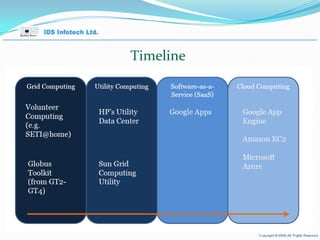
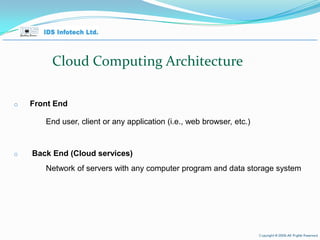
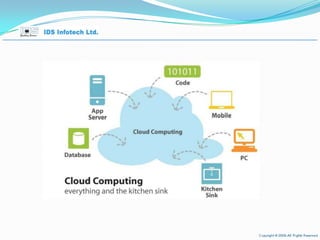
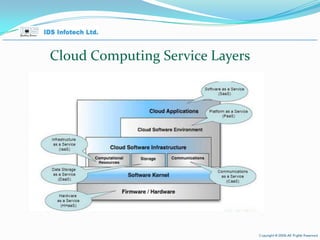
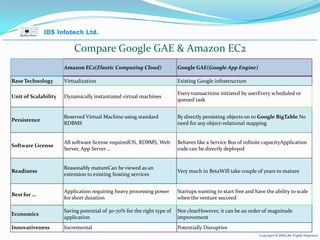
The document provides an overview of cloud computing, including key concepts such as cloud service layers, cloud service types, cloud computing architecture and timelines. It discusses cloud computing topics such as Software as a Service (SaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), benefits such as scalability and cost savings, and examples of public and private cloud models.