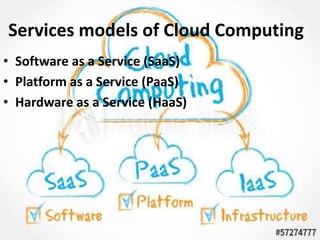
Cloud computing allows users to access applications and store data on remote servers accessed through the internet rather than installing software locally. Examples include web-based email services like Gmail where users access their accounts through a web interface rather than storing email on their own computer. Cloud computing systems divide the front end, which users access, from the back end servers. Services are provided through various models including Software as a Service (SaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Hardware as a Service (HaaS). Cloud deployment can be private, only for a single organization, public for any user, or hybrid using both public and private systems.