Embed presentation
Download to read offline



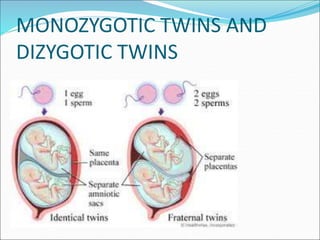




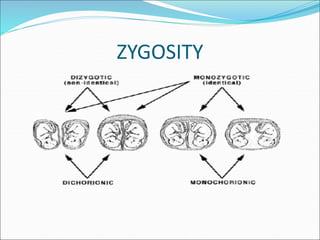









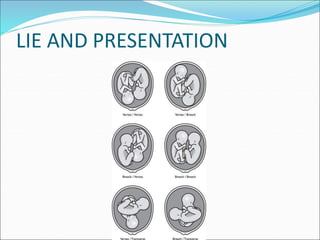









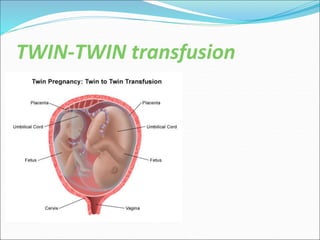
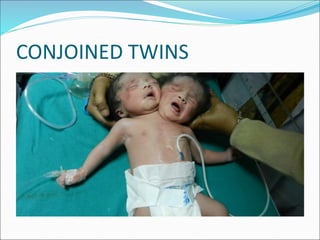













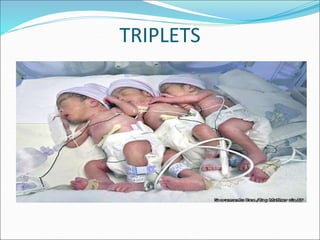

Multiple pregnancy occurs when more than one fetus develops simultaneously in the uterus. The most common type is twins, which can be either monozygotic (identical) or dizygotic (fraternal). Multiple pregnancies carry increased risks for both mother and babies, including anemia, preeclampsia, preterm birth, and low birth weight. Care involves frequent monitoring, treatment of any complications, and often delivery by caesarean section. The perinatal mortality rate is about 5 times higher for twins compared to singletons. Close antenatal care aims to prolong the pregnancy and improve outcomes for both mother and babies.














































