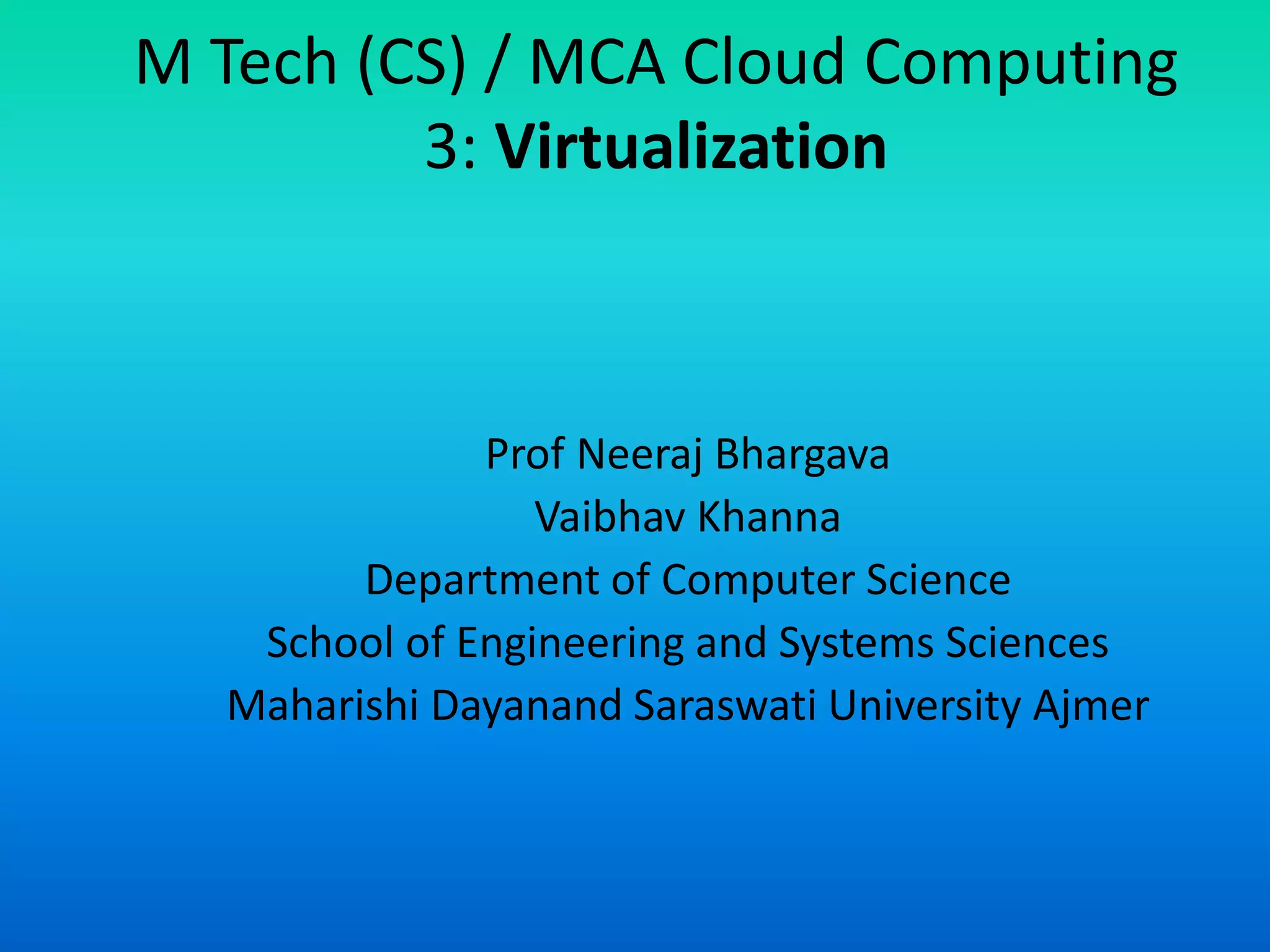
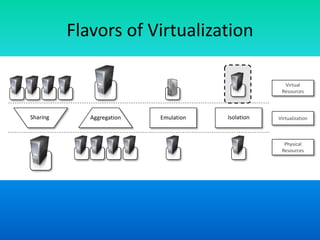
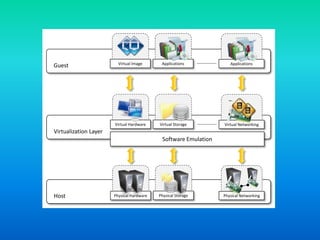
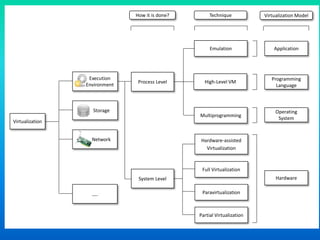
Virtualization is a technology that allows the creation of virtual versions of computer resources like operating systems, servers, storage devices, and networks. It works by partitioning physical resources and presenting them as virtual resources to users. This improves efficiency and allows multiple operating systems to run on a single system. Common types of virtualization include hardware, operating system, storage, and server virtualization. Virtualization provides benefits like increased performance, availability of resources, and automation. It is an important foundational technology for cloud computing.