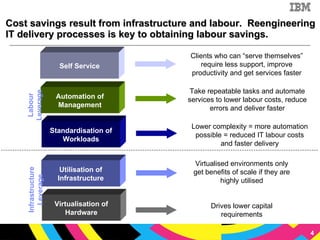
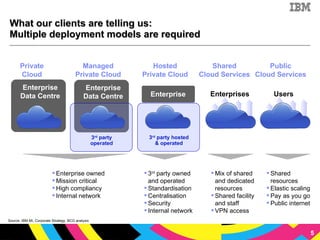
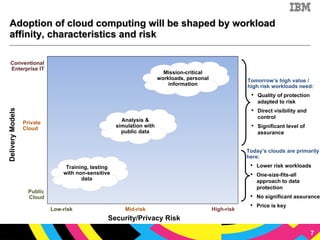
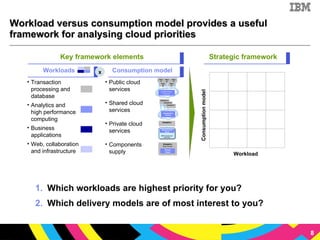
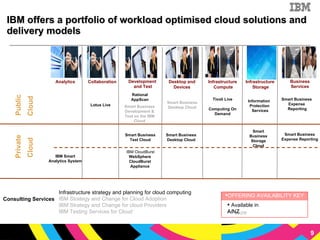
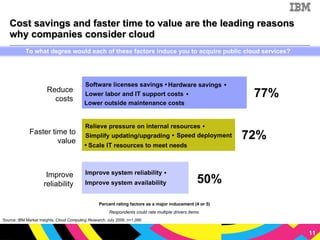
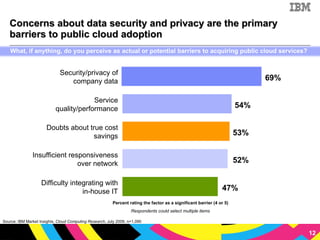
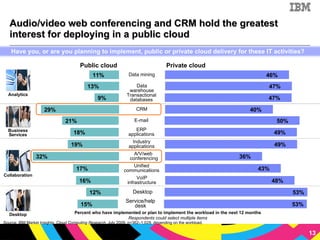
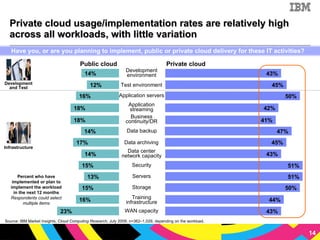
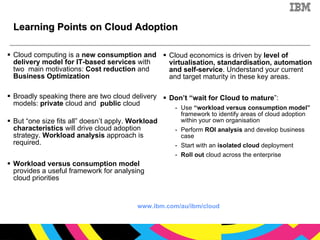
The document discusses cloud computing as a new IT delivery and consumption model inspired by consumer internet services. It is driven by virtualization, automation, and standardization which enable economies of scale, flexible pricing, and self-service. Adoption of cloud computing will be shaped by analyzing workload characteristics and risks to determine the best delivery models of public, private or hybrid cloud.