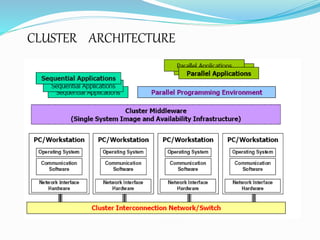
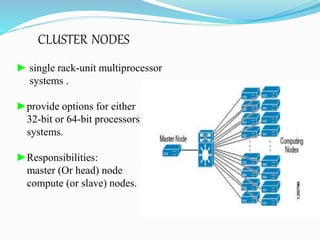
This document provides an overview of cluster computing. It defines a cluster as a collection of interconnected computers working together as a single system. The key components of a cluster are applications, middleware, operating systems, and an interconnect. Clusters can be used for parallel and distributed processing using multiple nodes. Nodes include master and compute nodes. Clusters provide benefits like availability, performance, and scalability through the use of commodity hardware and software. Popular tools for clustering include Linux, compilers, MPI and PVM. Example applications are Google Search and petroleum simulation.











![REFERENCES
[1] R. Buyya (ed.), High Performance Cluster Computing: Architectures and Systems, vol.
1, Prentice Hall, 1999.
[2] T. E. Anderson, D. Culler, and D. A. Patterson, "A Case for NOW (Network of
Workstations)," IEEE Micro, vol. 15, pp. 54-64, Feb. 1995.
[3] A. Chien, S. Pakin, M. Lauria, M. Buchanan, K. Hane, L. Giannini, and J. Prusakova,
“High Performance Virtual Machines (HPVM): Clusters with Supercomputing APIs and
Performance,” Proc. 8th SIAM Conference on Parallel Processing for Scientific
Computing (PP97), Minneapolis, USA, Mar. 1997.
[4] G. F. Pfister, In Search of Clusters, 2nd Edition, Prentice Hall, 1998.
[5] T. Shanley, Infiniband Network Architecture, Addison-Wesley, Nov. 2002.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/clustercomputing-160826160535/85/Cluster-computing-15-320.jpg)
![continued
[6] N. J. Boden, D. Cohen, R. E. Felderman, A.E. Kulawik, C.L. Seitz, J.N. Seizovic, and
Wen-King Su, “Myrinet: A Gigabit-per-second Local Area Network,” IEEE Micro, vol. 15,
Feb. 1995, pp. 29-36.
[7] K. Alnaes, E. H. Kristiansen, D. B. Gustavson, and D. V. James, “Scalable Coherent
Interface,” Proc. 1990 IEEE International Conference on Computer Systems and Software
Engineering (CompEuro ’90), Tel-Aviv, Israel, May 1990, pp. 446-453.
[8] D. Cameron, and G. Regnier, Virtual Interface Architecture, Intel Press, Apr. 2002.
[9] Message Passing Interface (MPI) Forum, http://www.mpi-forum.org
[10] M. Baker, A. Apon, R. Buyya, and H. Jin, “Cluster Computing and Applications,”
Encyclopedia of Computer Science and Technology, vol. 45, A. Kent, and J. Williams (eds.),
Marcel Dekker, Jan. 2002, pp. 87-125.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/clustercomputing-160826160535/85/Cluster-computing-16-320.jpg)
