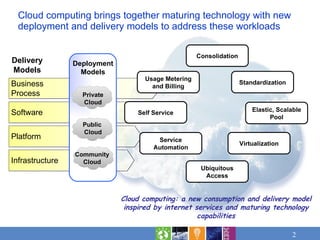
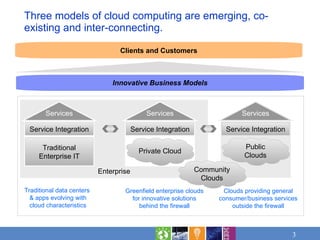
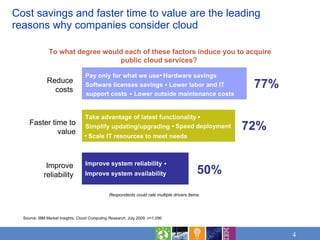
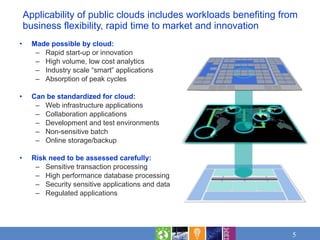
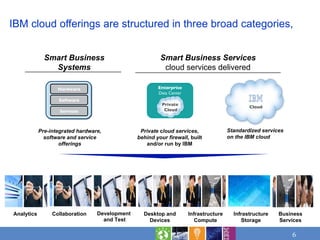
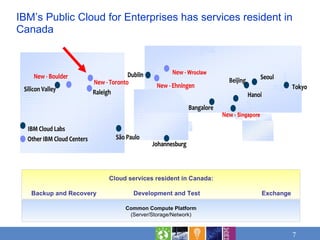
Cloud computing brings together maturing technology and new delivery models to address workloads in three emerging models: private cloud within organizations, public cloud outside organizations, and community clouds sharing resources. Cost savings and faster time to value are leading reasons for considering cloud. Applicable workloads include those benefiting from flexibility, rapid time to market, and innovation. Risks need assessment for sensitive workloads. IBM offers cloud services structured in analytics, collaboration, development and test, infrastructure, and business services.


![Thank you! For more information, please visit: ibm.com/cloud Or contact me at: [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ibmcloudcomputing-thejourneytocloud-crystalball-v3-15minutepitch-110418110851-phpapp01/85/CloudOps-evening-presentation-from-IBM-9-320.jpg)