1) Clonal propagation is the multiplication of genetically identical copies of a plant cultivar through asexual reproduction. This can be done in vivo through methods like cutting, layering, and grafting, or in vitro through tissue culture techniques.
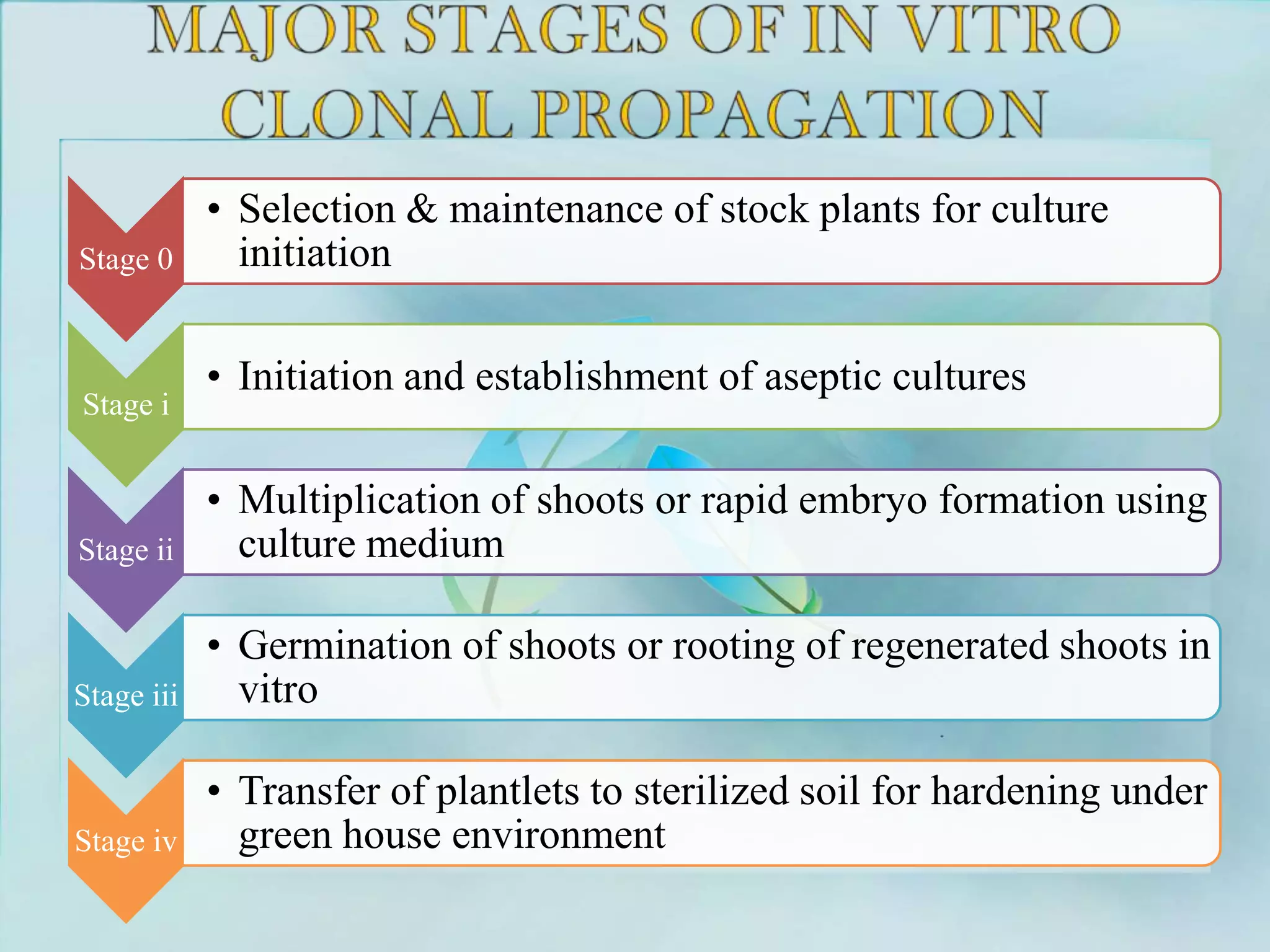
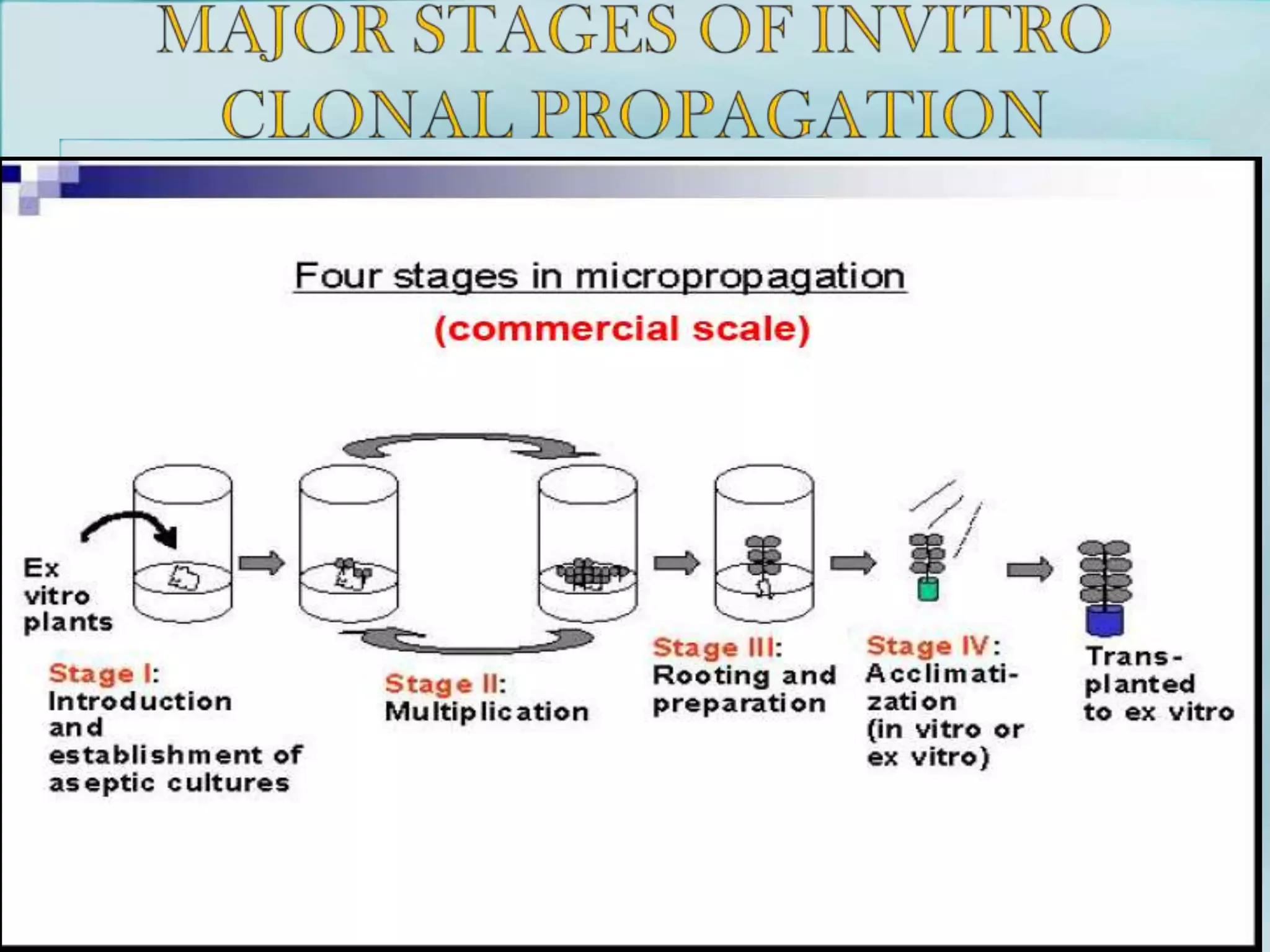
2) Micropropagation through tissue culture involves taking explants like shoot tips or meristems and culturing them on nutrient media to induce multiplication. Common methods are meristem culture, organogenesis, and somatic embryogenesis.
3) Clonal propagation has advantages like producing true-to-type plants, allowing off-season production, reducing life cycles, enabling large-scale production, and facilitating germplasm conservation and genetic transformation. However, it can be costly and labor intensive