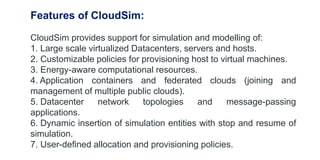
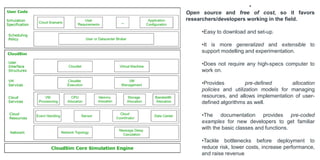
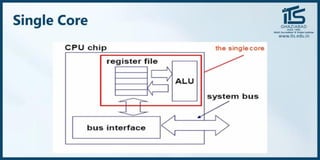
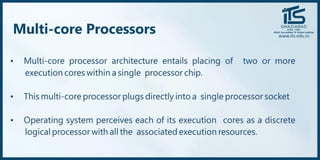
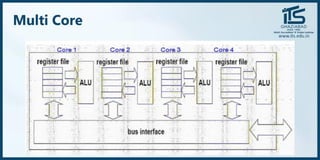
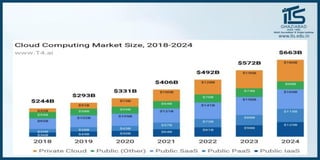
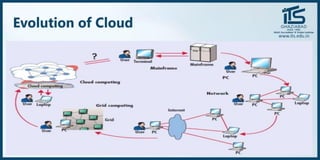
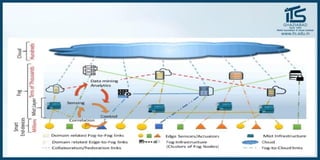
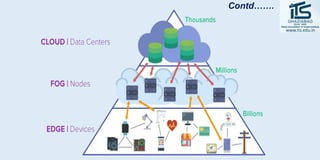
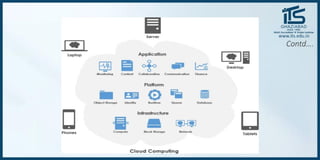
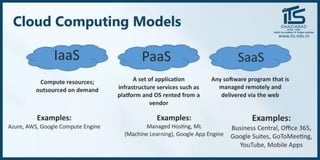
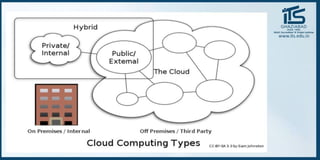
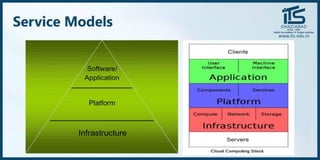
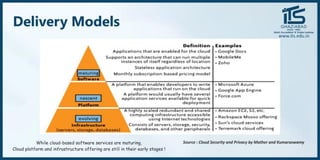
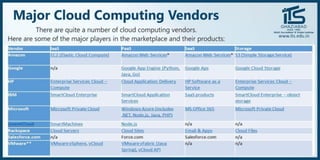
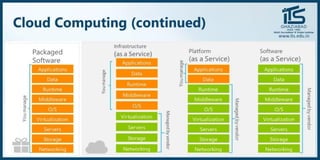
The document provides recommendations for books on cloud computing concepts and technologies. It then discusses the history and drivers of the Fourth Industrial Revolution powered by cloud, social, mobile, IoT, and AI technologies. The document defines cloud computing and discusses characteristics such as on-demand access to computing resources, utility computing models, and service delivery of infrastructure, platforms, and applications. It also outlines some major cloud platform providers including Eucalyptus, Nimbus, OpenNebula, and the CloudSim simulation framework.














































![Contd…
3. Open Nebula
• OpenNebula is one of the most feature-rich open sources VI manager. It was initially
conceived to manage local virtual infrastructure, but has also included remote interfaces
that make it viable to build public clouds. Altogether, four programming APIs are available:
XML-RPC and libvirt for local international; a subset of EC2 (Query) APIs and the
OpenNebula Cloud API (OCA) for public access.
• Its architecture is modular, encompassing several specialized pluggable components. The
Care module orchestrates physical servers and their hypervisors, storage nodes, and
network fabric. Management operations are performed through pluggable Driver, which
interact with APIs of hypervisors, storage and network technologies, and public clouds.
The Scheduler module, which is in charge of assigning pending VMrequest to physical
host, offers dynamics resource allocation features. Administration can choose between
different scheduling objectives such as packing VMs in fewer hosts or keeping the load
balanced. Via integration with the Haizea lease scheduler [66], OpenNebula also supports
advance reservation of capacity and queuing of best-effort leases.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cloud-computing-dr-sunilkr-pandey-unit-1-220128023927/85/Cloud-Computing-Introduction-70-320.jpg)