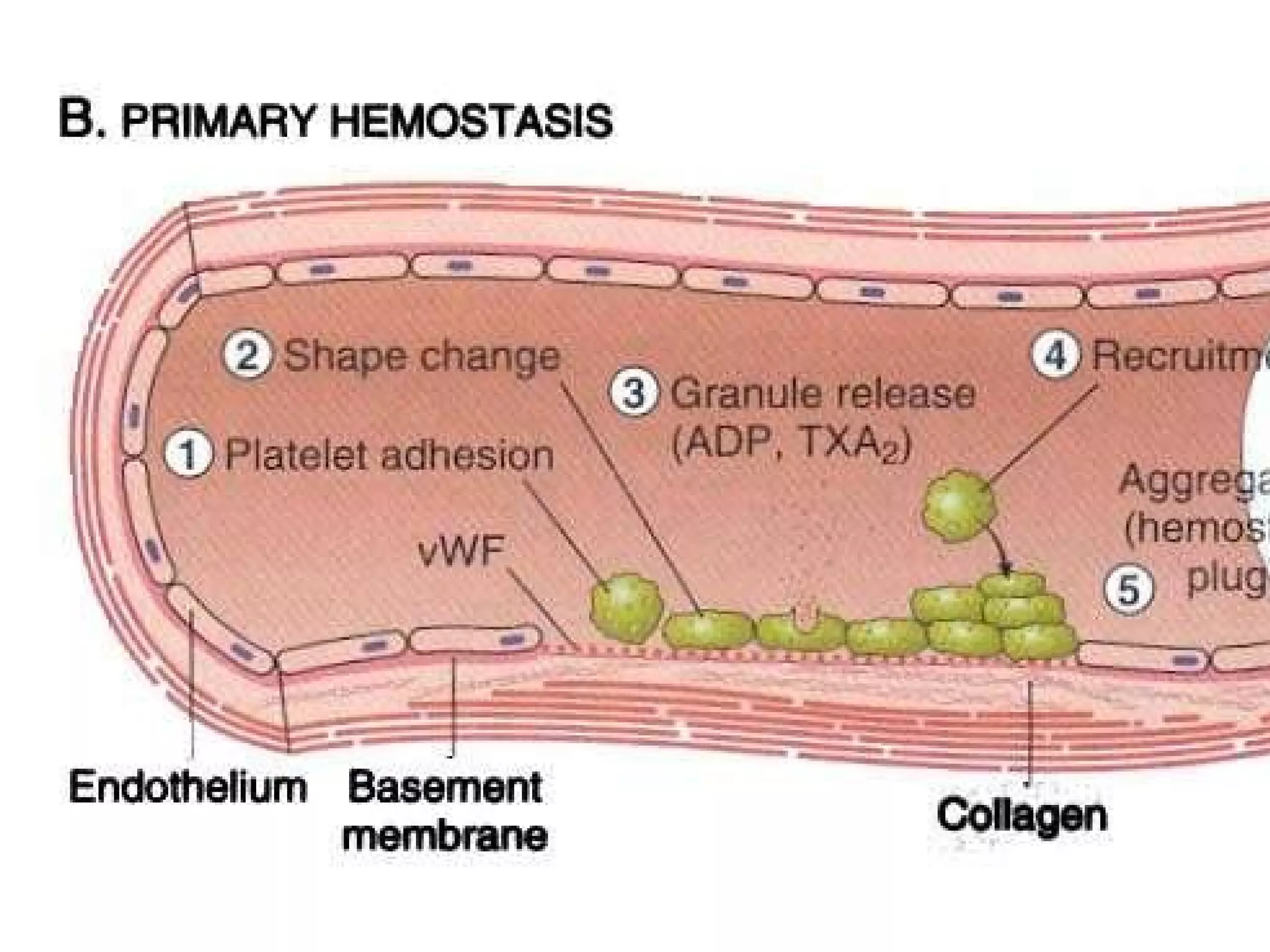
![No one can hide the insults from them…… ADHESION – [vWF] SECRETION-[TxA2,ADP] AGGREGATION Leads to PRIMARY HEMOSTASIS](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/coagulationdisordersandanaesthesia29finalfinal97-2003animated-091009071734-phpapp01/75/Coagulation-Disorders-and-Anesthesia-Basic-pathophysiology-11-2048.jpg)



















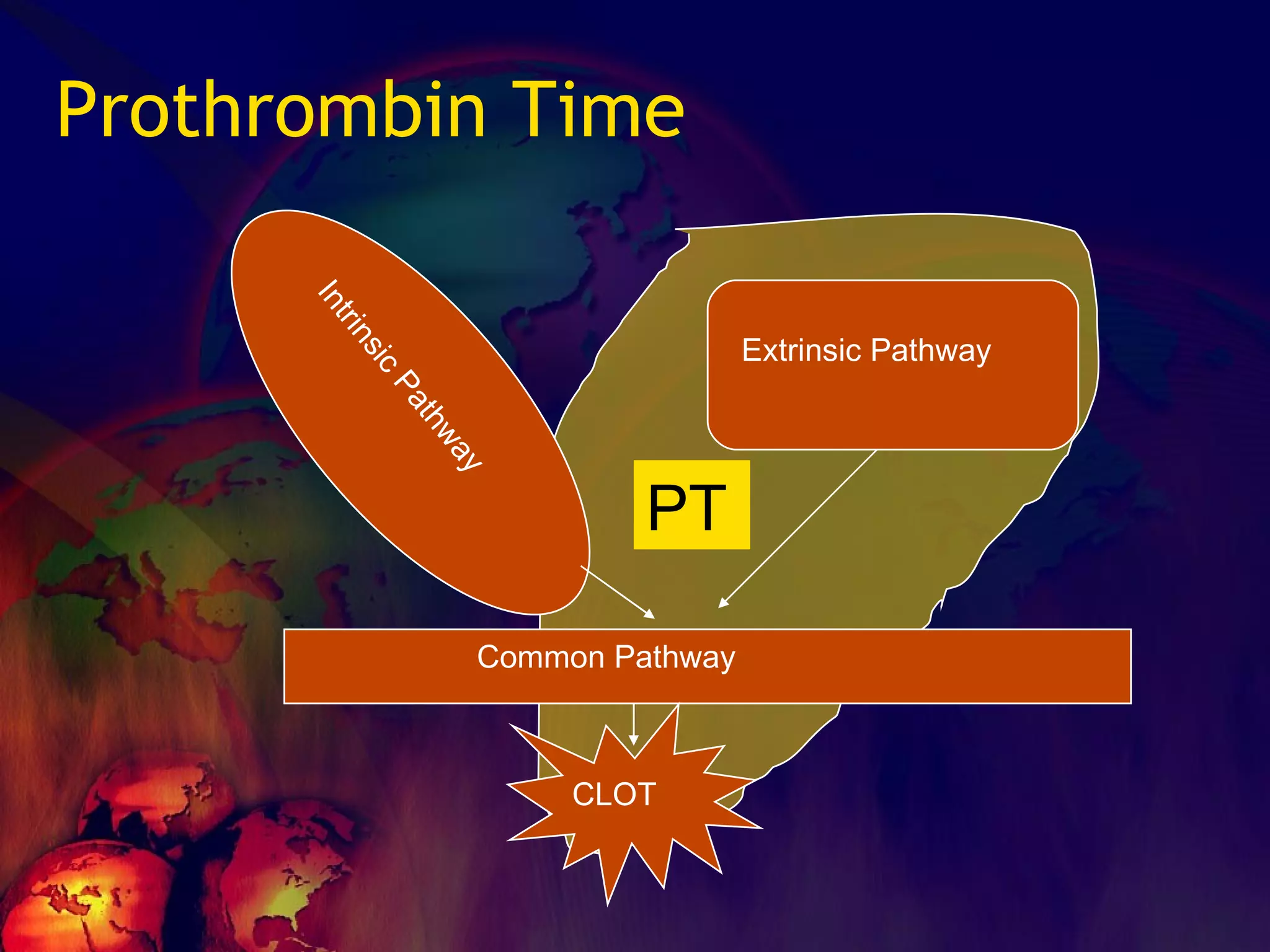
![What is INR? The aim is standardization of PT values ISI expresses the sensitivity of the PT reagent of a particular lab to that of WHO reagent. Patient PT / mean normal PT [PT ratio]^ ISI](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/coagulationdisordersandanaesthesia29finalfinal97-2003animated-091009071734-phpapp01/75/Coagulation-Disorders-and-Anesthesia-Basic-pathophysiology-52-2048.jpg)


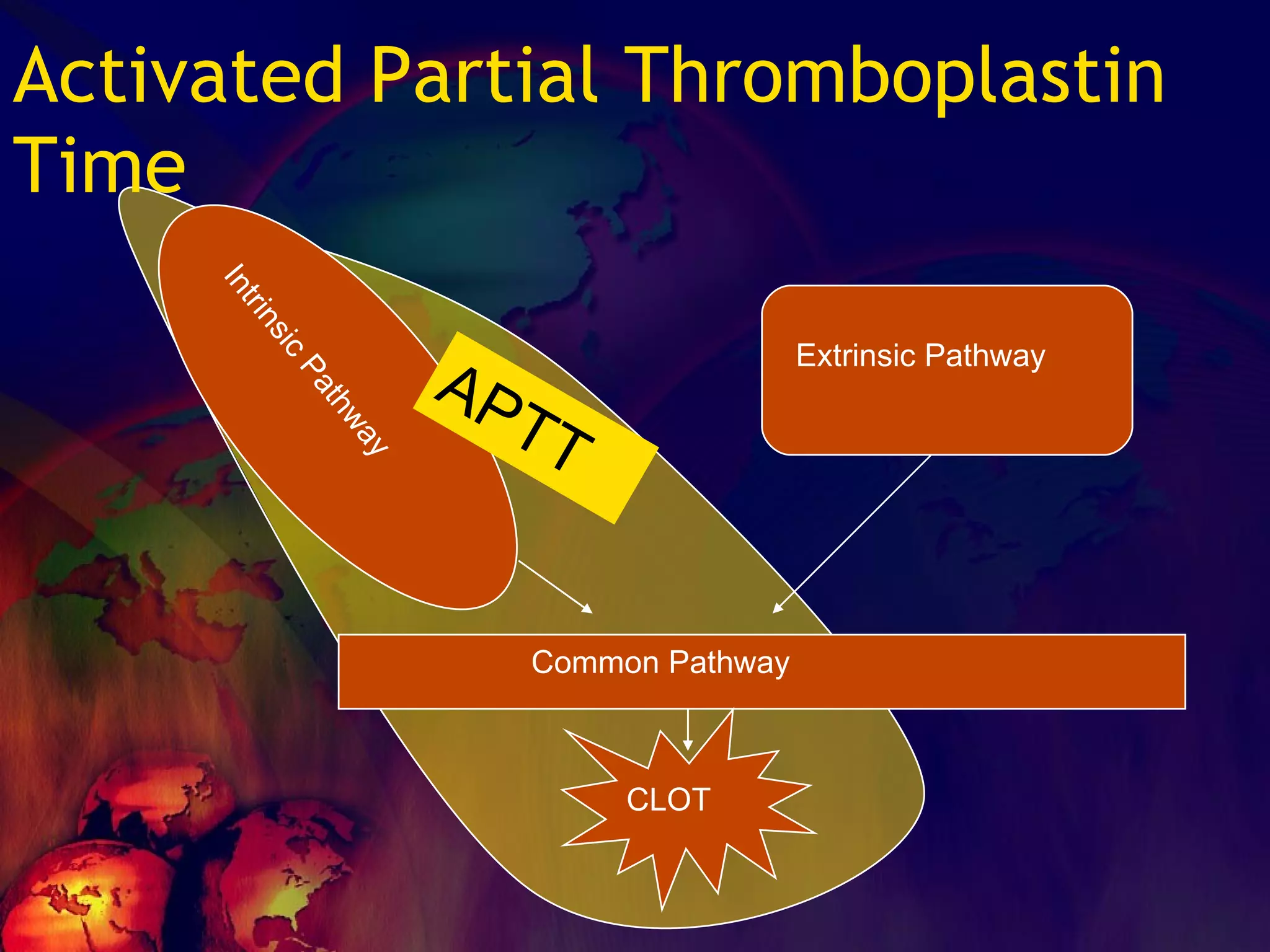

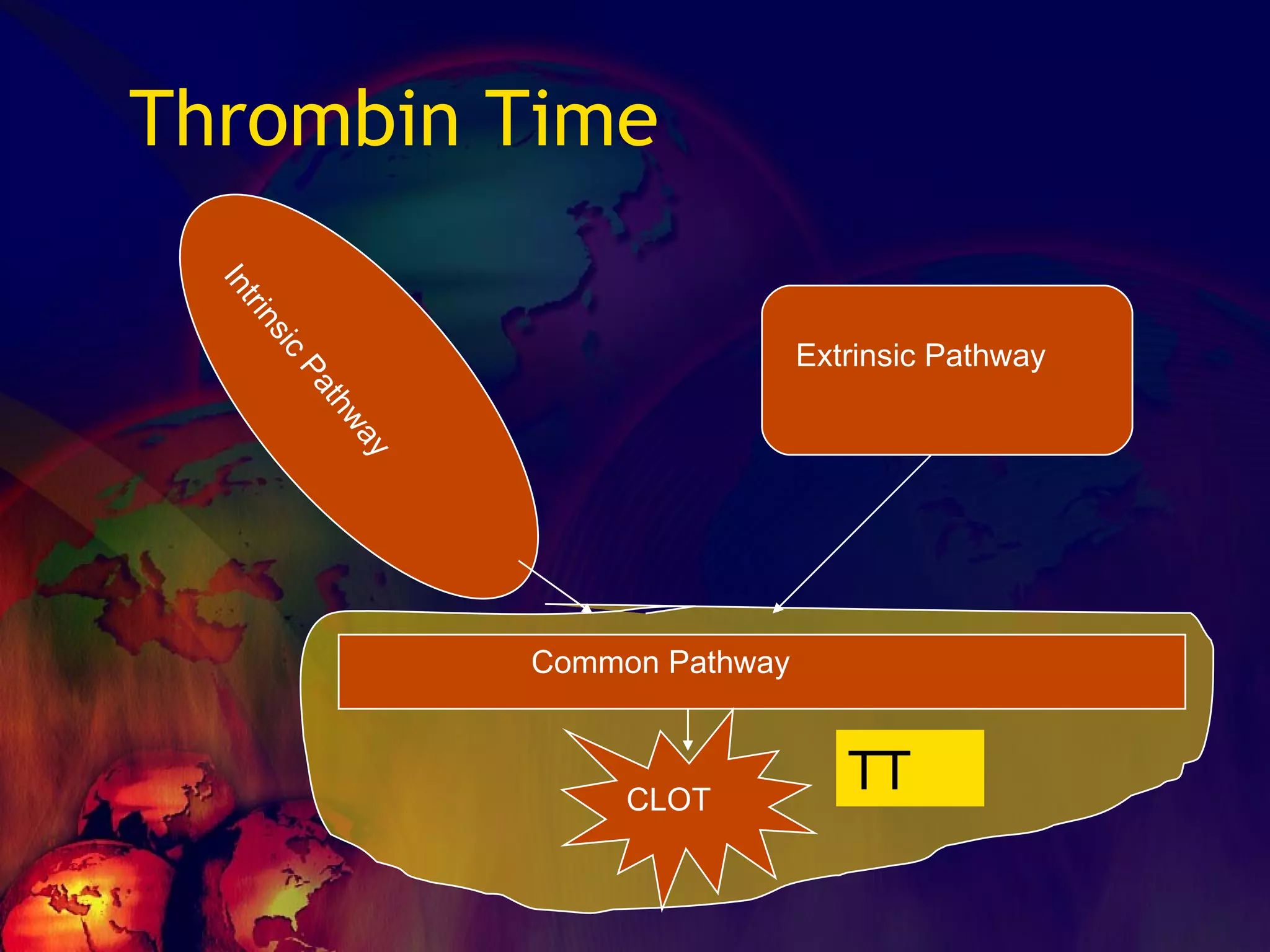


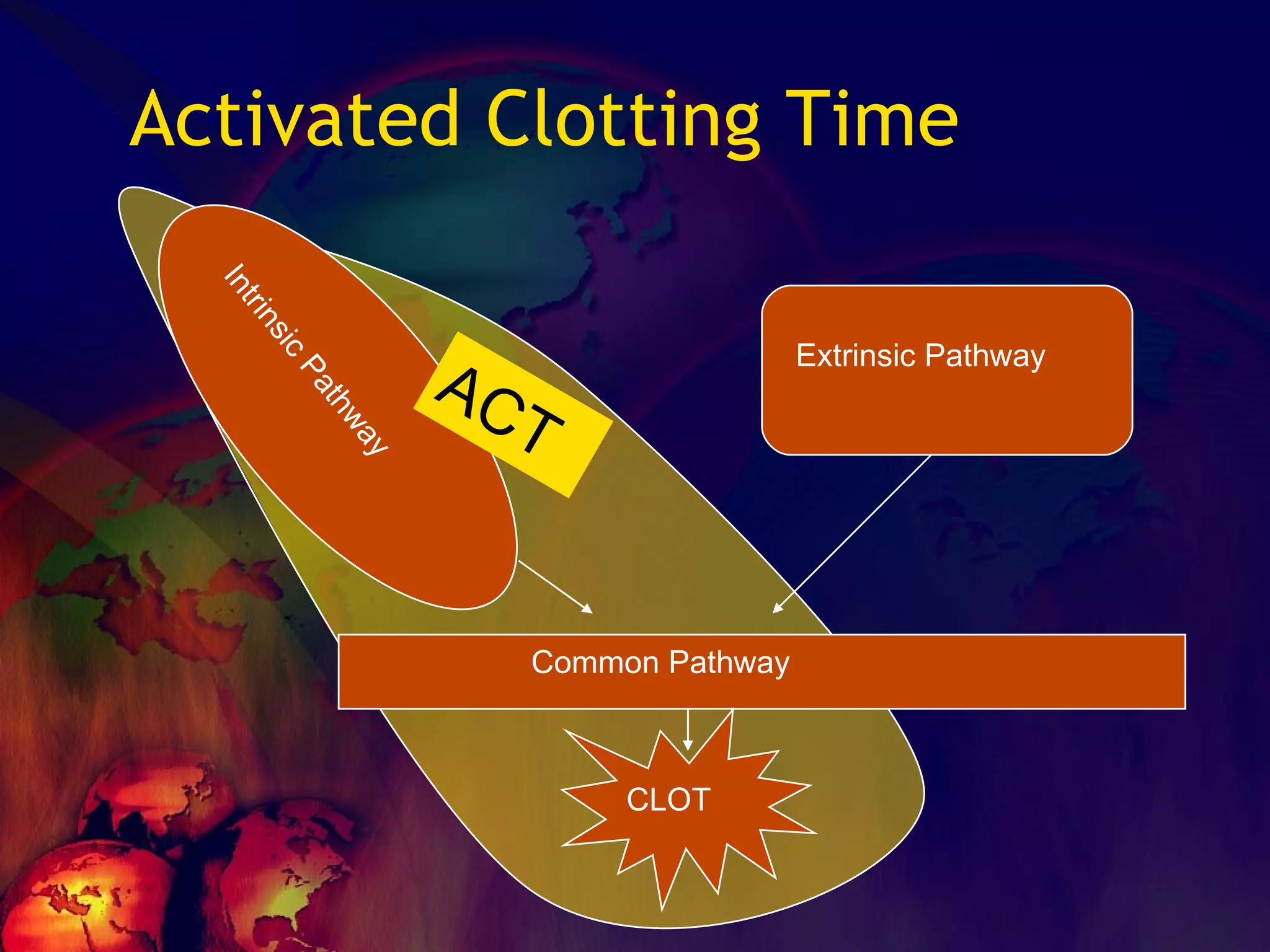

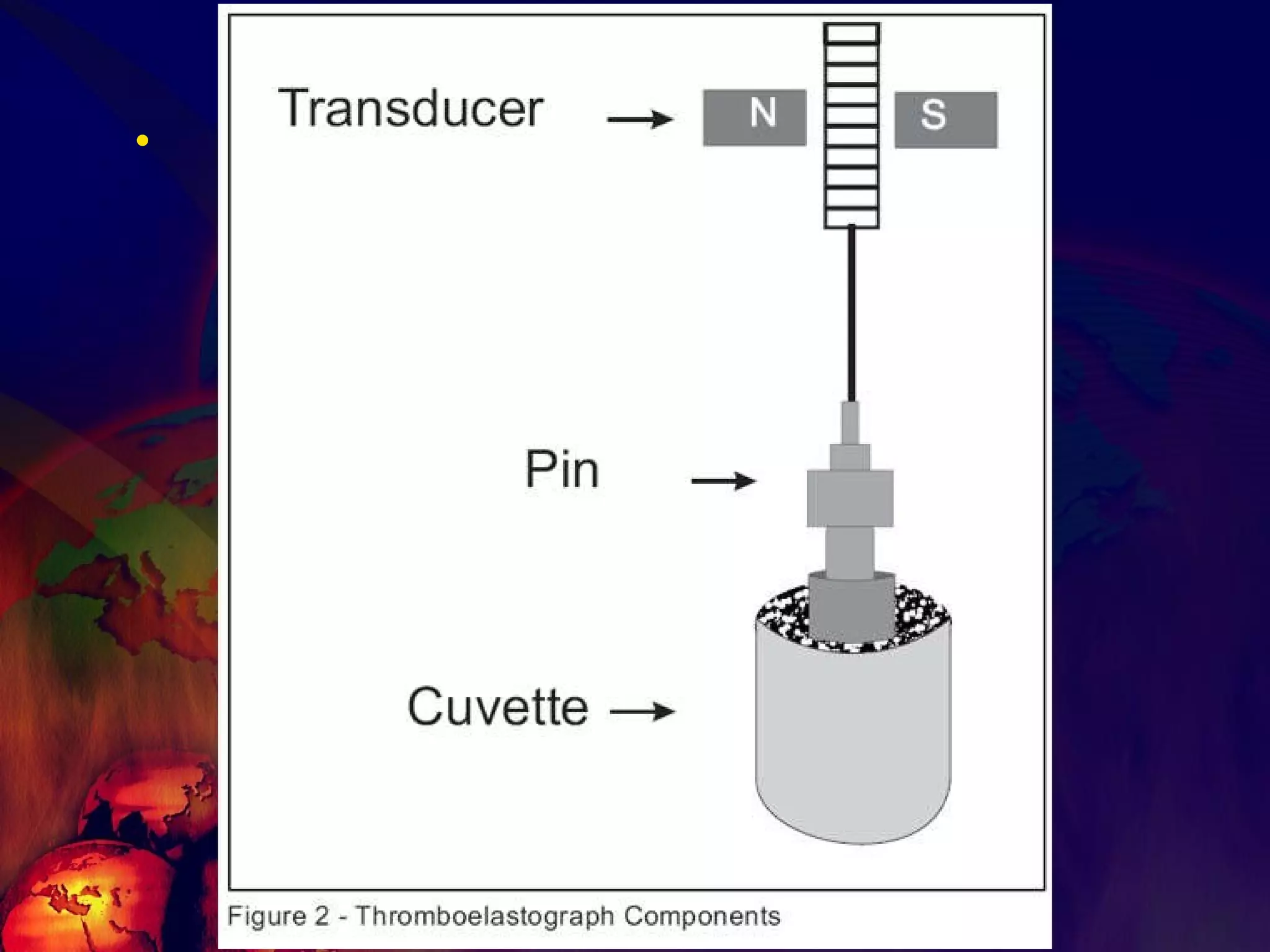
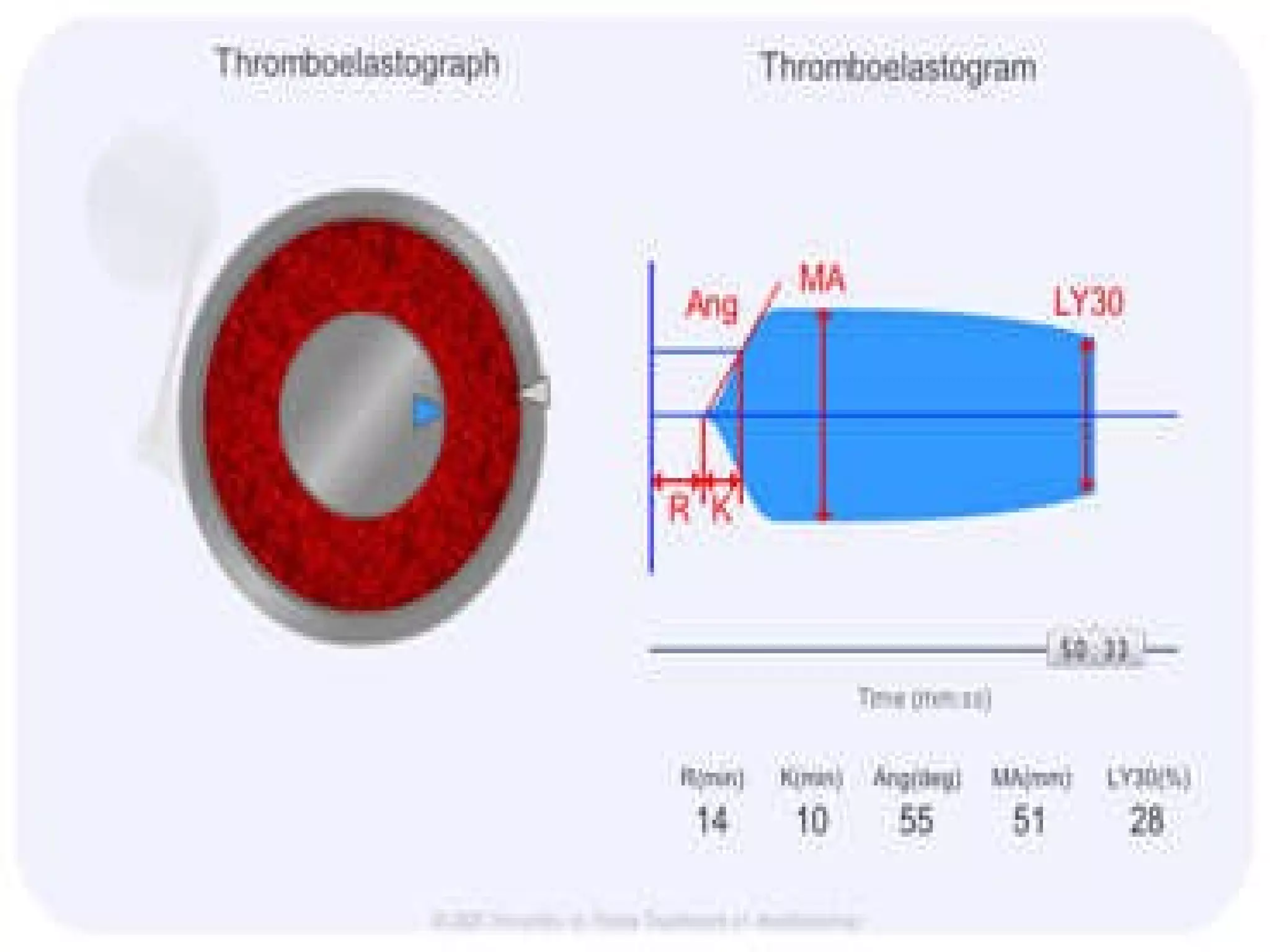

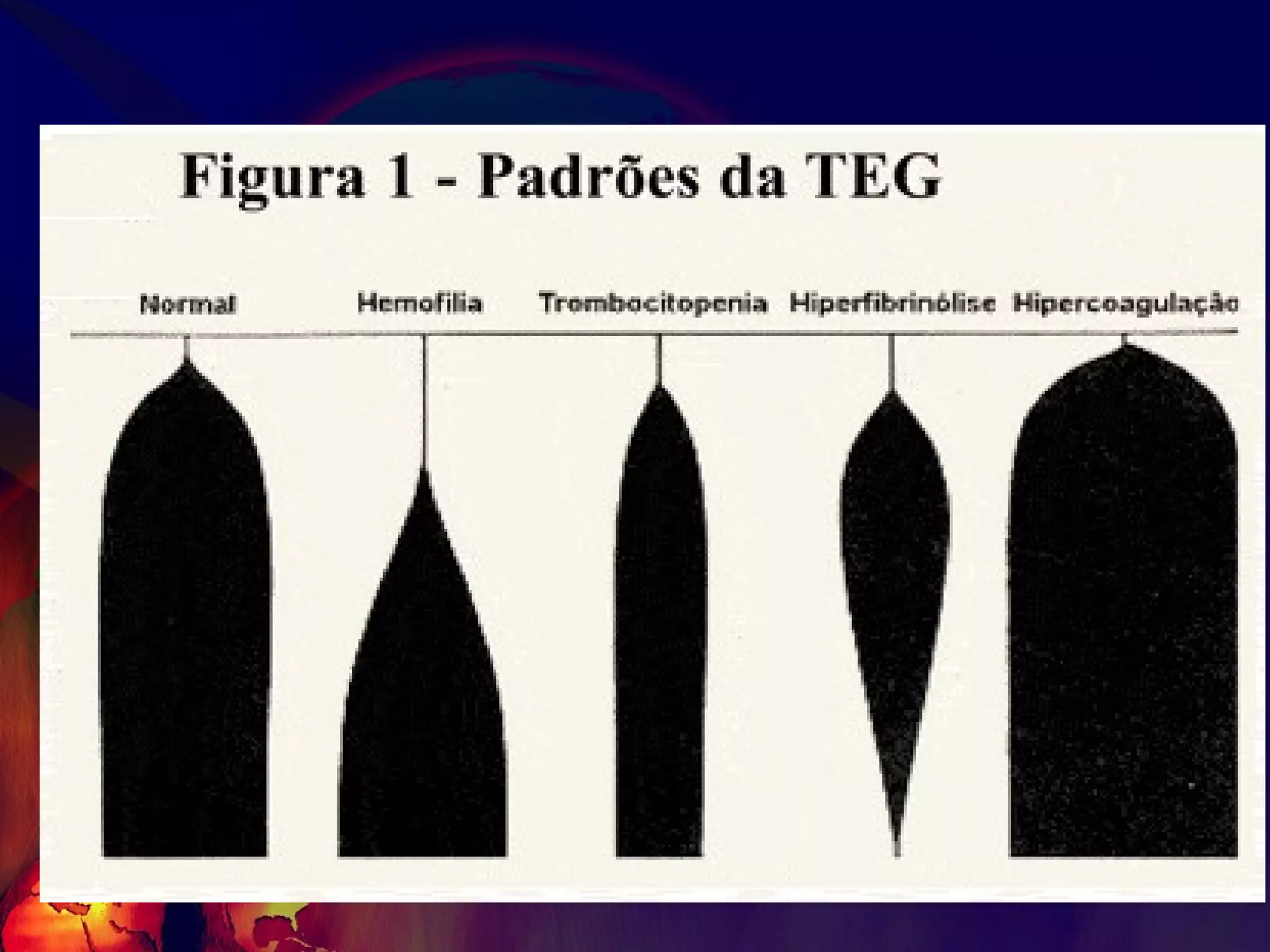




















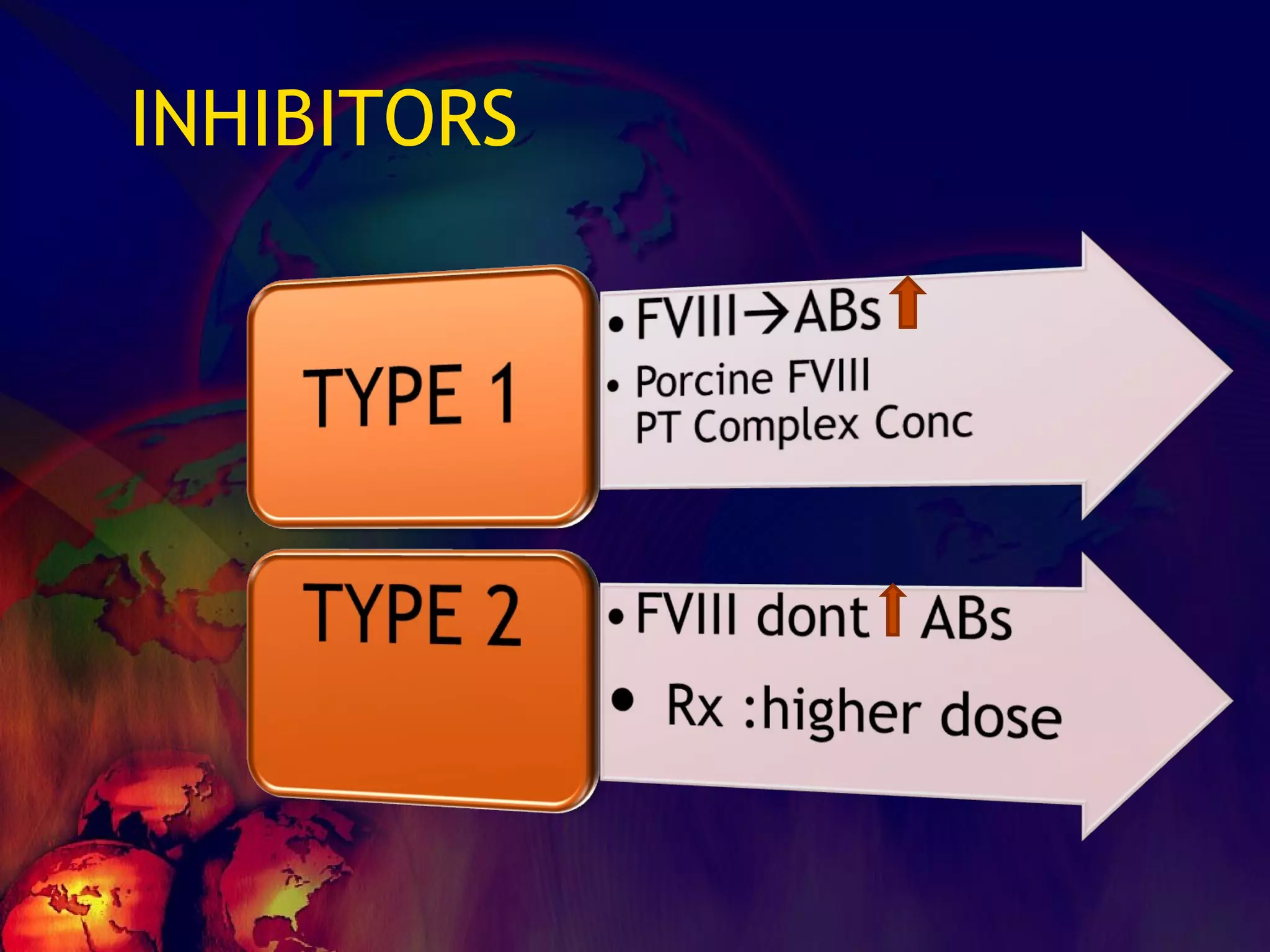

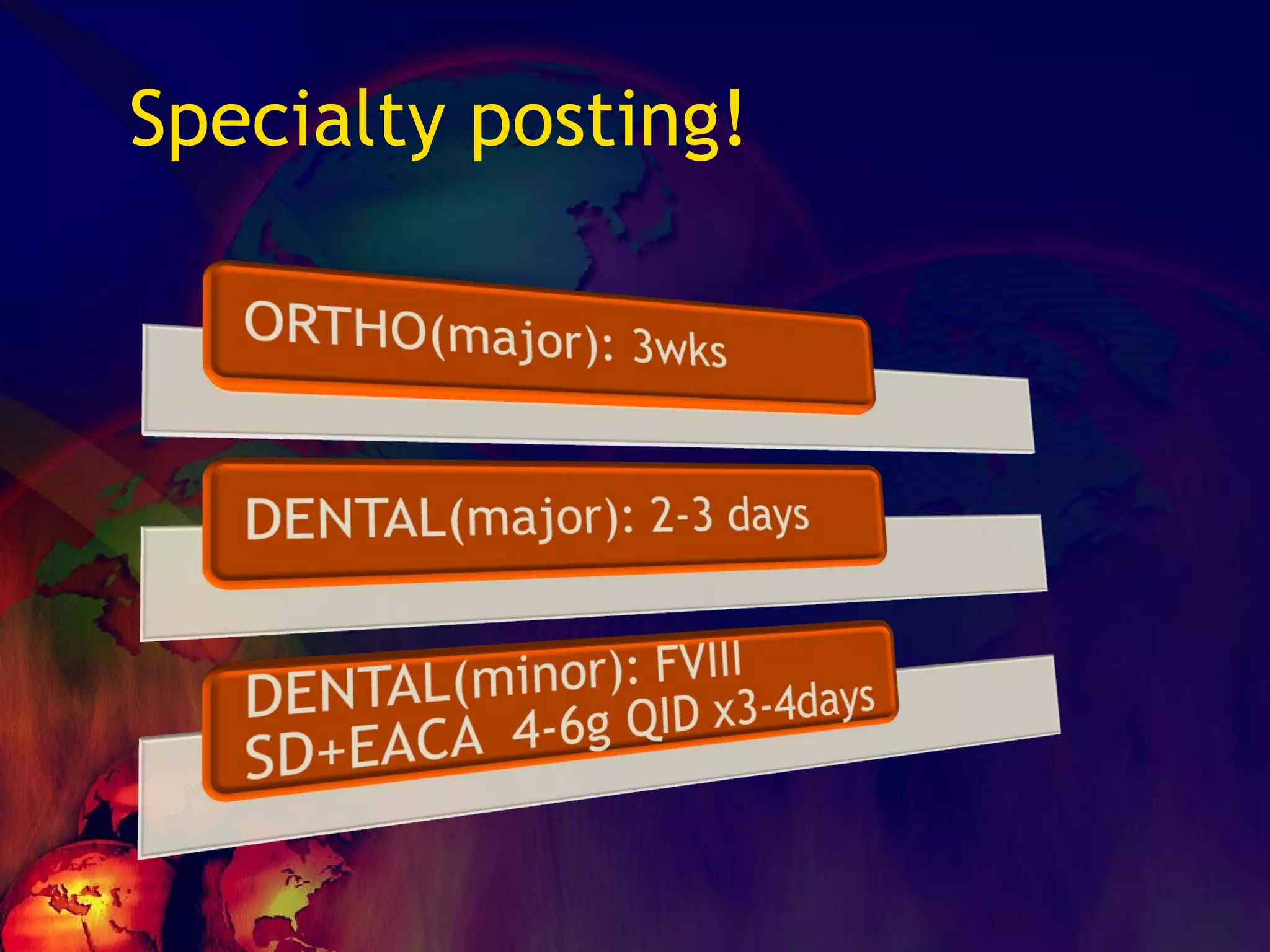
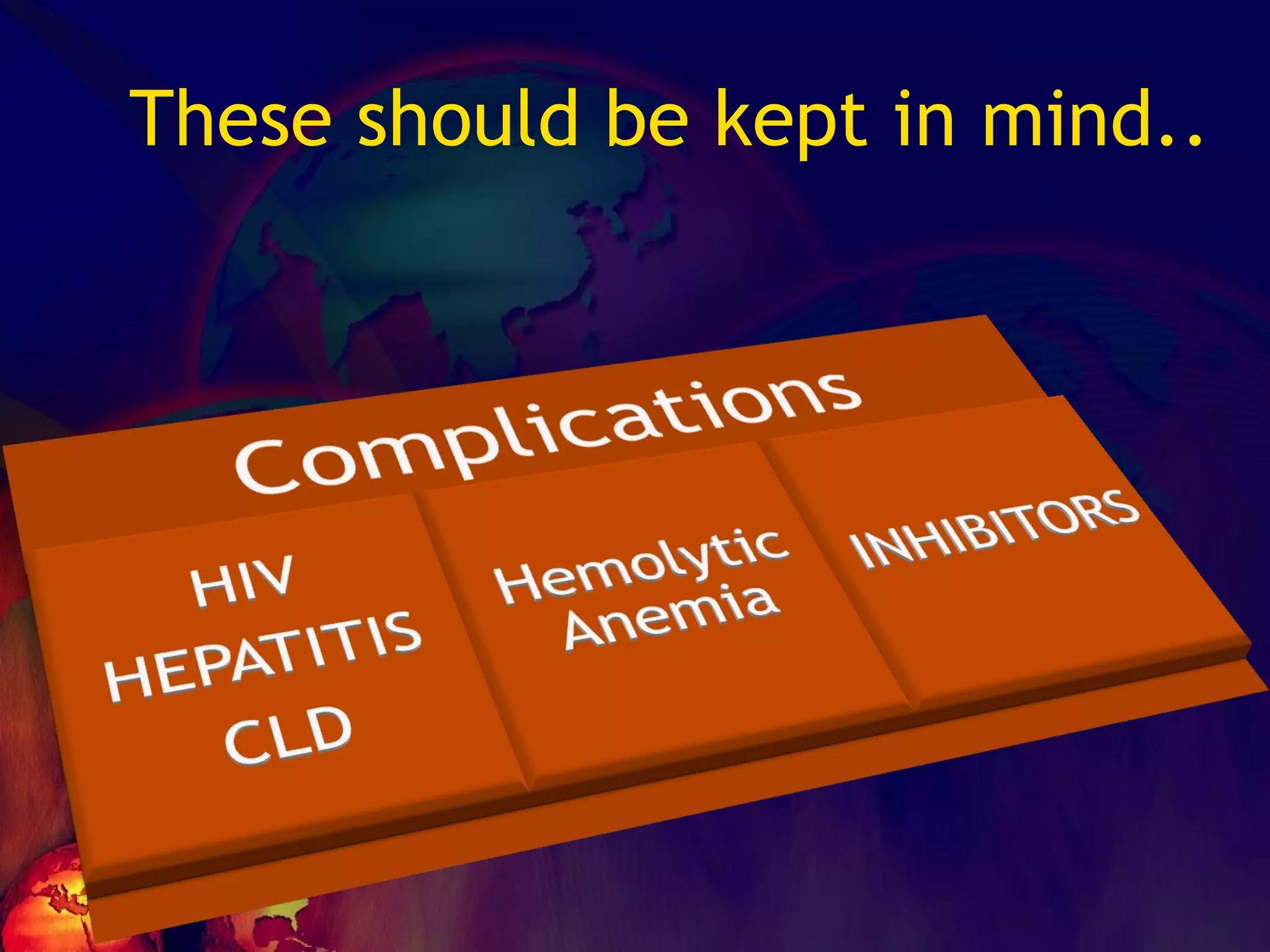


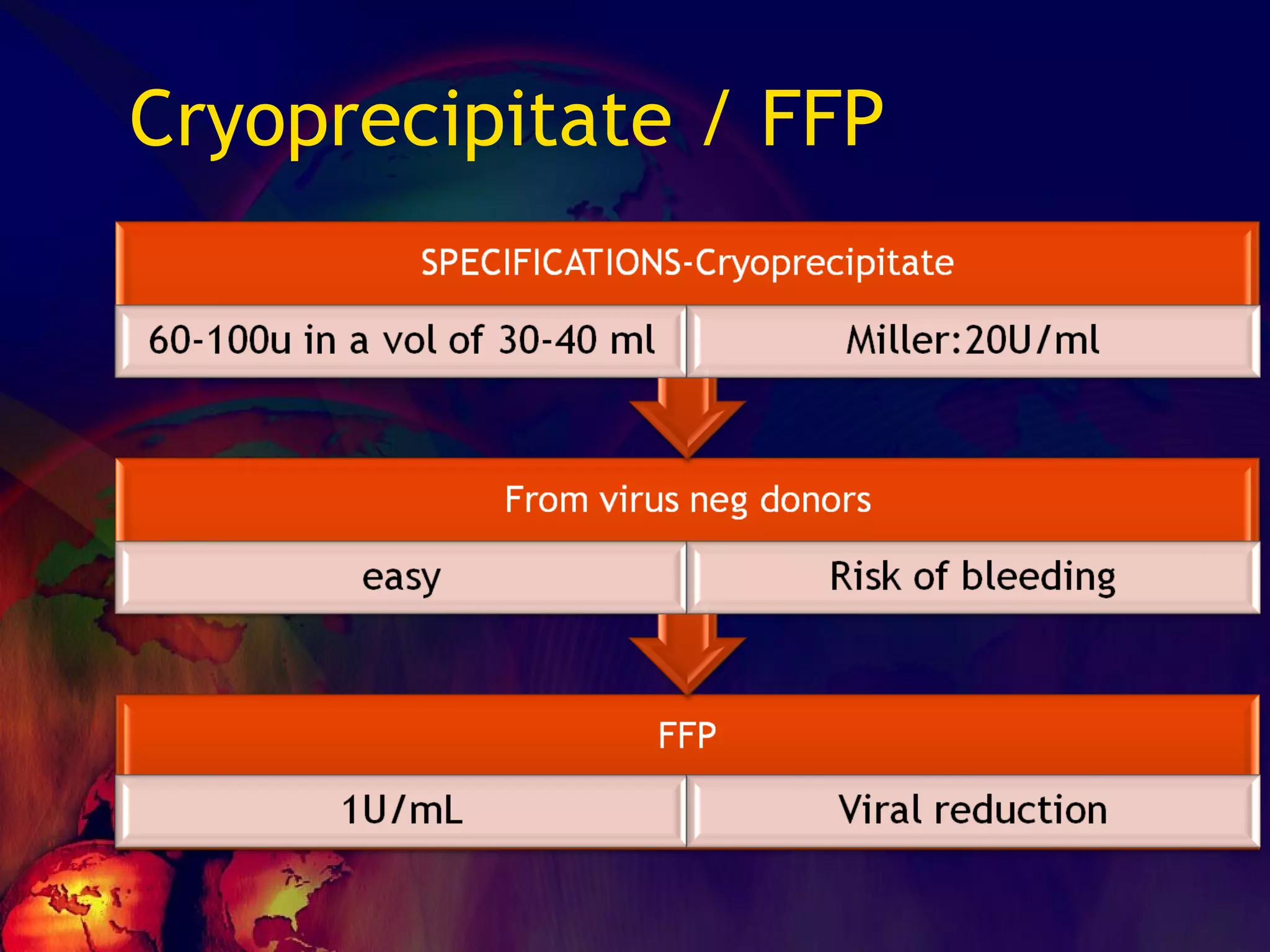

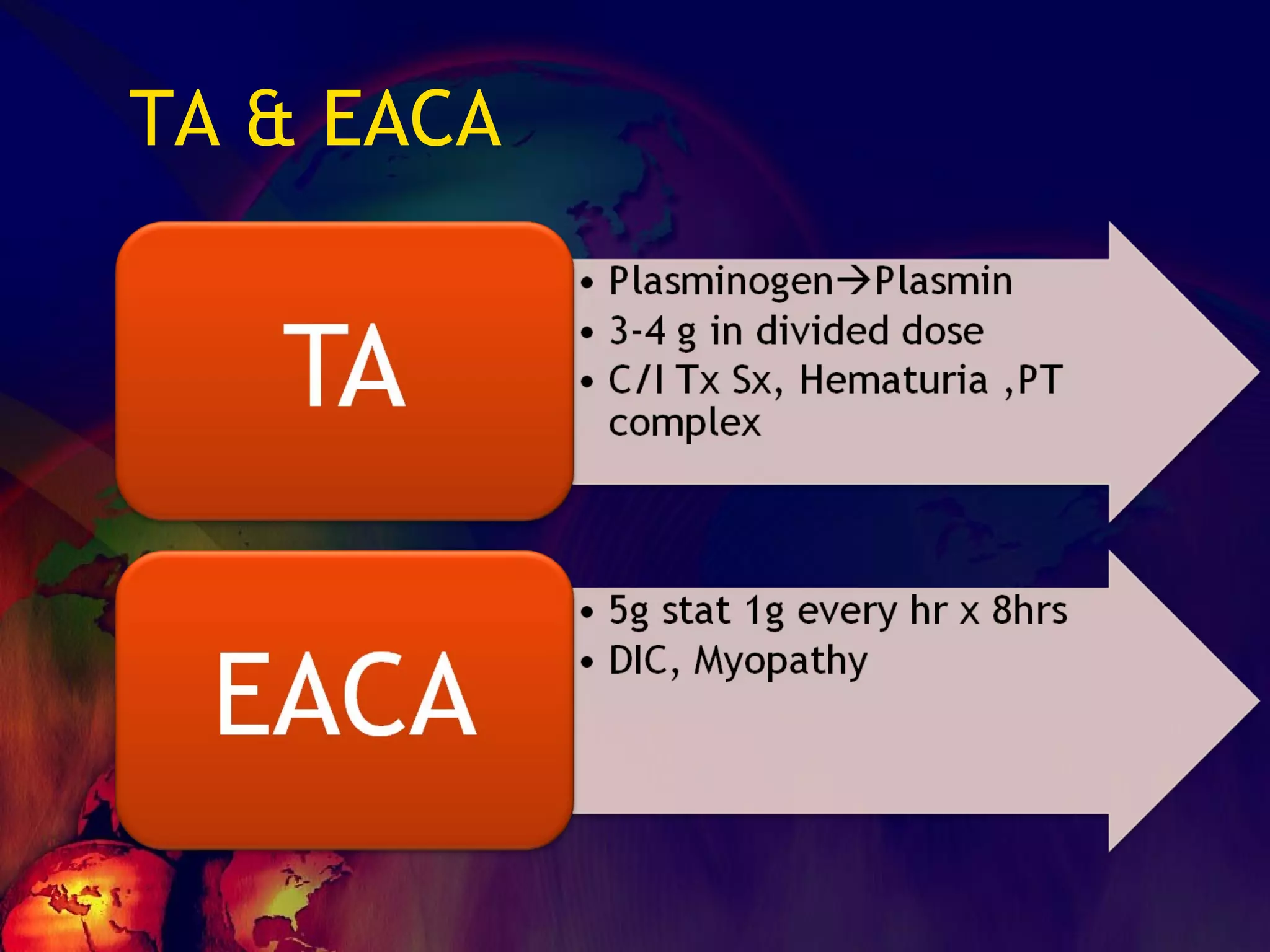

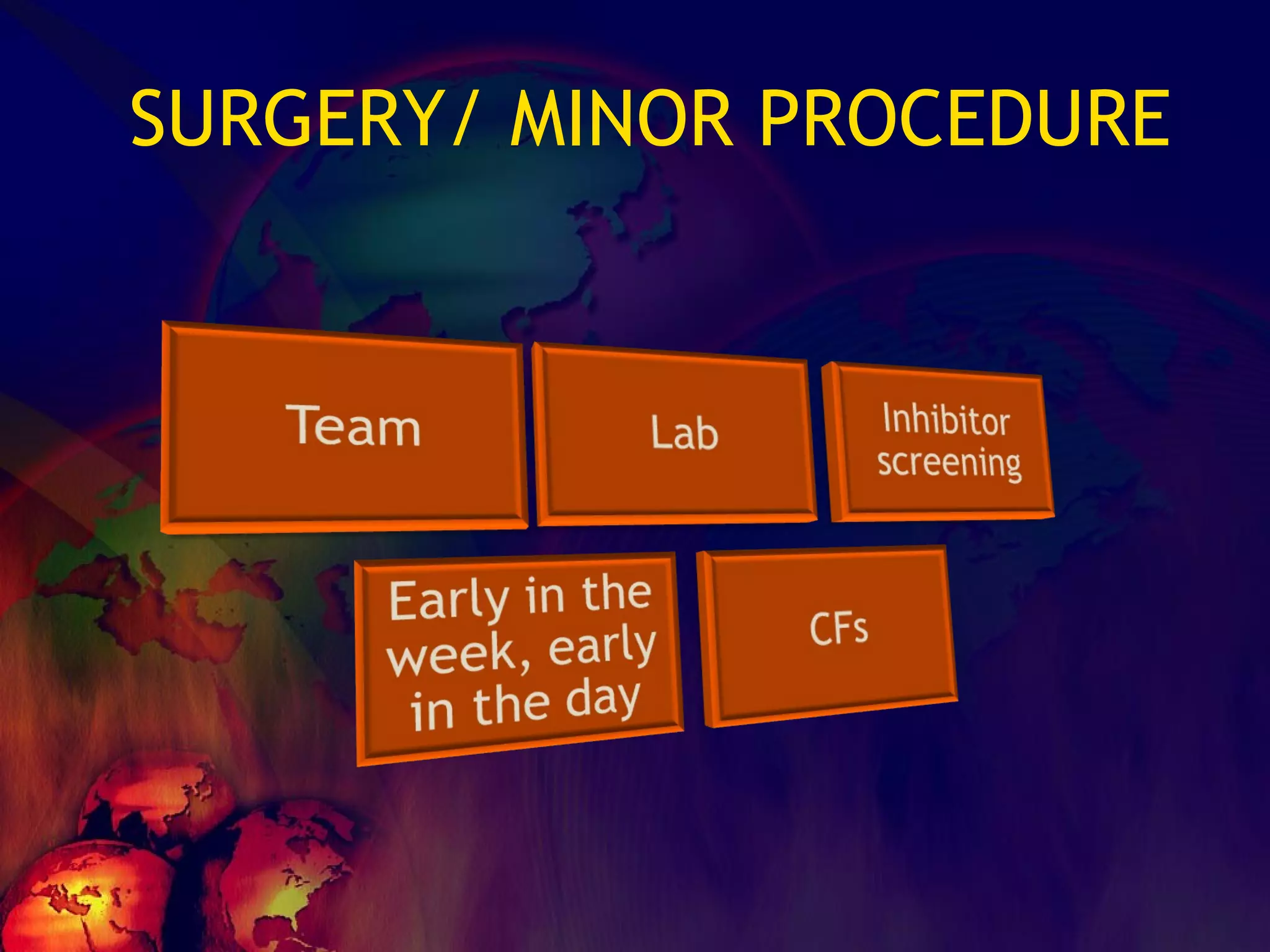



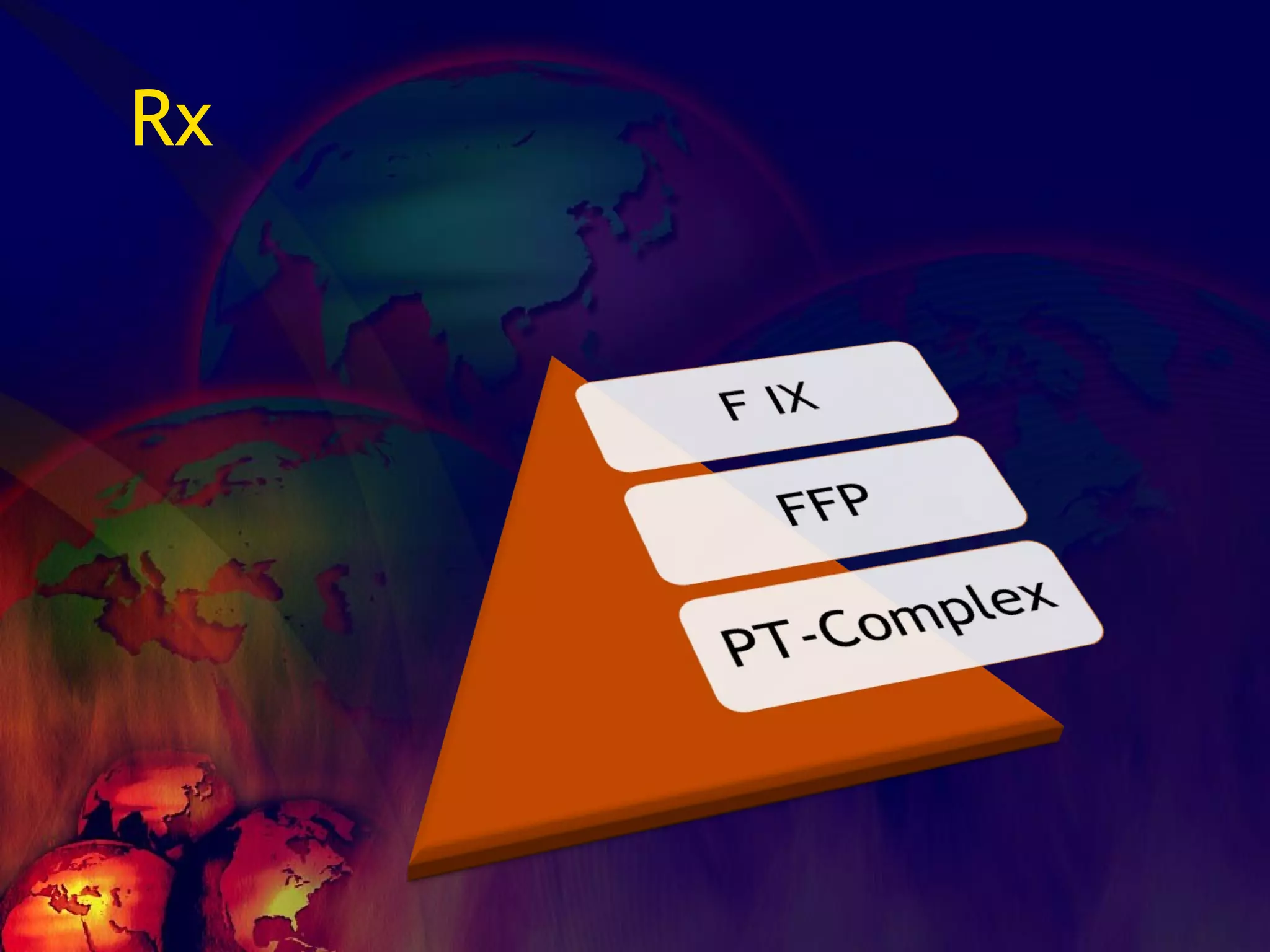

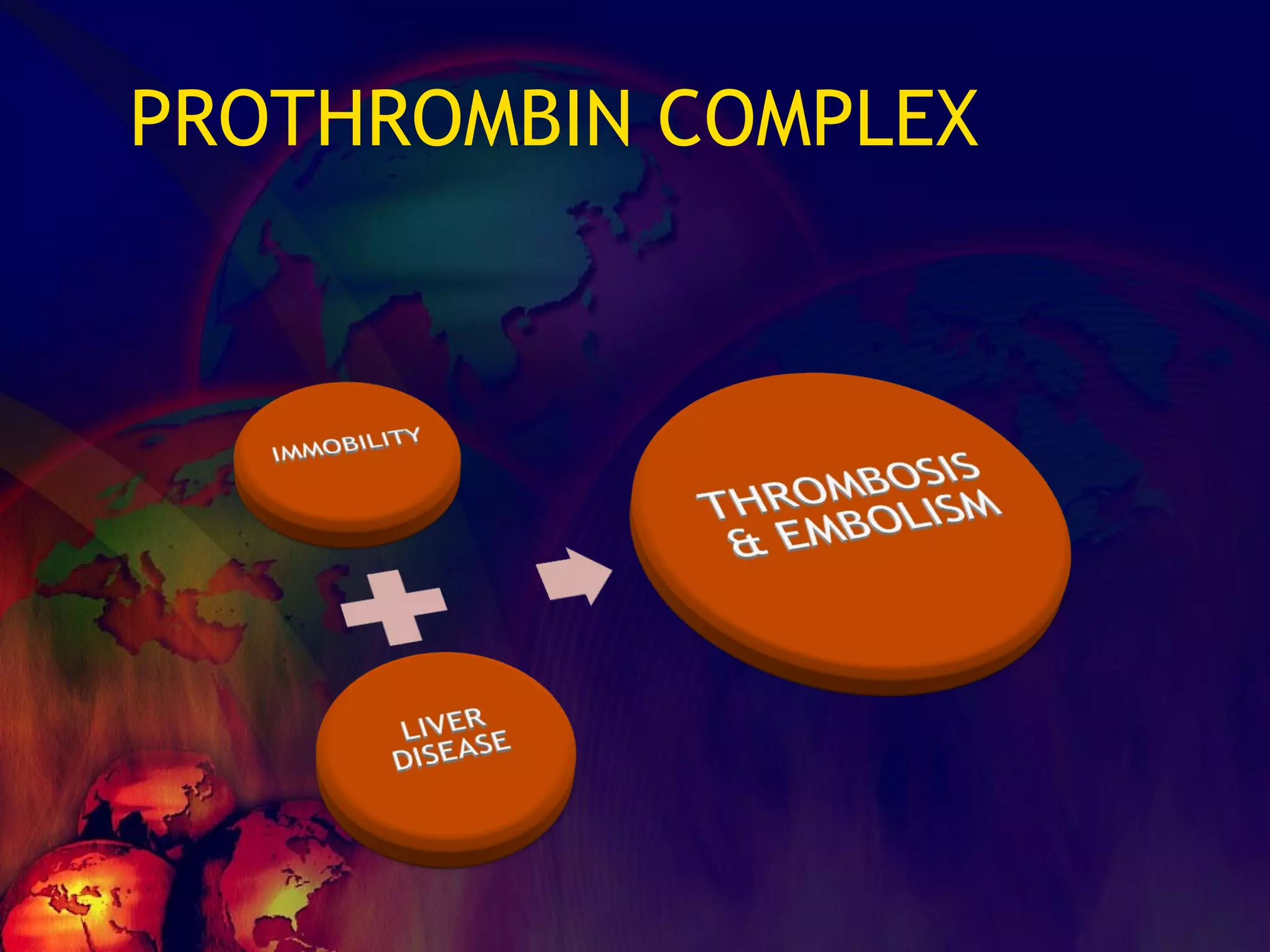










![What’s it? Useless Heparin!!! Govt supply?? Very energetic F II & F V! DIC ,Liver disease, heparin Rx OCPs ? Hmm.. No. Rx :AT III [A/C] Oral Anti coagulants [C/C]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/coagulationdisordersandanaesthesia29finalfinal97-2003animated-091009071734-phpapp01/75/Coagulation-Disorders-and-Anesthesia-Basic-pathophysiology-121-2048.jpg)