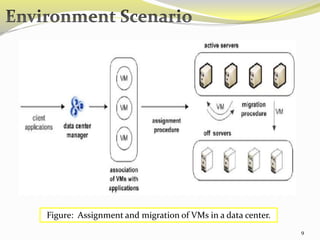
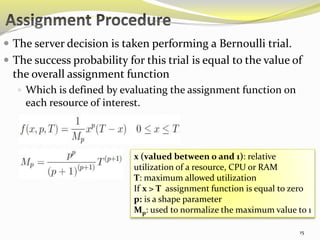
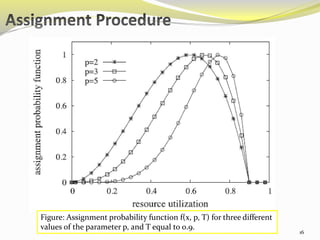
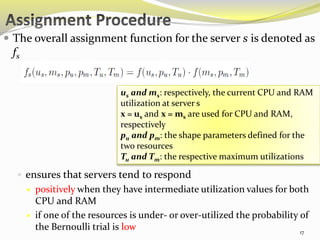
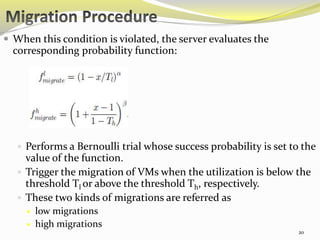
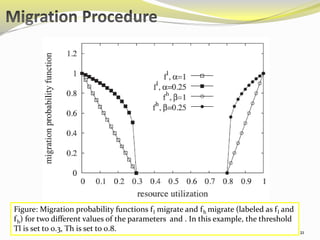
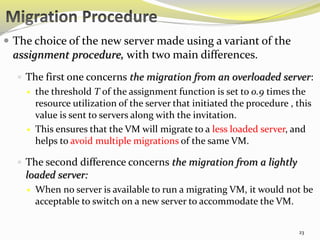
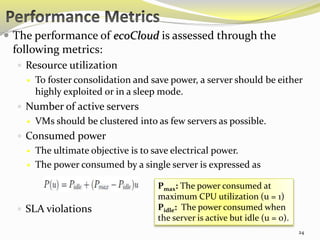
The document describes an approach called ecoCloud for efficiently consolidating virtual machines (VMs) across physical servers in cloud data centers to reduce power consumption. EcoCloud uses probabilistic procedures driven by local information to dynamically assign and migrate VMs, allowing servers to autonomously increase utilization and consolidate workload over time. The goal is to maximize the number of servers switched off or in low-power modes through continuous optimization of VM placement in response to changing resource demands.