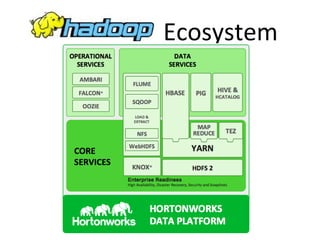
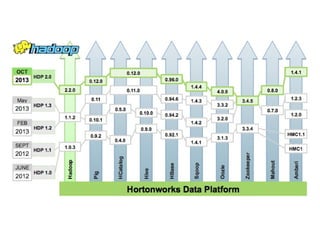
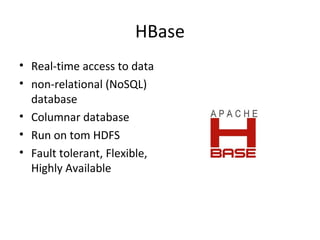
The document provides an overview of the big data ecosystem, detailing various tools and frameworks associated with Apache Hadoop, such as MapReduce, HDFS, and YARN. It highlights different approaches in managing data and emphasizes the importance of real-time analytics, data processing, and machine learning within the Hadoop architecture. Additionally, it mentions specific tools for data management, security, and workflow management that enhance the functionality of big data applications.