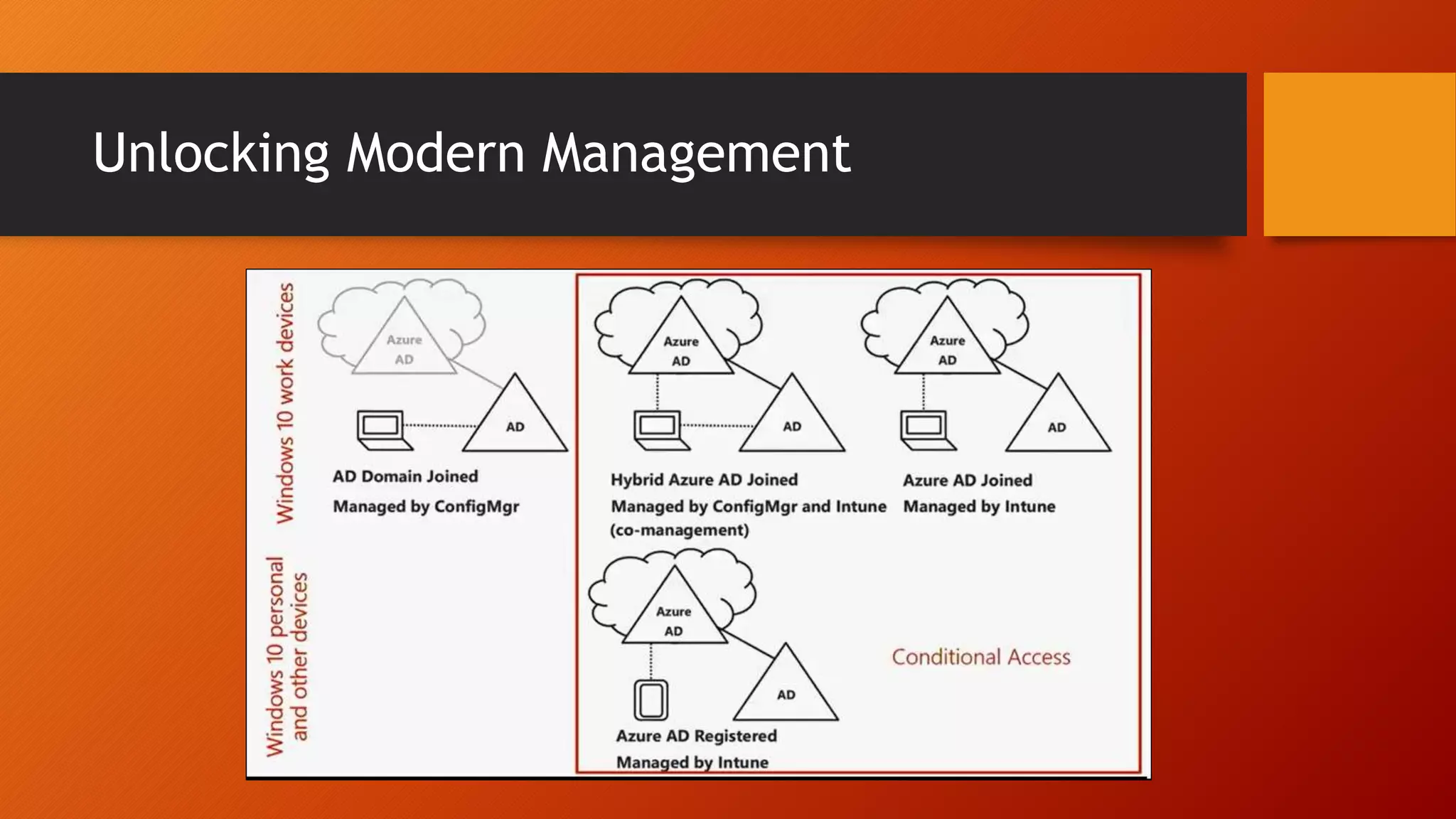
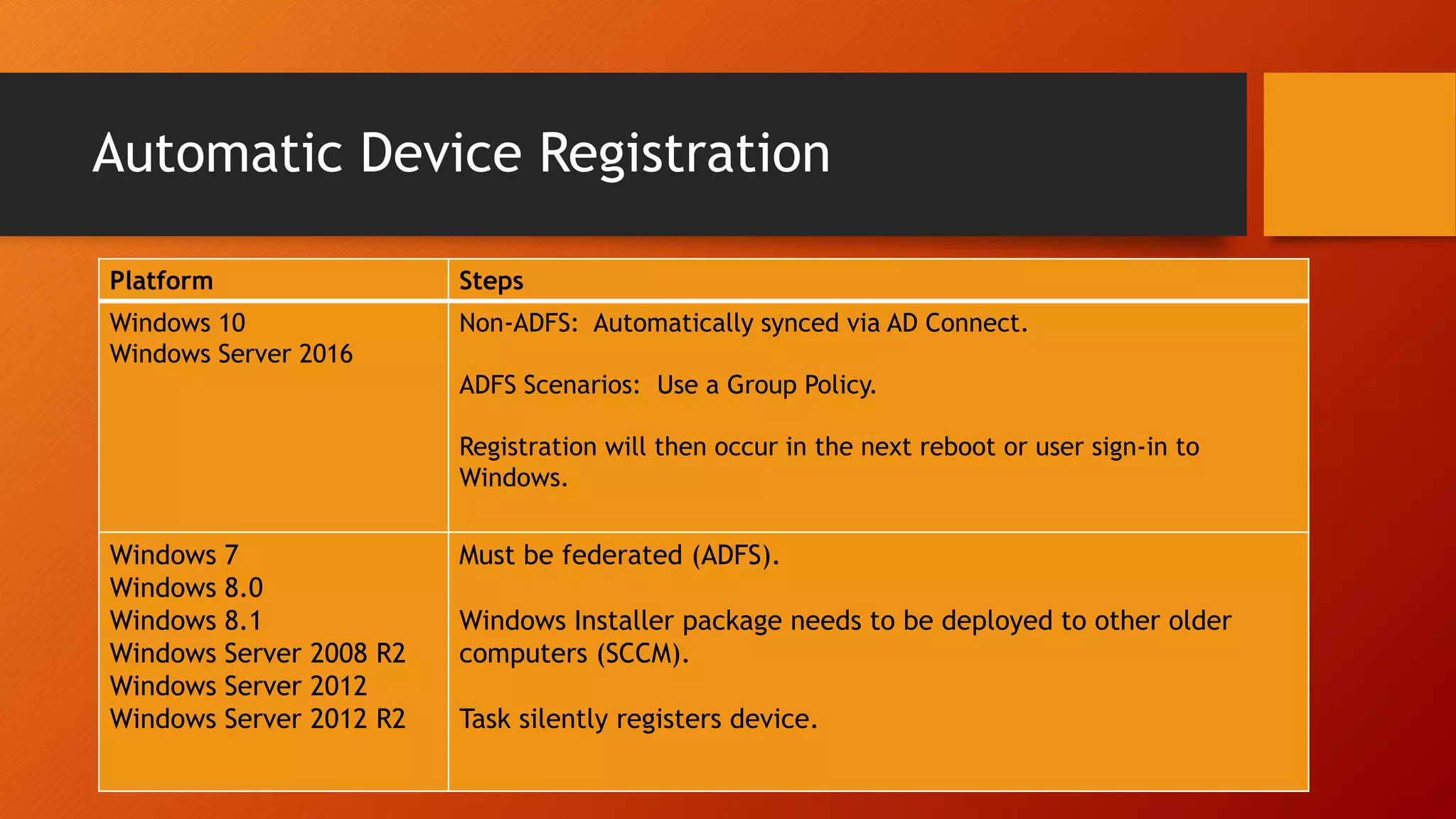
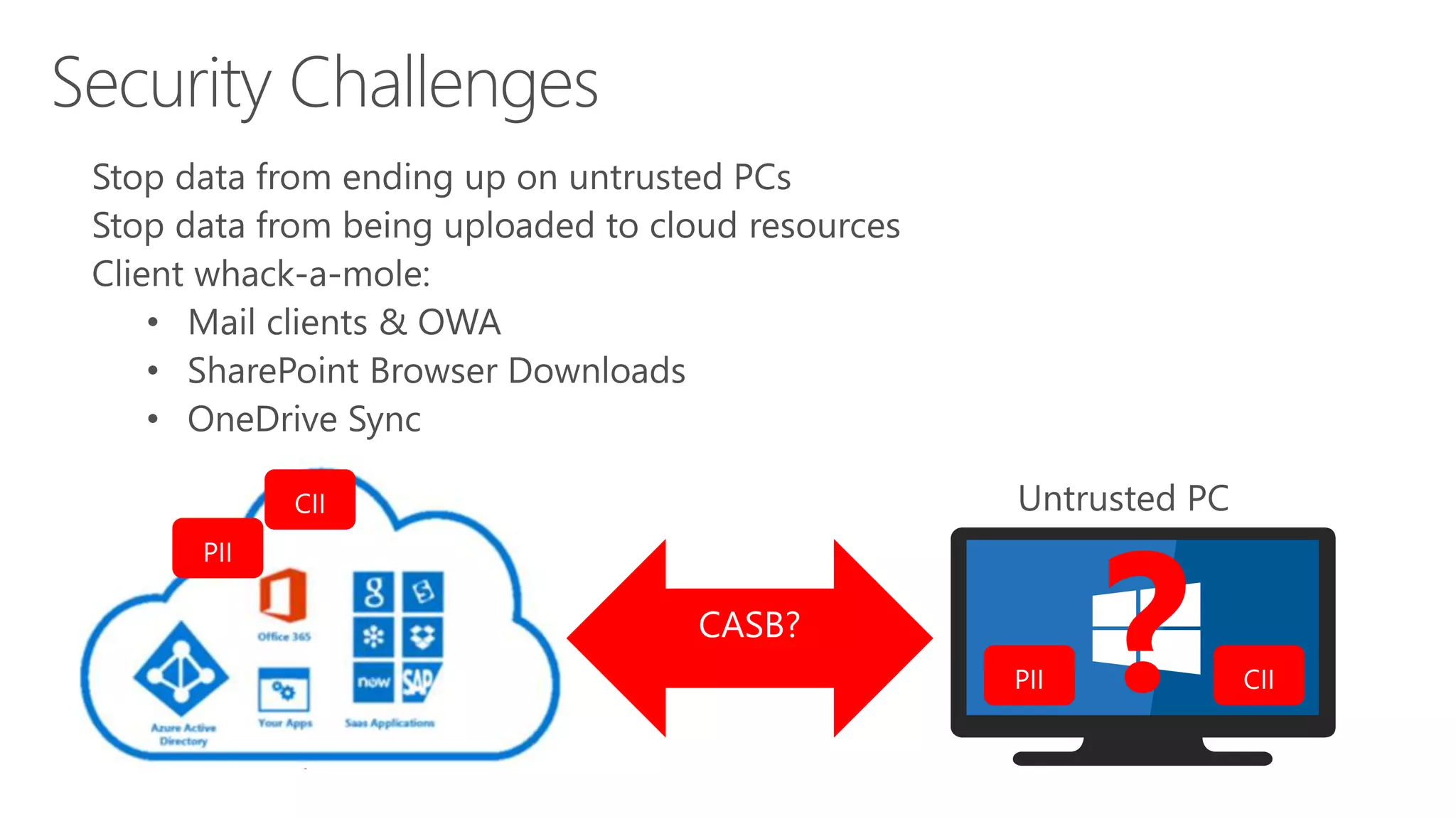
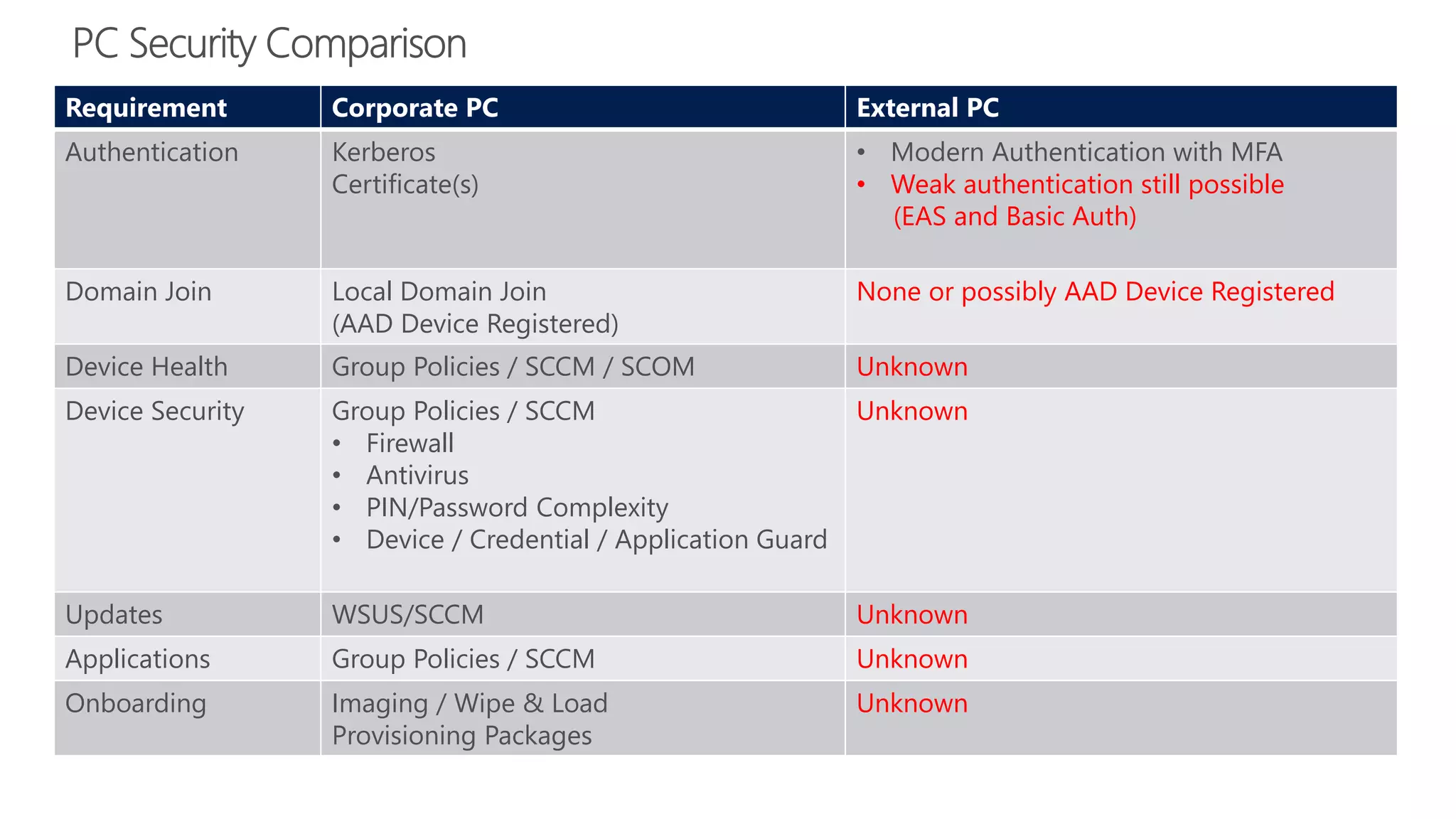
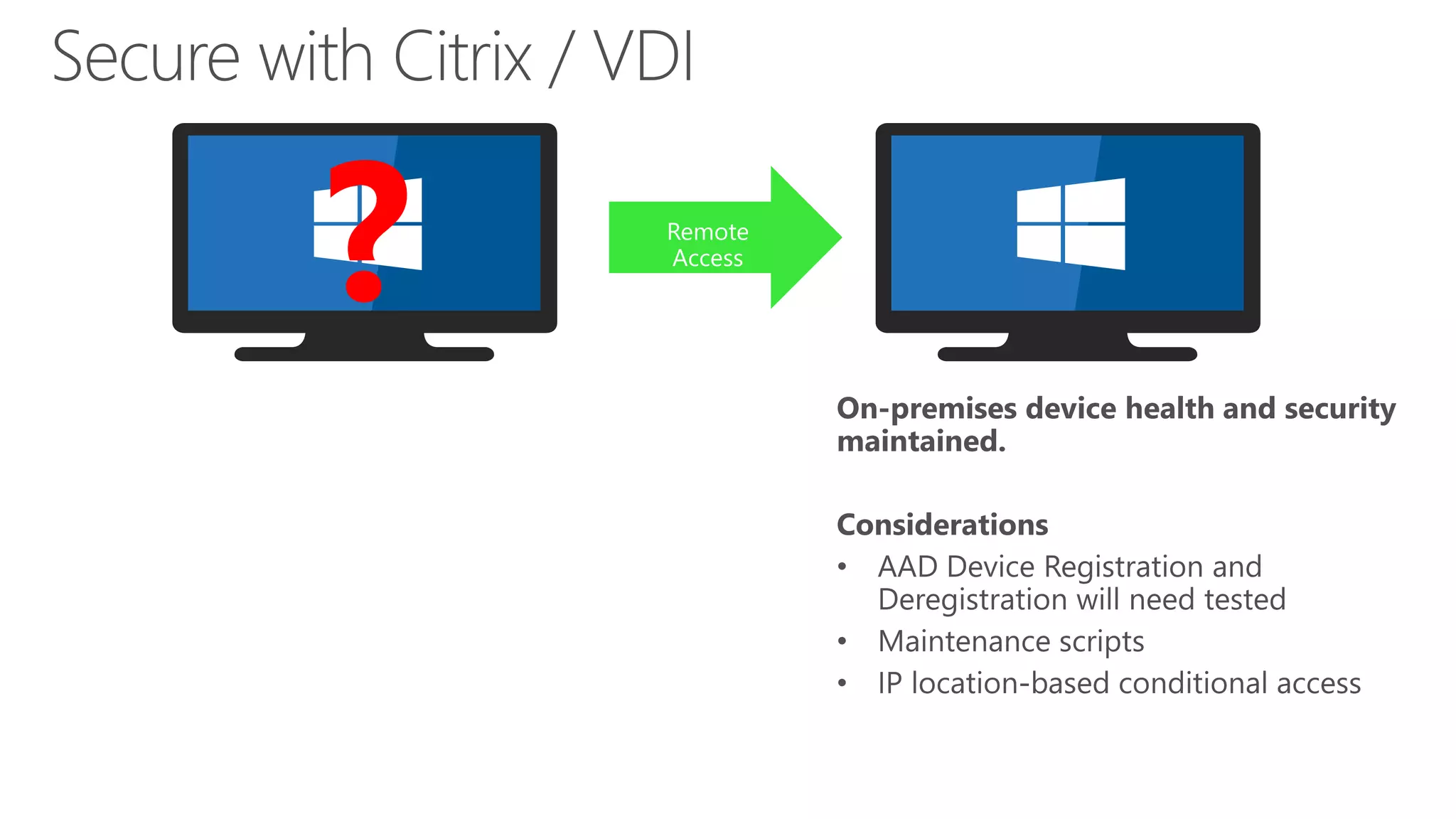
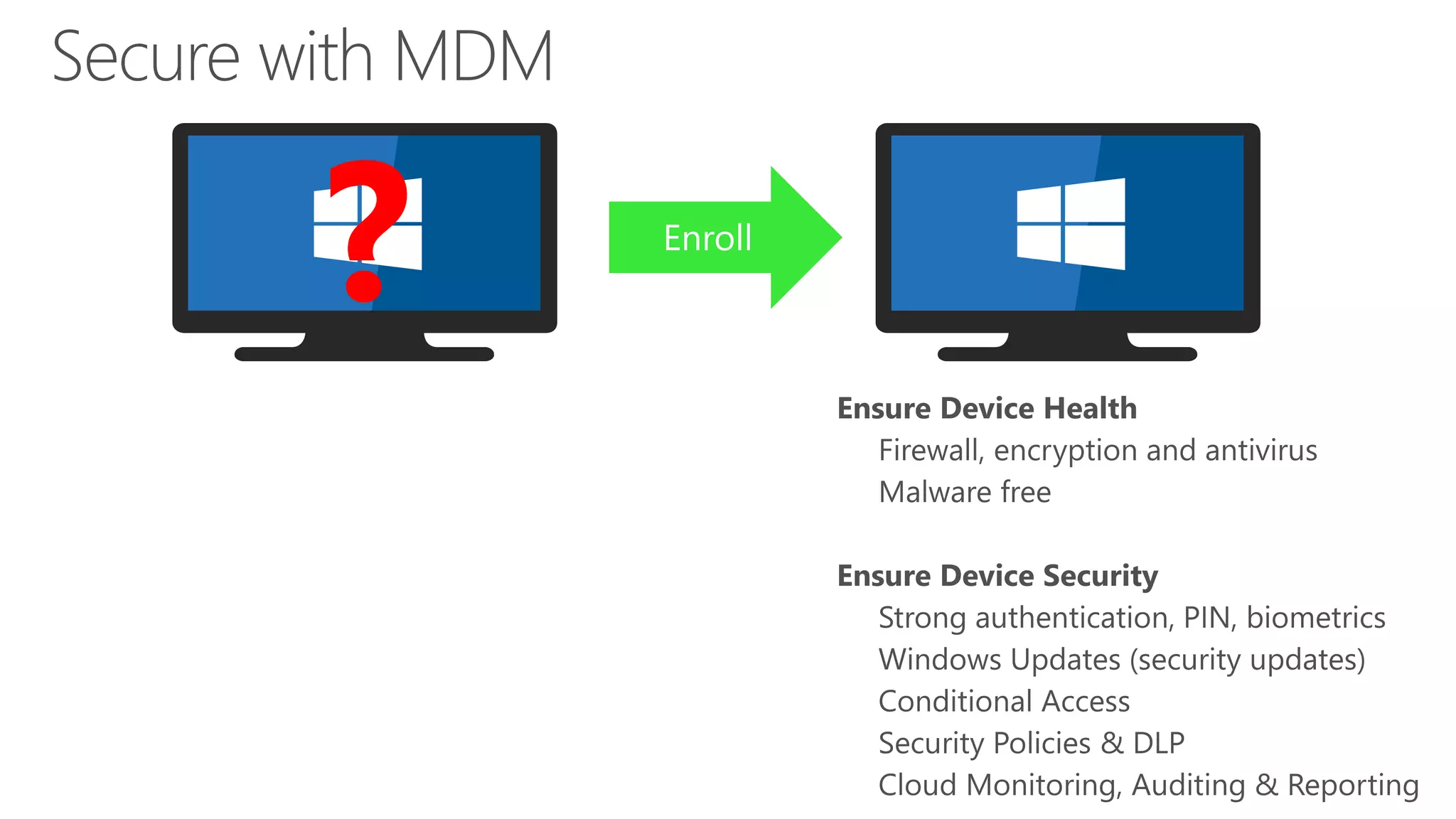
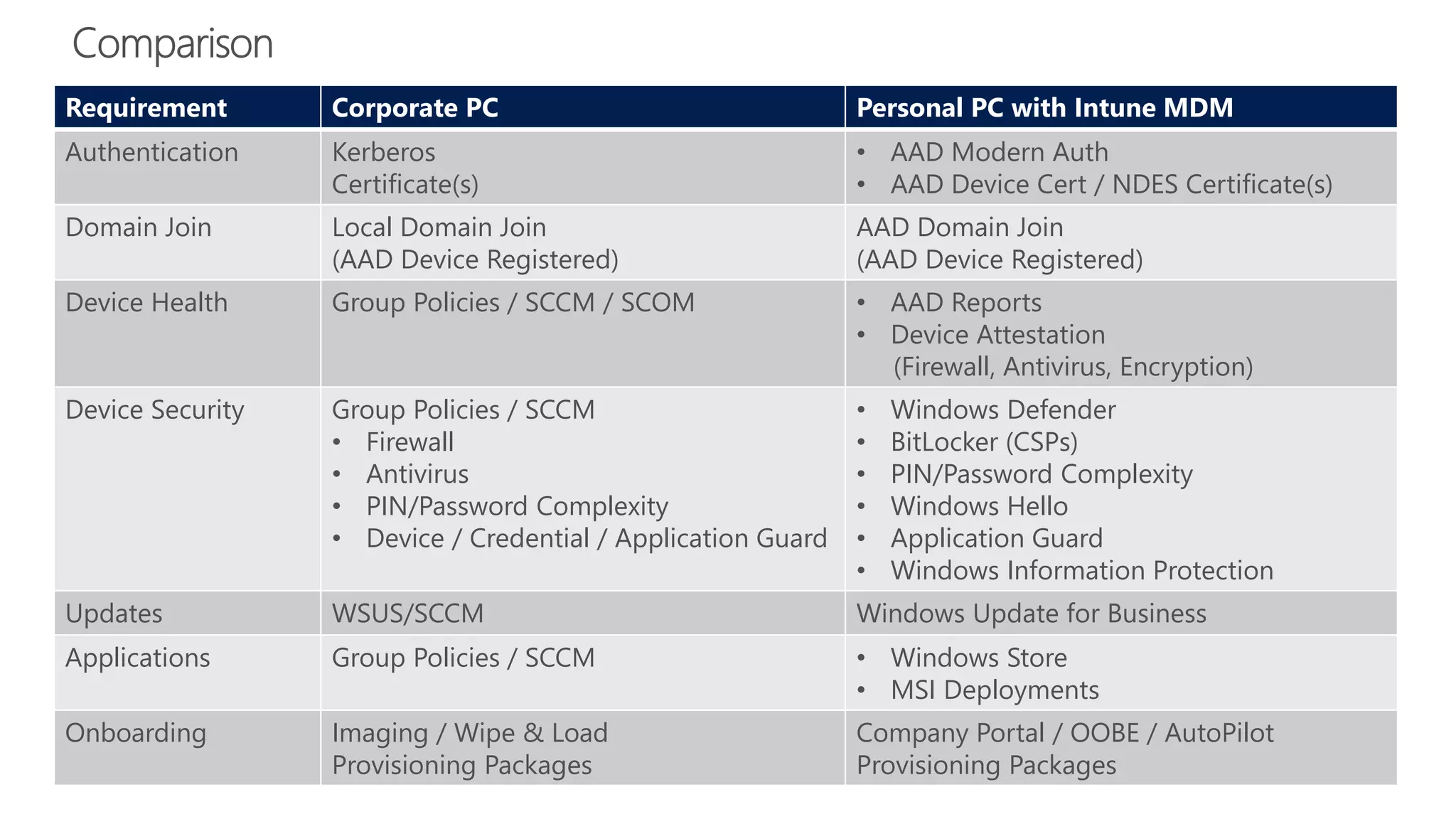
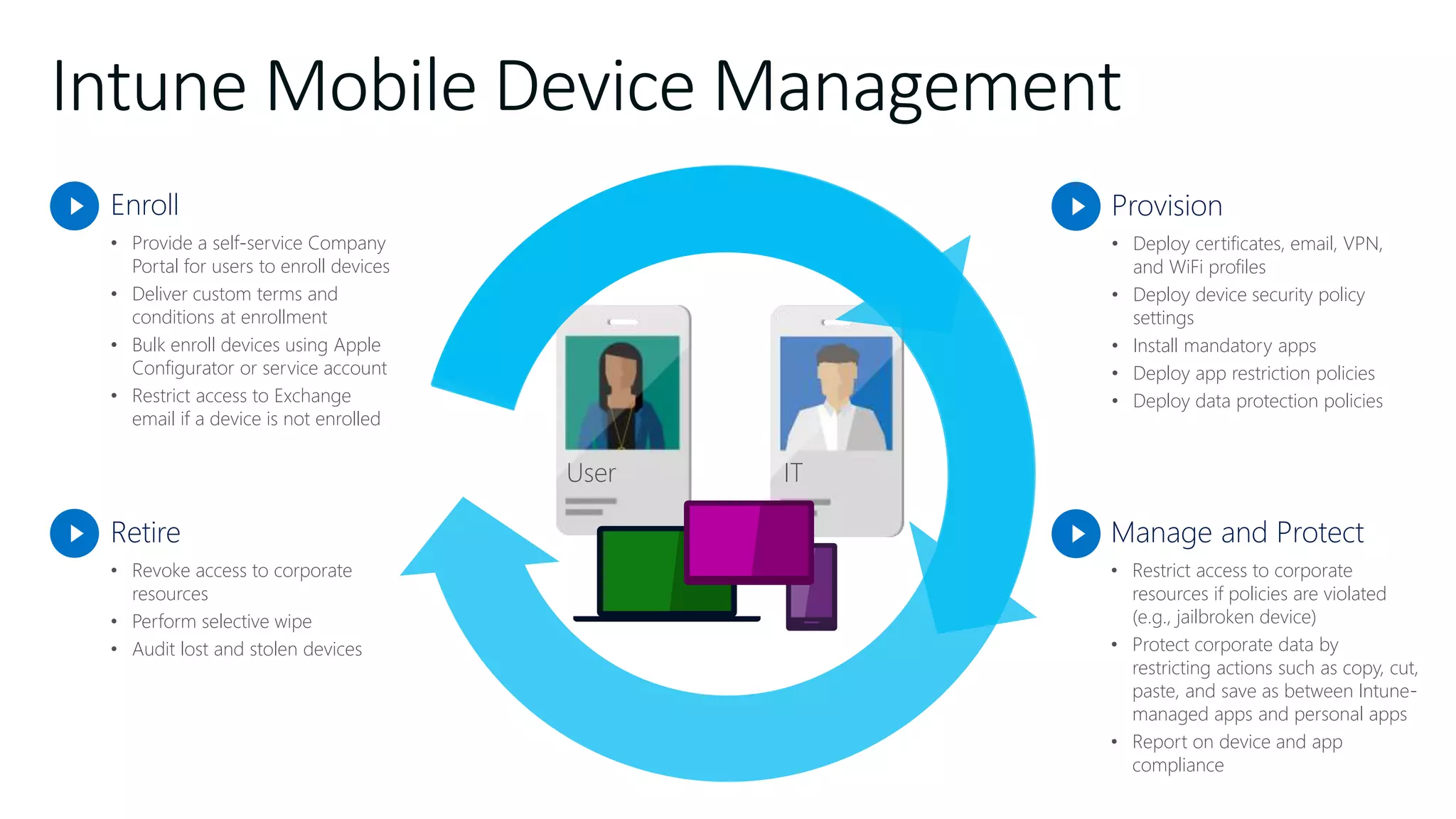
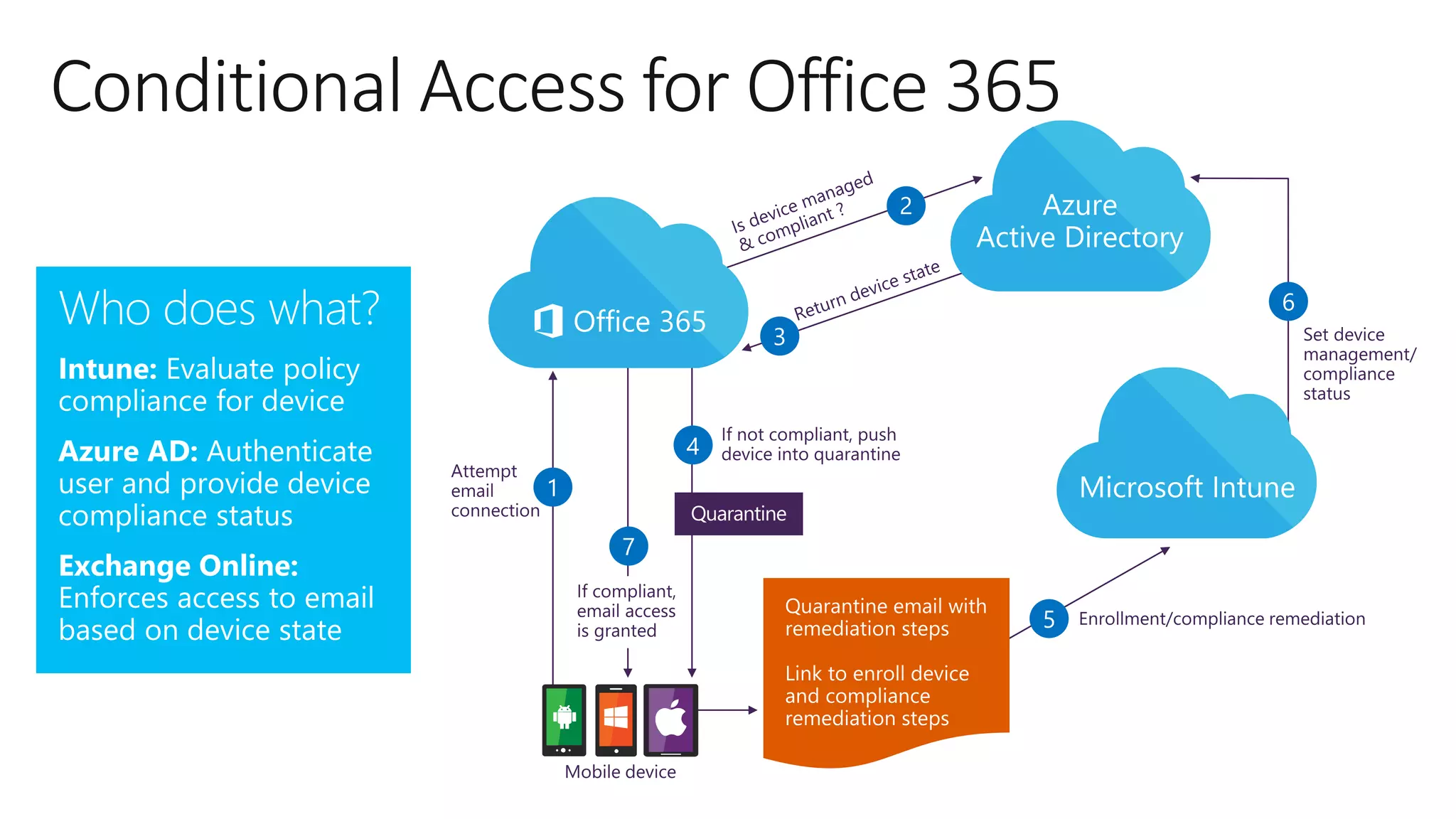
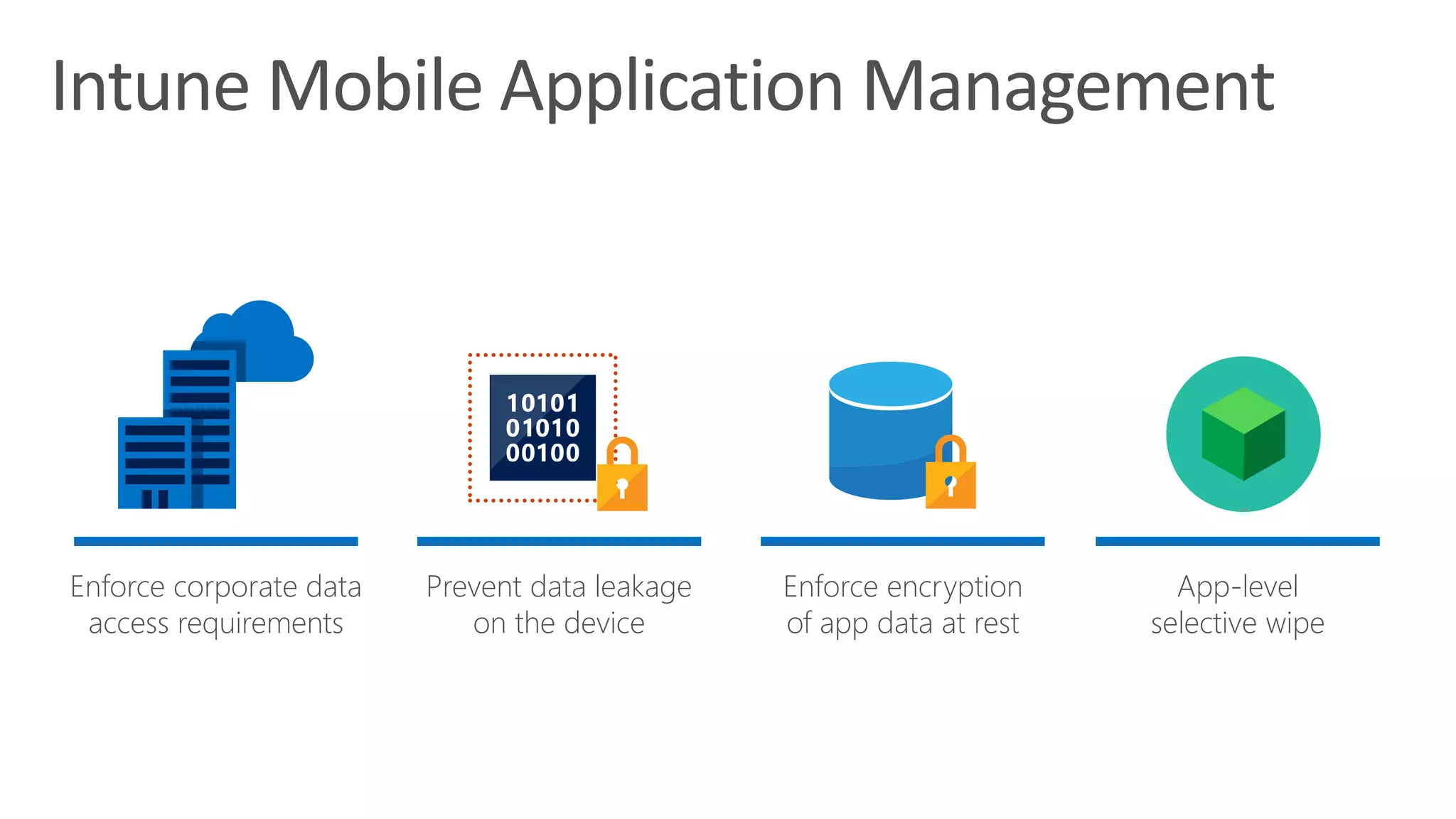
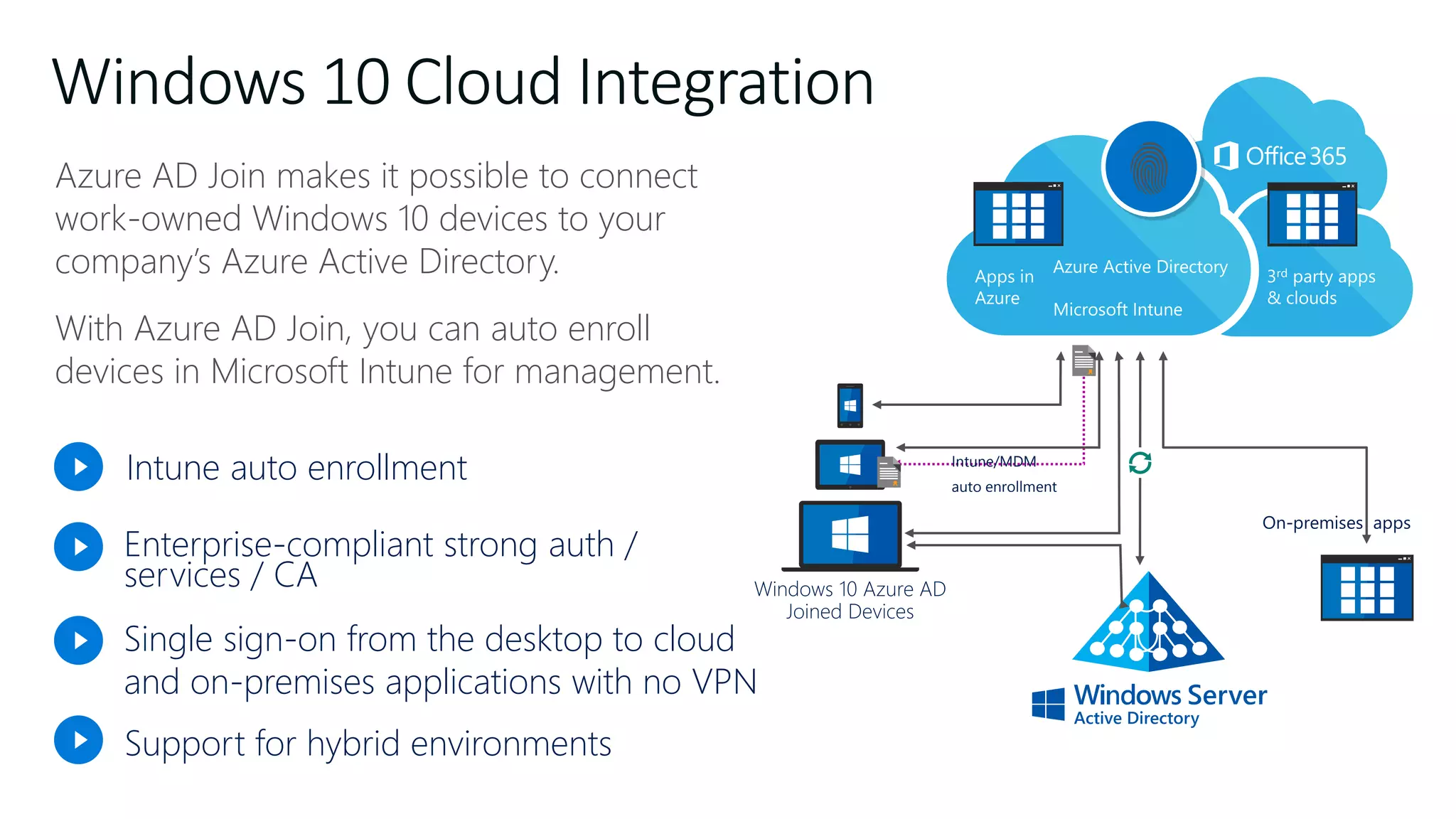
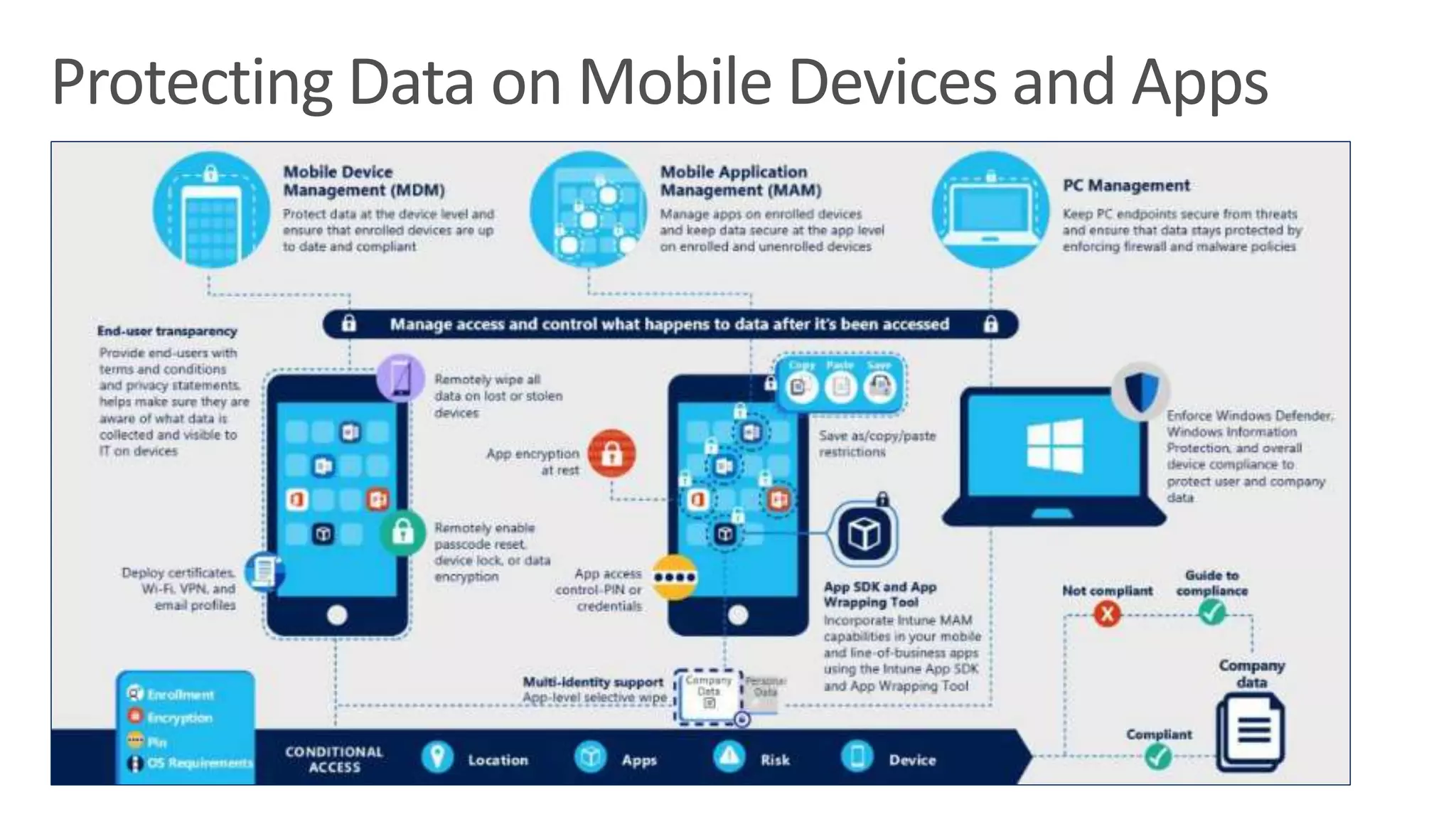
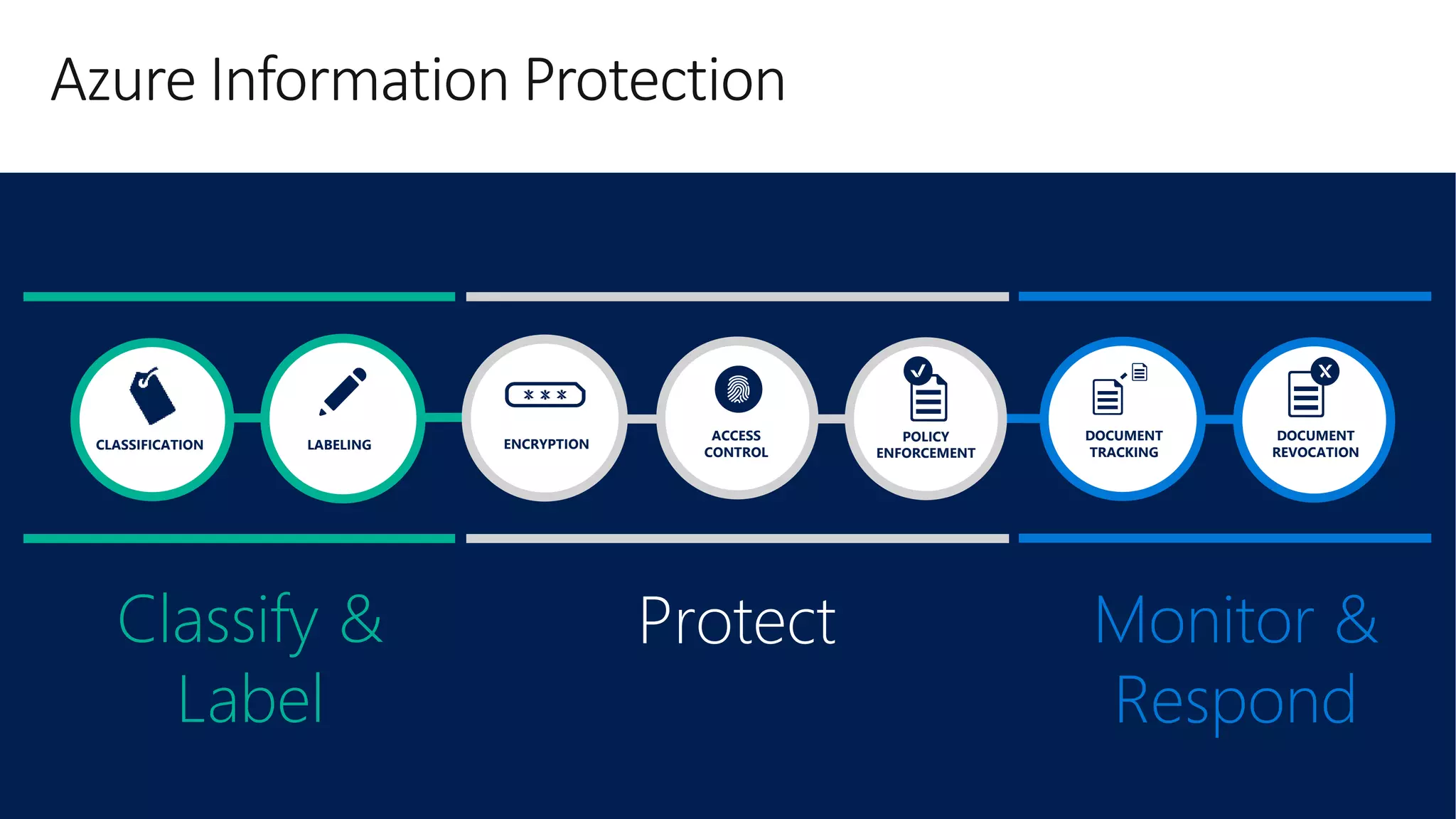
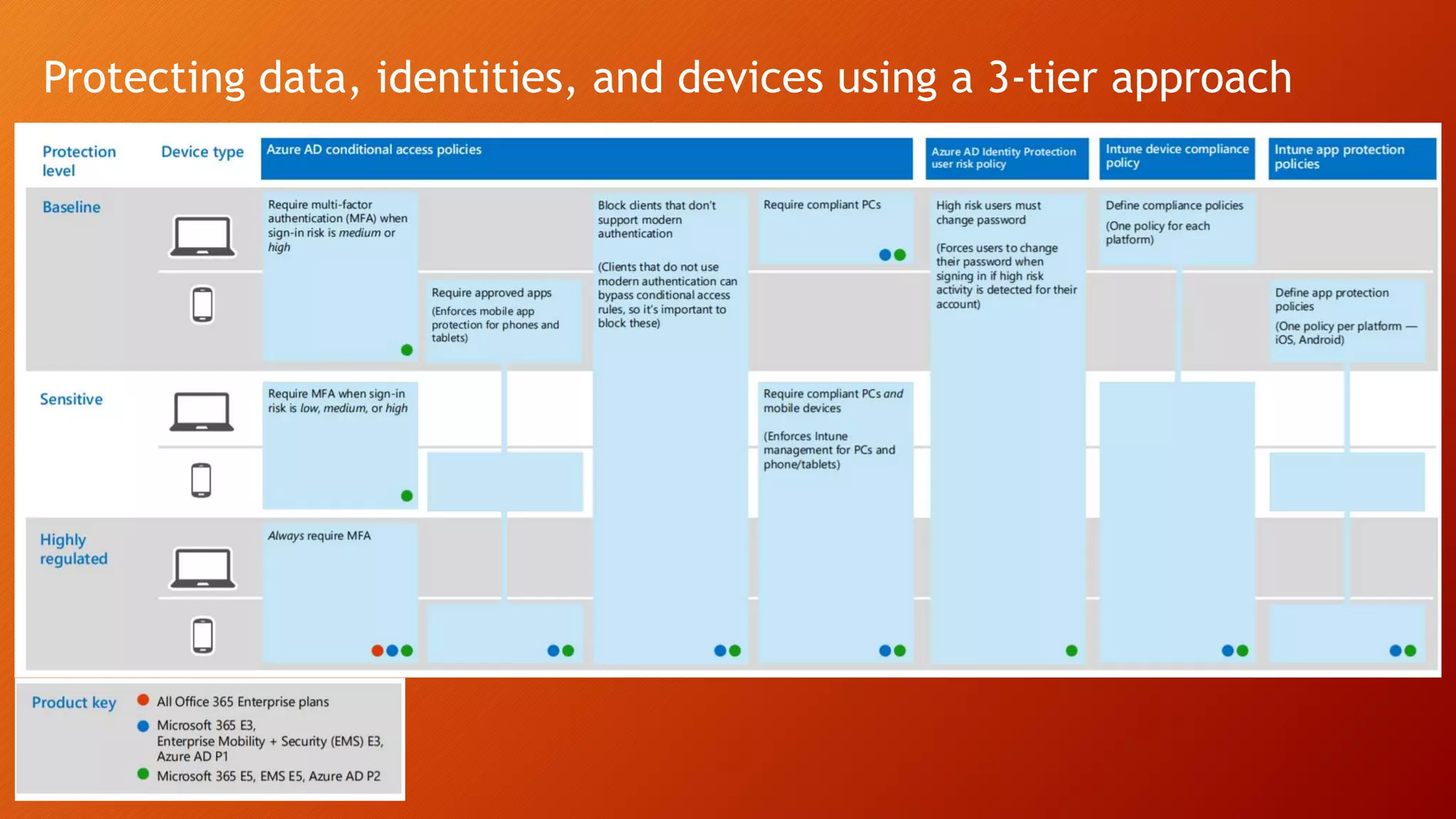
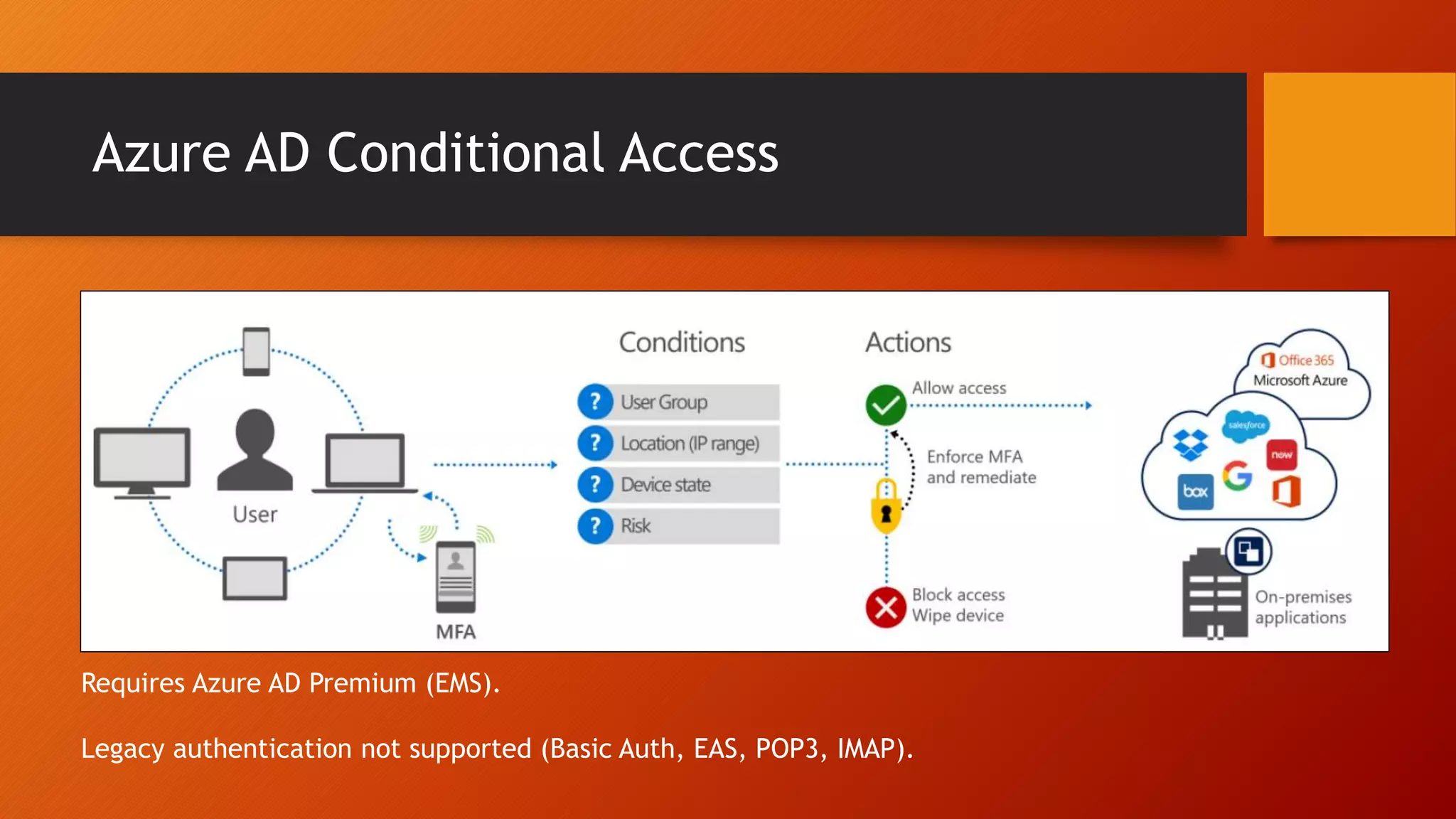
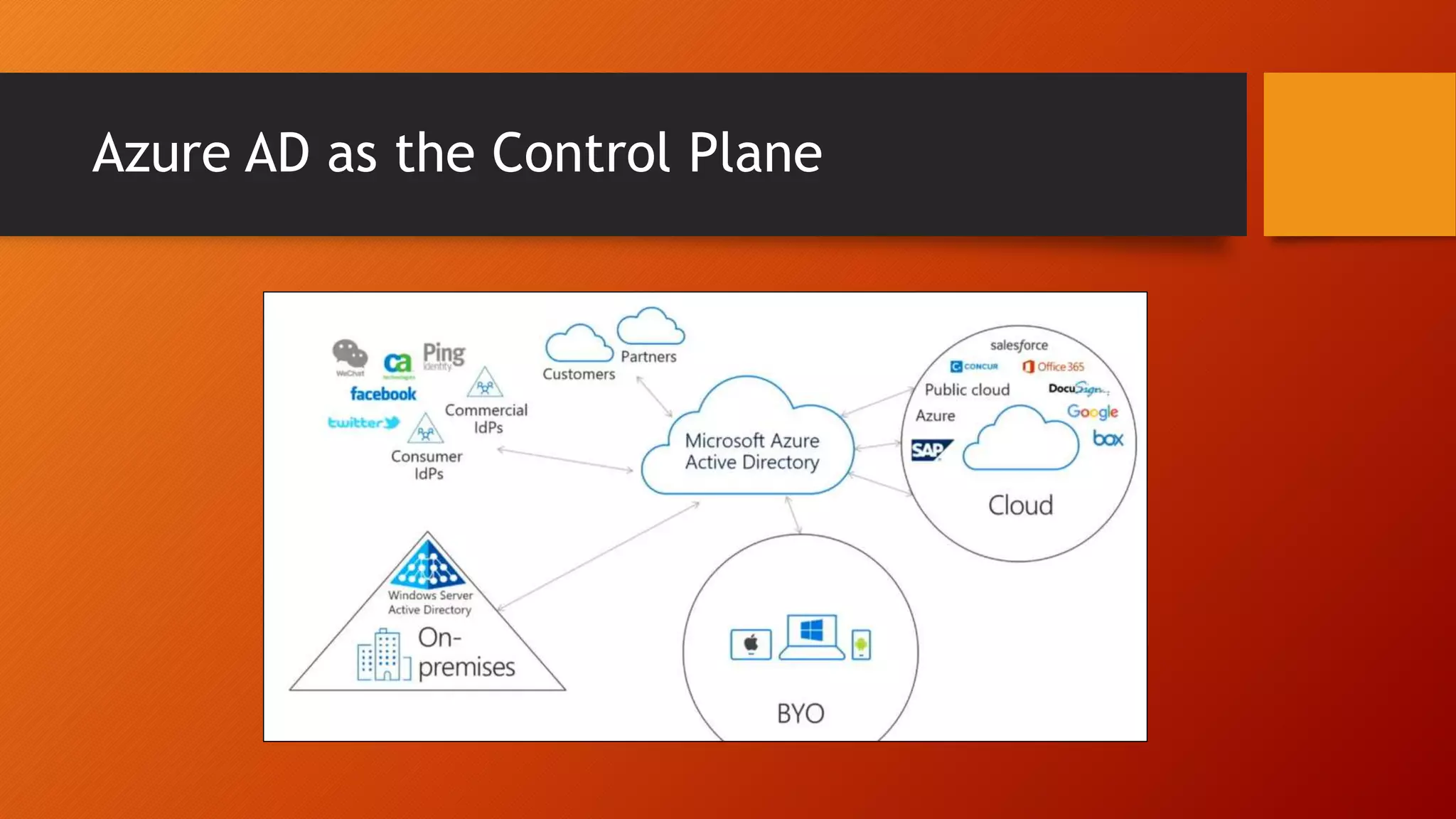
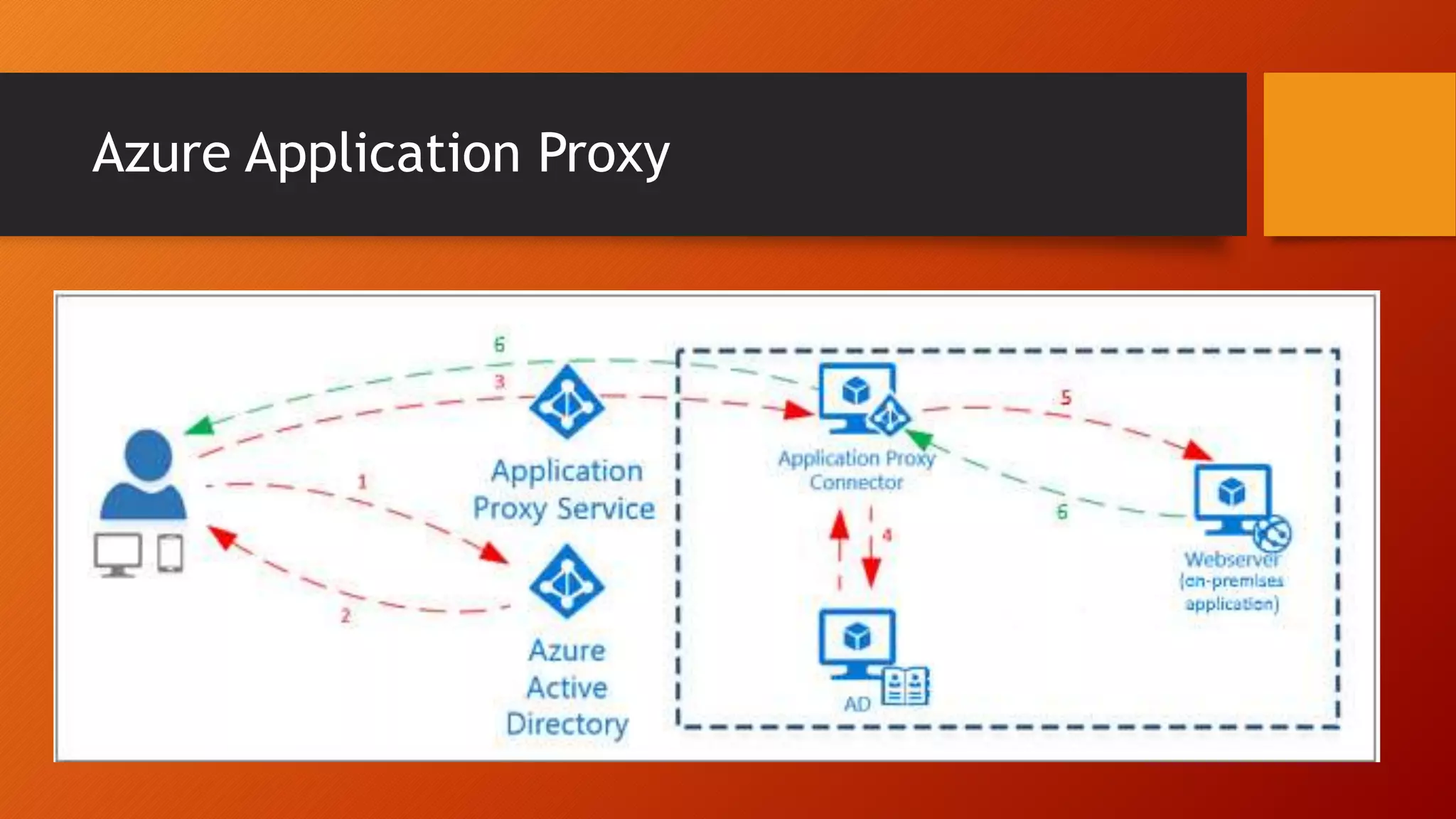
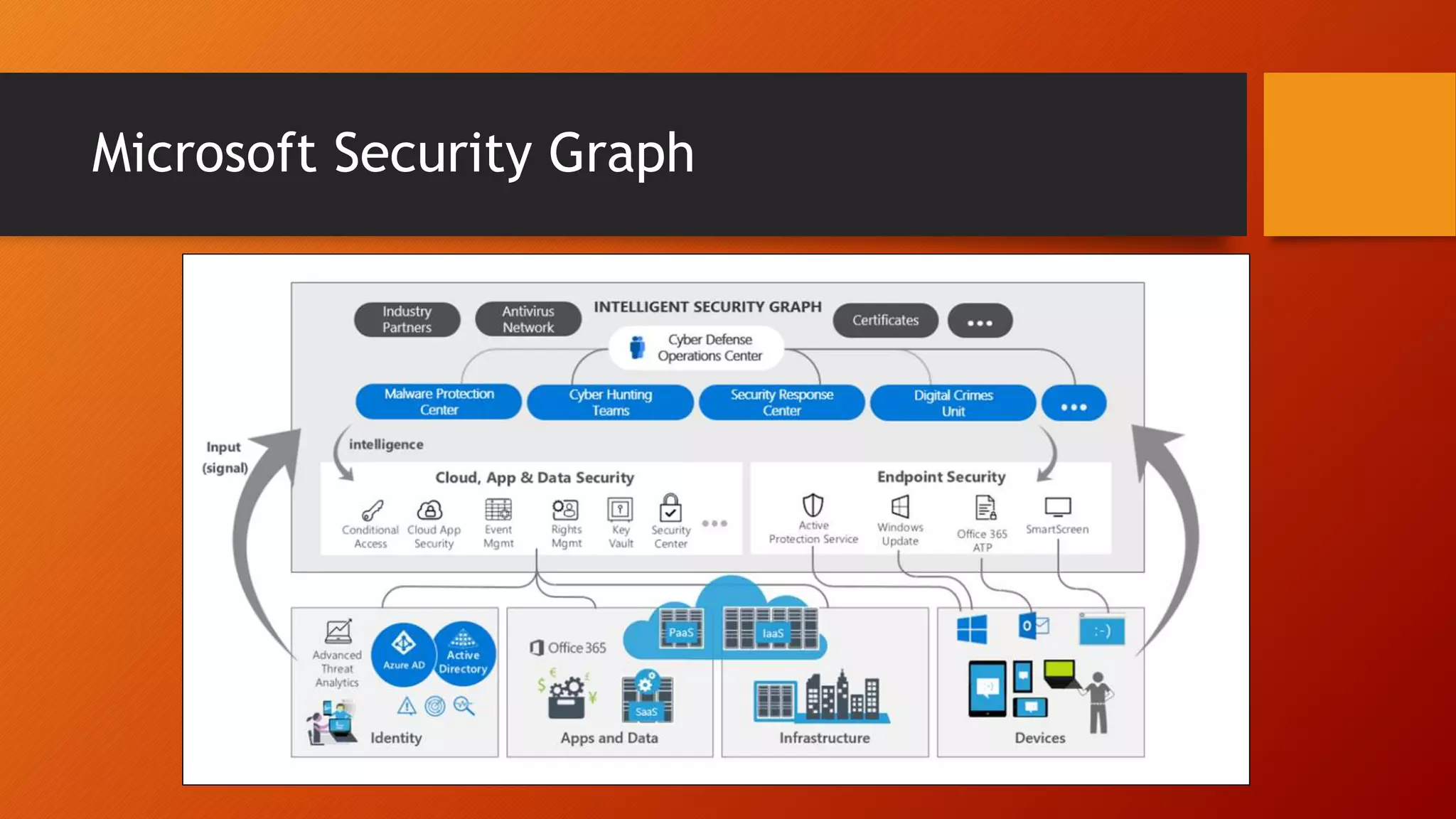
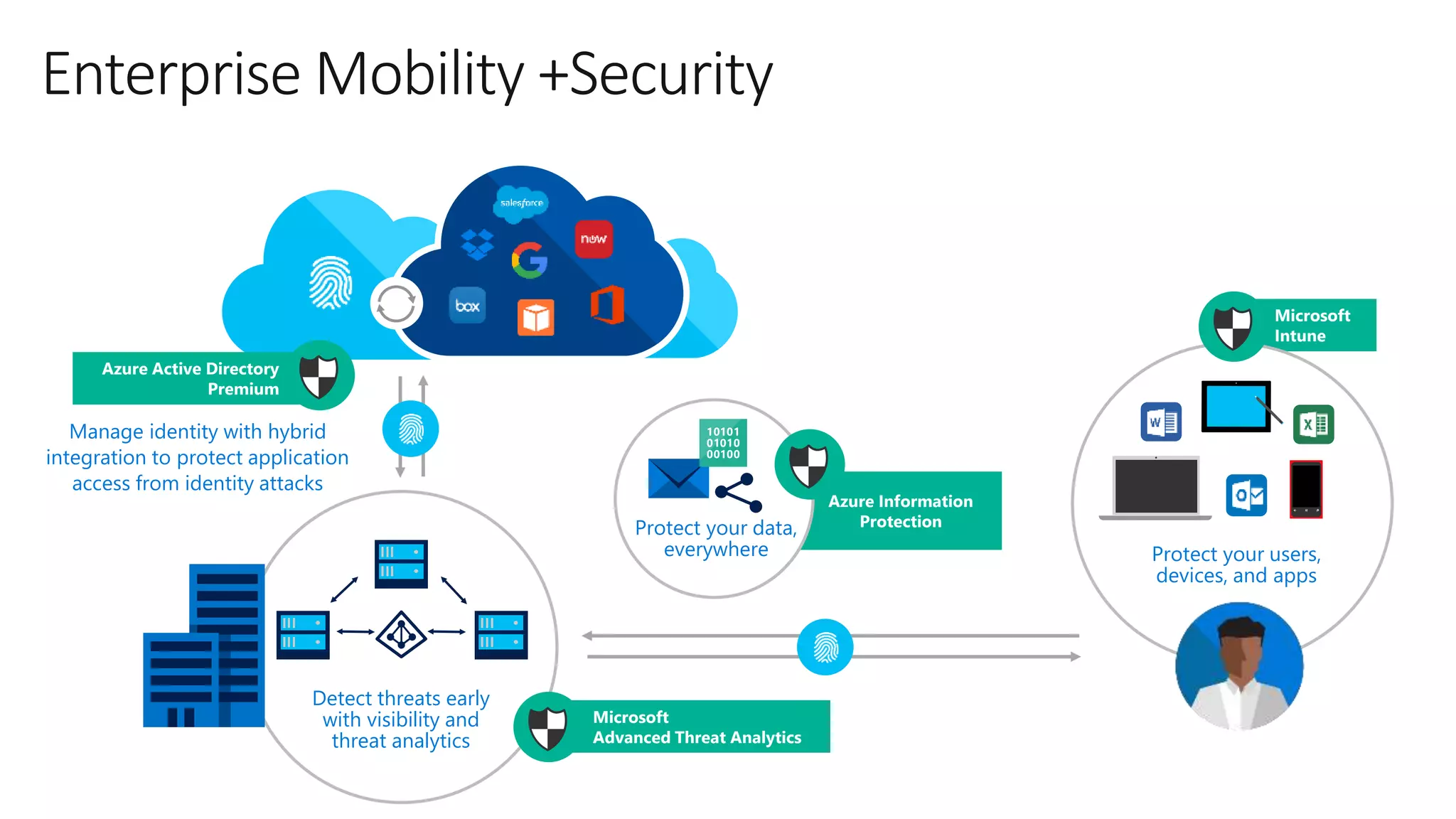
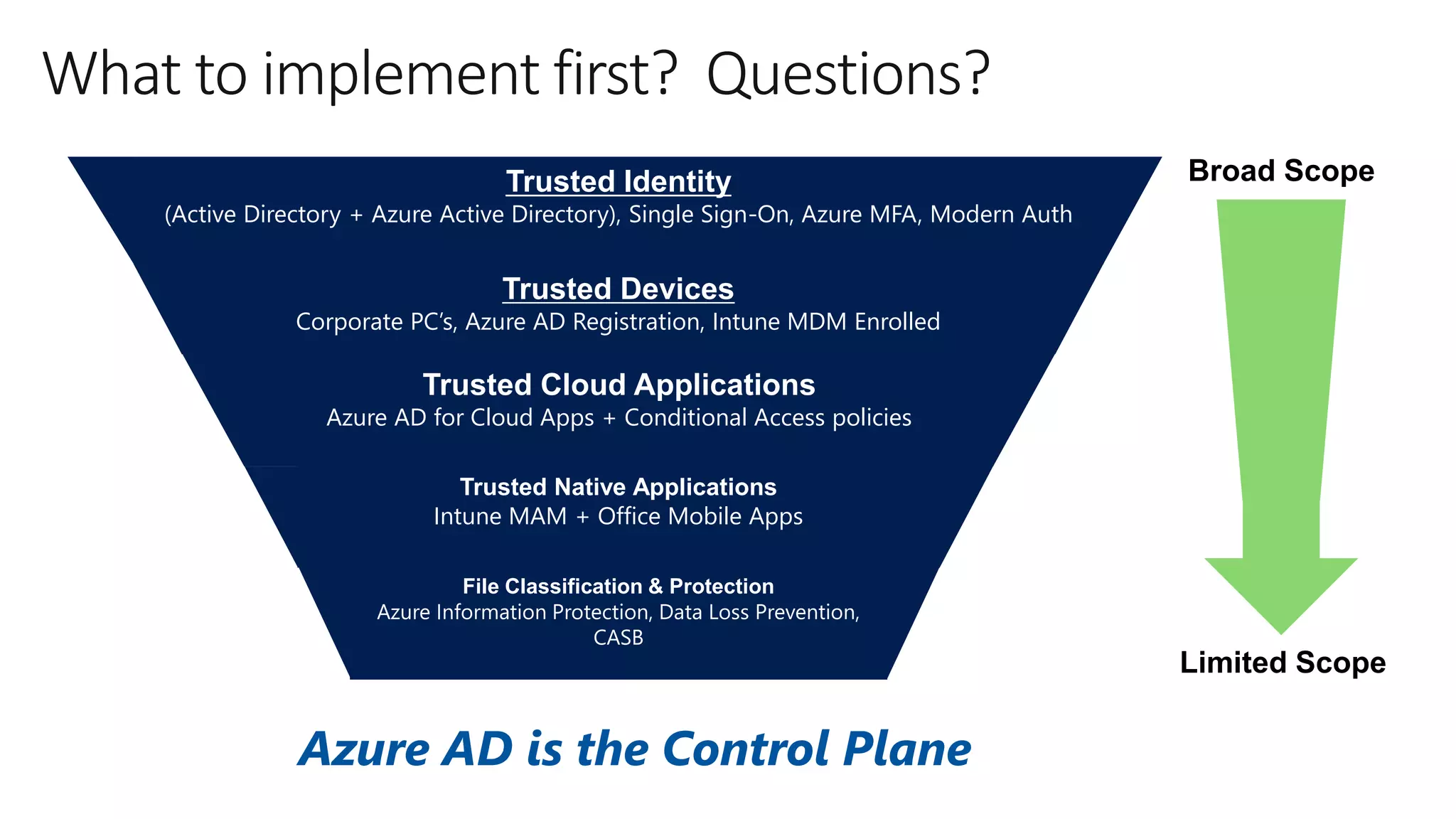
The document outlines Microsoft Cloud Security fundamentals, emphasizing the importance of maximizing security posture, adopting cloud security standards, and transitioning from legacy to modern authentication methods. It discusses the configuration and management of devices and applications, with a focus on secure access, multi-factor authentication, and device registration with Azure Active Directory. Additionally, it highlights strategies for protecting data and enhancing security through tools like Azure Information Protection and Intune, while addressing the integration of cloud and on-premises solutions.