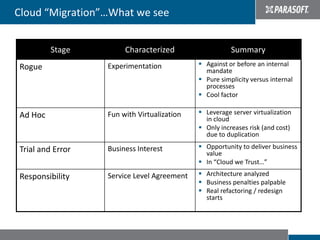
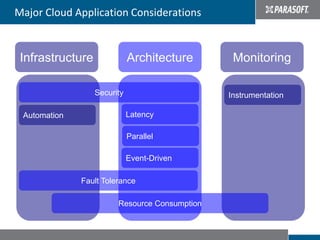
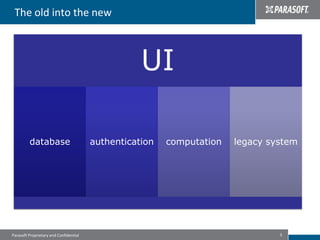
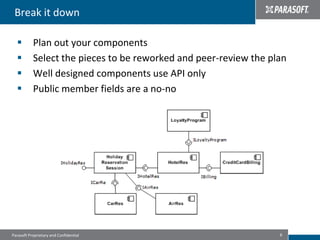
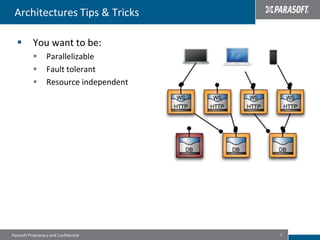
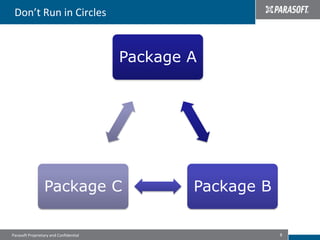
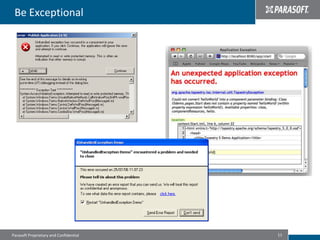
This document discusses best practices for migrating applications to the cloud. It identifies common stages in cloud migrations like experimentation, virtualization trials, and business-driven efforts. Major considerations for cloud applications include infrastructure, architecture, monitoring, security, instrumentation, and automation. The document provides tips for cloud migrations such as breaking applications into well-designed components, avoiding monolithic structures, designing for parallelism and fault tolerance, and emphasizing security through input validation and policy enforcement.