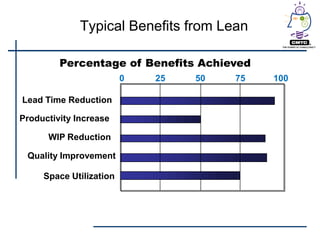
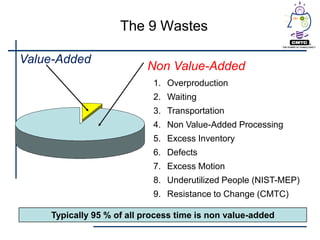
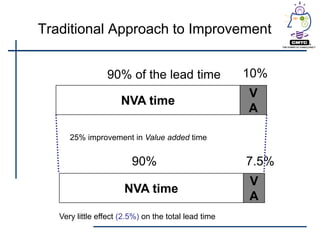
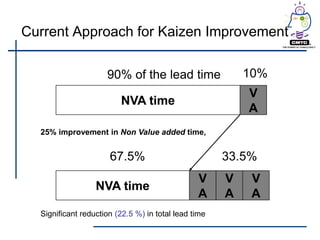
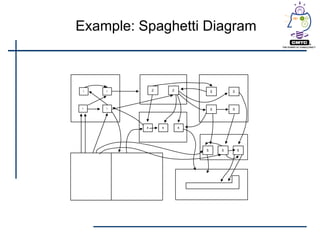
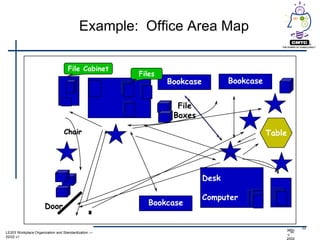
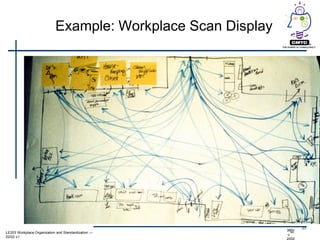
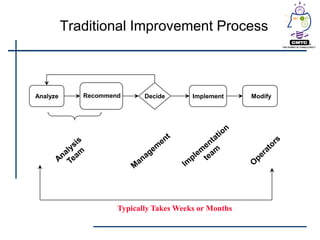
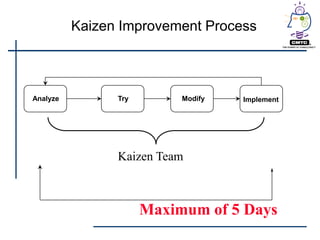
This document provides an introduction to lean principles and methodology. It defines lean as a systematic approach to identifying and eliminating waste through continuous improvement. The key aspects of lean covered are the nine types of waste, value-added vs non-value added activities, typical benefits of lean such as lead time reduction and productivity increases, and lean tools like value stream mapping, 5S, and kaizen events. Kaizen events are described as a focused team approach to eliminating waste through rapid improvement over a short period of time.