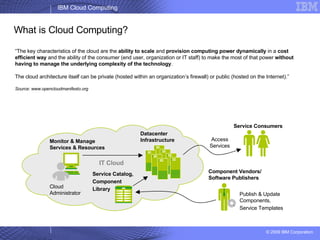
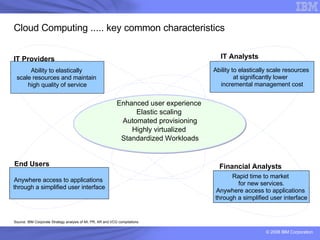
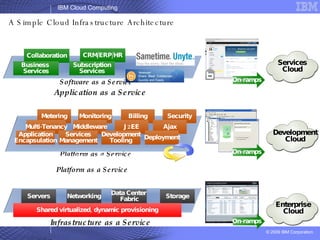
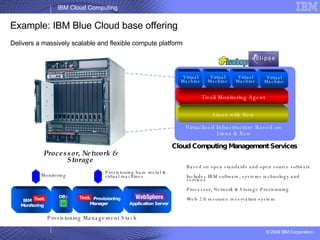
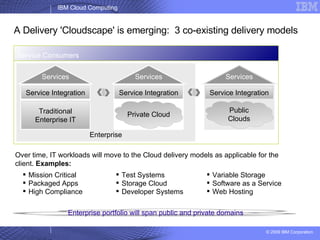
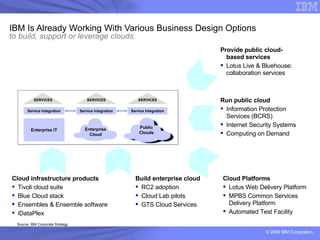
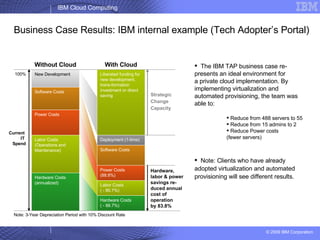
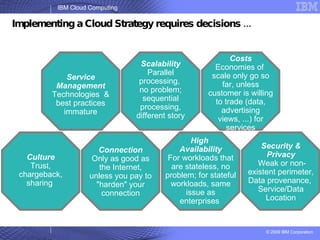
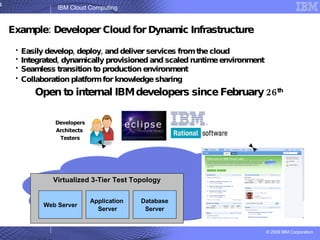
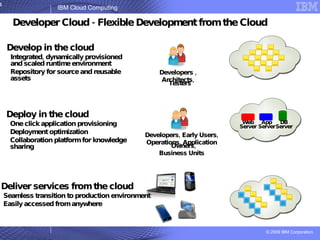
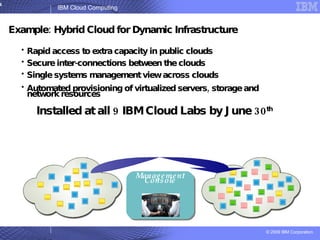
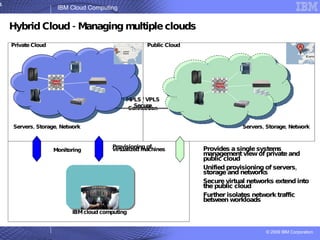
The document provides an overview of IBM's cloud computing initiatives, highlighting Ireland as a pivotal hub for IBM's global research and innovation in this field. It discusses the characteristics and benefits of cloud computing, including scalability, cost efficiency, and simplified user experience, while outlining various service models. The document also presents IBM's internal business case demonstrating significant cost savings and efficiency improvements achieved through cloud implementation.
![IBM Cloud Computing An overview Pol Mac Aonghusa Dublin Cloud Lab April 2009 [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pma-poweredbyibmcloud-april2009-090421062907-phpapp02/75/Emerging-Technology-in-the-Cloud-Real-Life-Examples-Pol-Mac-Aonghusa-1-2048.jpg)