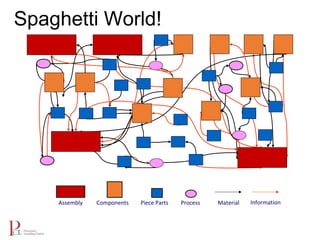
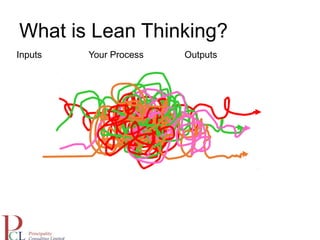
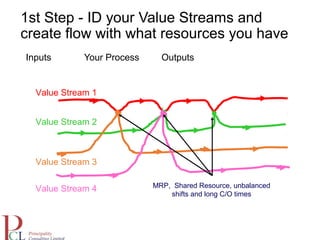
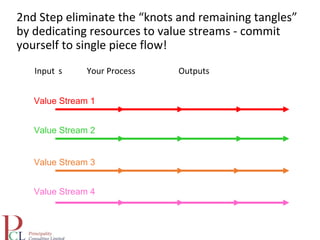
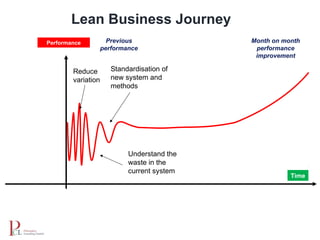
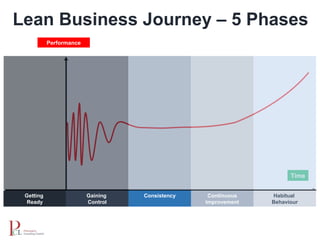
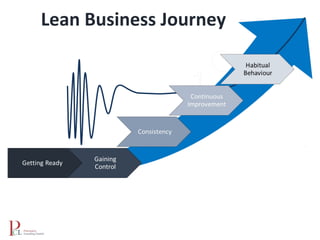
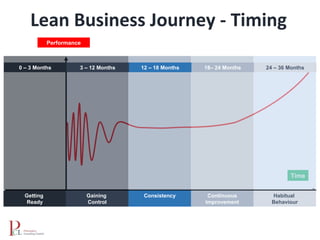
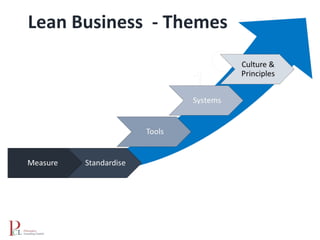
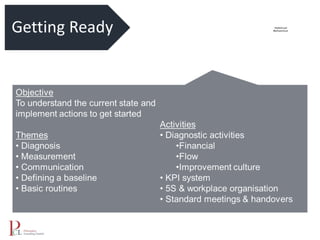
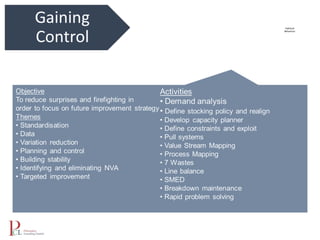
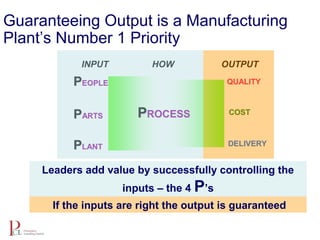
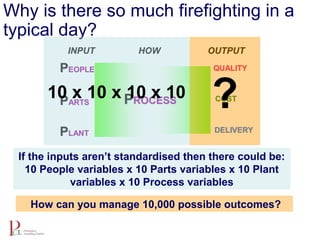
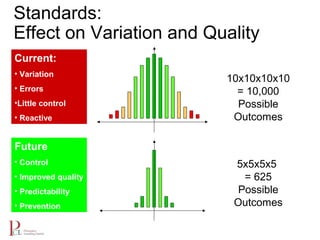
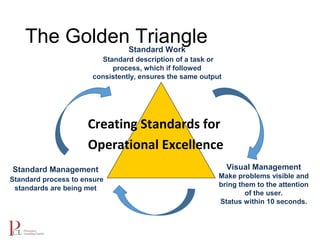
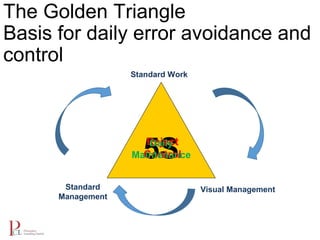
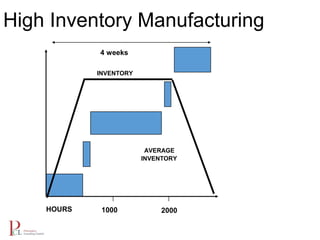
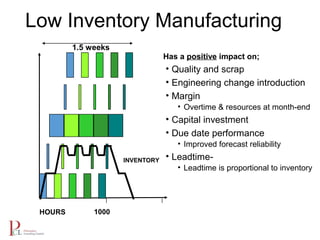
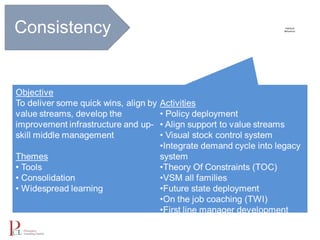
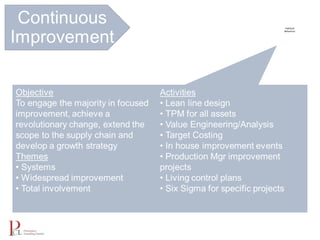
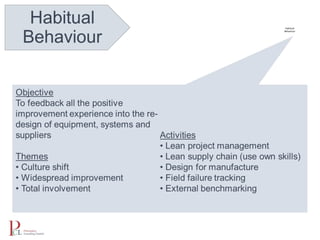
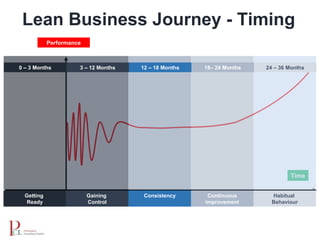
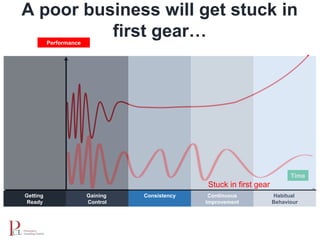
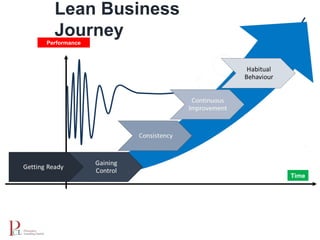
The document outlines the lean business model aimed at maximizing profitability and generating cash through value stream management, waste elimination, and continuous improvement. It describes the lean business journey in five phases: getting ready, gaining control, consistency, continuous improvement, and habitual behavior, while highlighting the importance of standardization and reducing variation. Additionally, it addresses common challenges in implementing lean practices and the importance of establishing basic stability in operations.