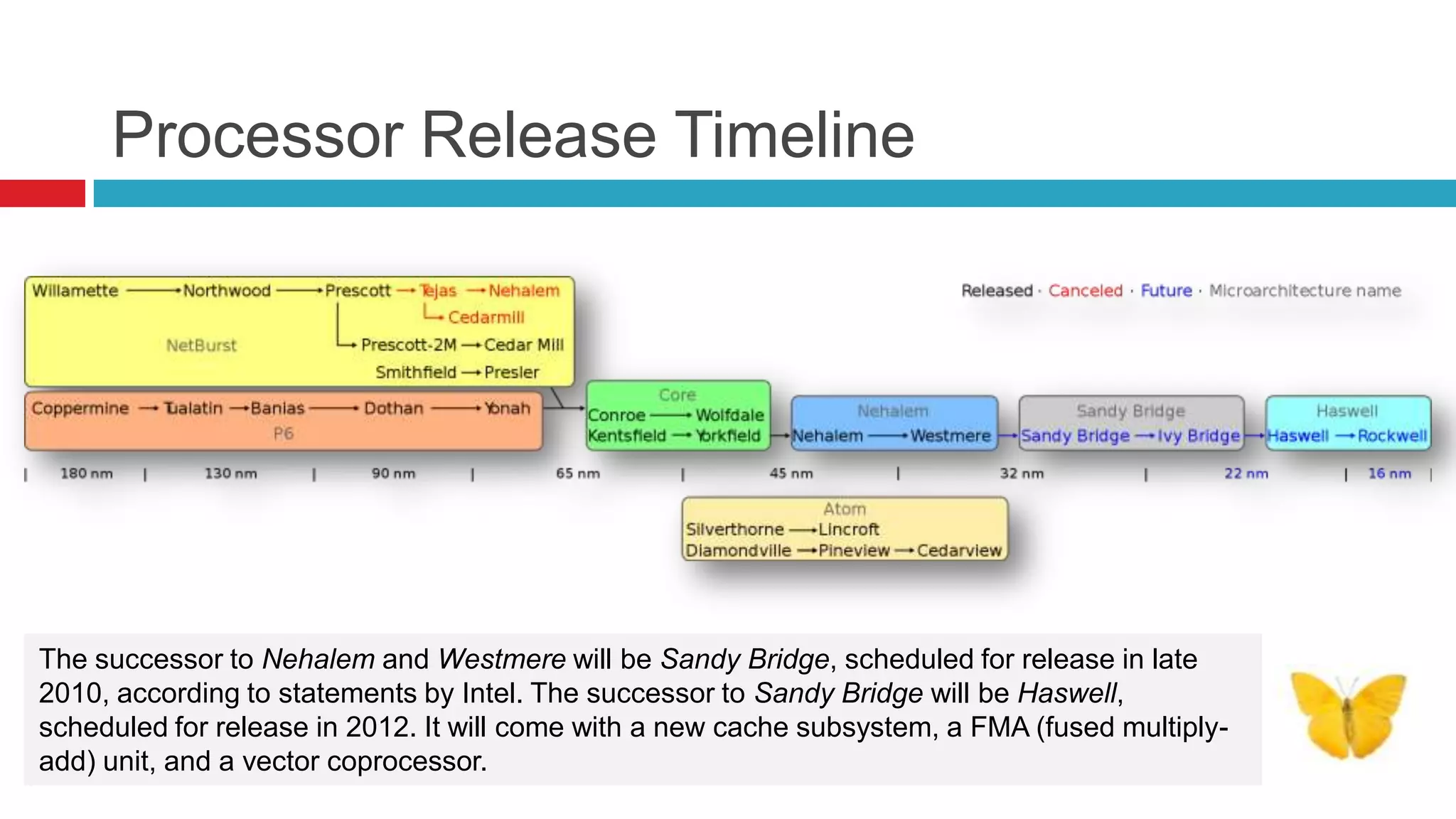
Microarchitecture refers to how an instruction set architecture is implemented in a processor. It focuses on aspects like chip area, power consumption, and complexity. Nehalem was Intel's latest microarchitecture at the time, featuring an integrated memory controller, QuickPath interconnect, and improvements in performance and power efficiency over previous architectures. Its successors included Westmere, Sandy Bridge, and Haswell.