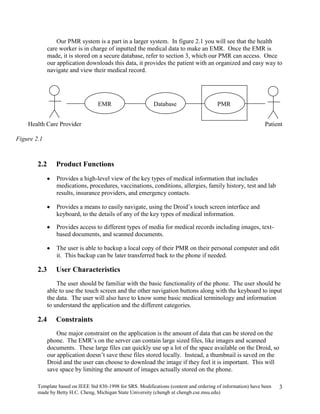
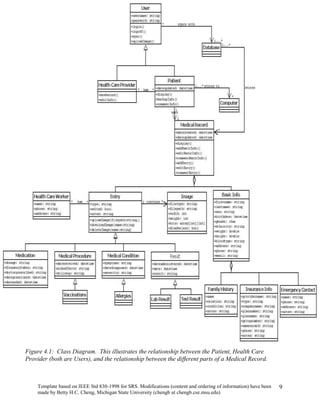
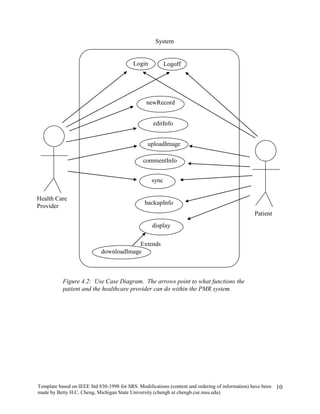
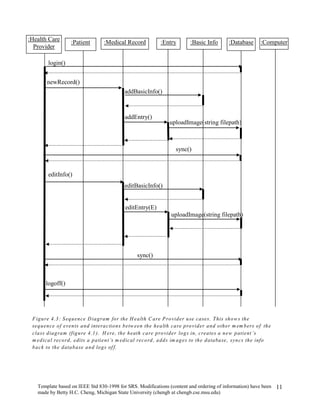
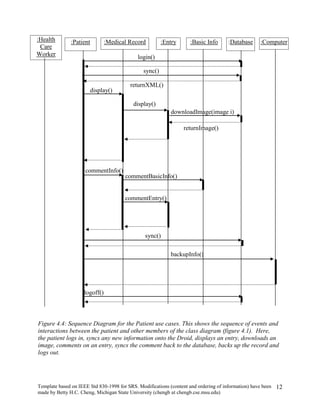
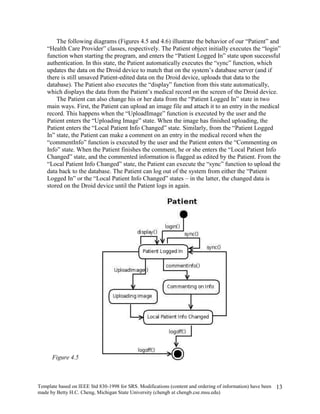
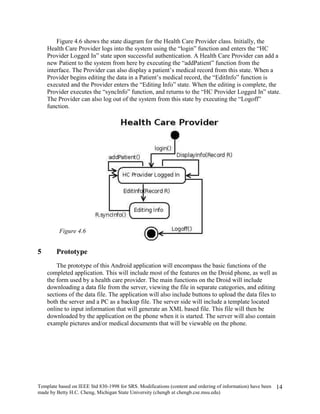
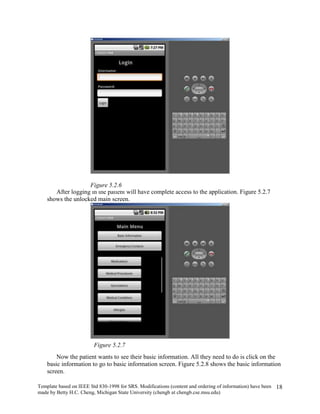
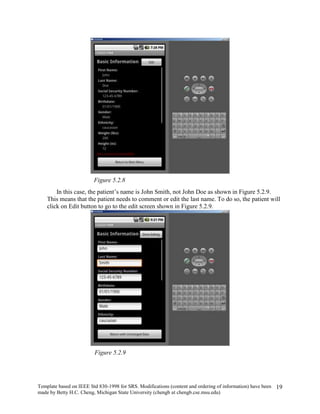
The document provides an overview of a software requirements specification for a Personal Medical Record (PMR) mobile application designed for the Motorola Droid phone. The PMR app will allow users to store, access, and comment on their medical records from their phone. Medical records will be stored on a central database and the app will download the latest records from the server. The document outlines the purpose, scope, definitions, organization, description of key functions and user characteristics, constraints, assumptions, and specific requirements of the PMR app.