The document discusses neurophysiology and factors controlling cerebral blood flow (CBF). Some key points:
- The brain has high metabolic needs but no oxygen storage, so it relies on continuous CBF. CBF parallels metabolic activity and averages 50 ml/100g/min.
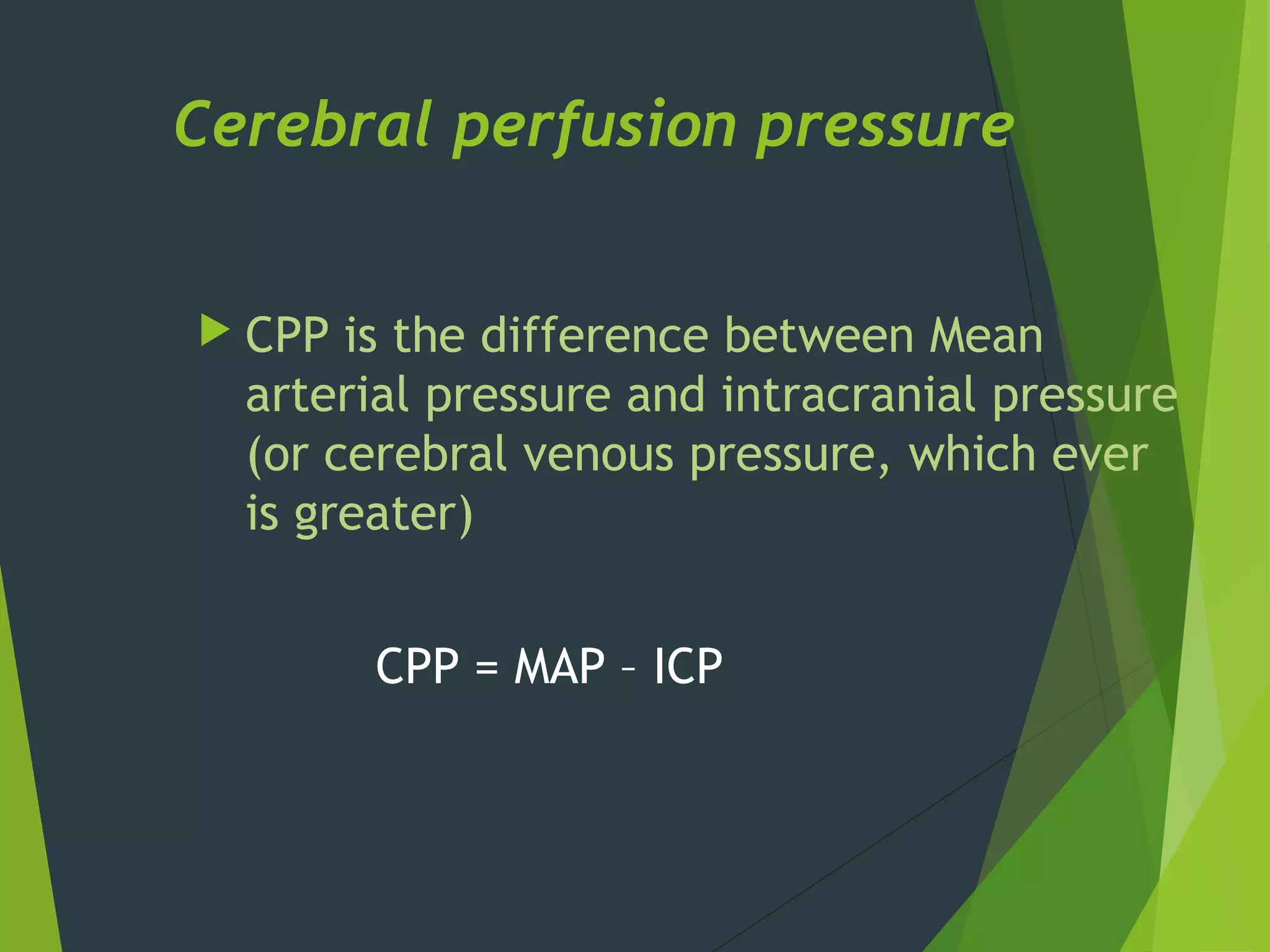
- CBF is controlled by cerebral perfusion pressure (CPP), which depends on mean arterial pressure and intracranial pressure. Autoregulation normally keeps CBF constant over a wide range of pressures.
- Important factors influencing CBF include carbon dioxide, which causes vasodilation; oxygen; hematocrit; temperature; and anesthetic agents, many of which are cerebral vasodilators. Barbiturates