This document discusses various topics related to cerebral physiology:
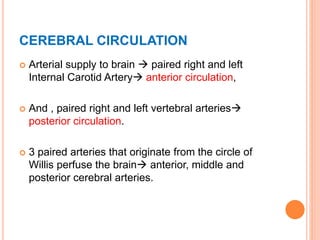
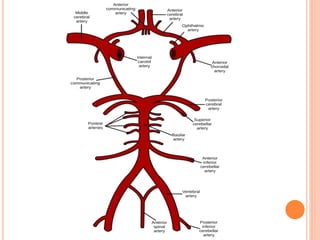
- Cerebral circulation involves blood flow to the brain through paired internal carotid and vertebral arteries. Cerebral blood flow is tightly regulated to maintain adequate oxygen and glucose delivery to brain tissue.
- Cerebral metabolism relies heavily on glucose and oxygen to produce ATP and support neuronal activity, particularly in gray matter. Interruption of blood flow can cause rapid loss of consciousness and irreversible damage.
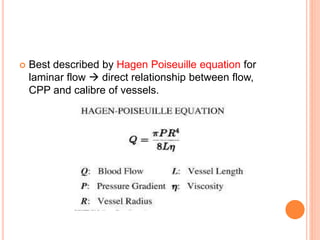
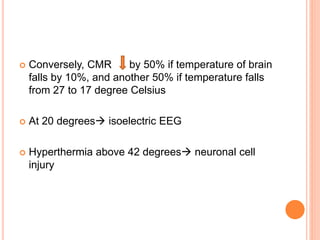
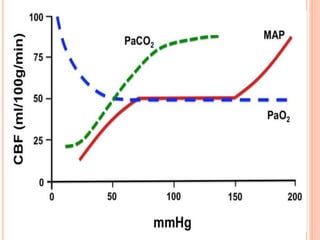
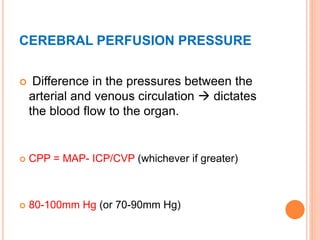
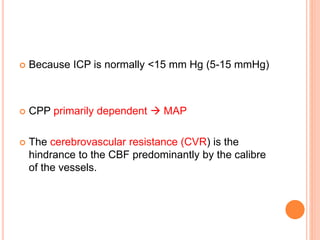
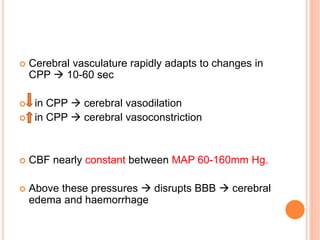
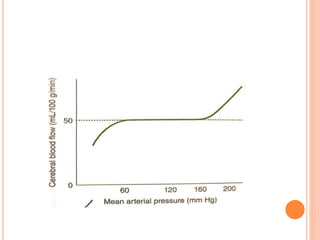
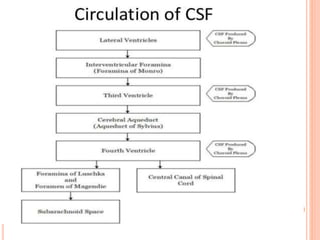
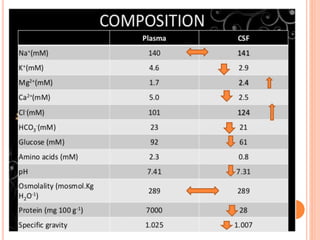
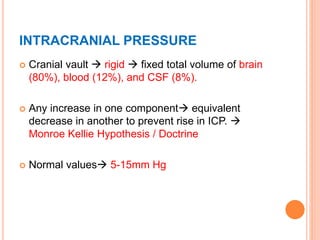
- Factors like cerebral perfusion pressure, blood gas levels, temperature, and viscosity influence cerebral blood flow through mechanisms like autoregulation. The blood-brain barrier restricts passage of molecules into brain tissue. Cerebrospinal fluid protects the brain and helps regulate int