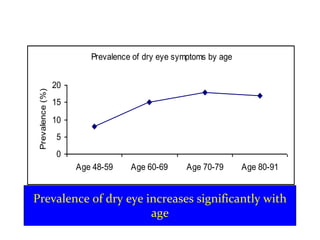
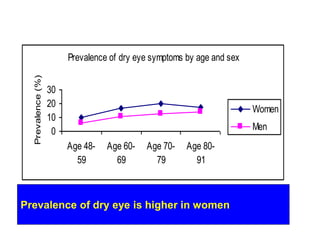
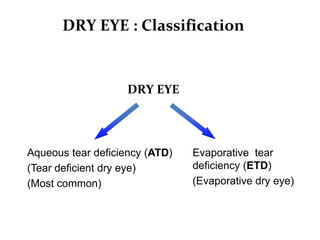
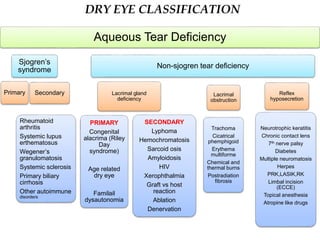
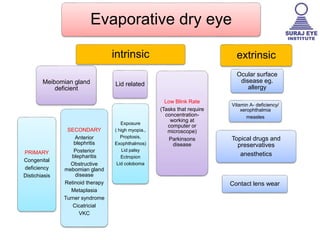
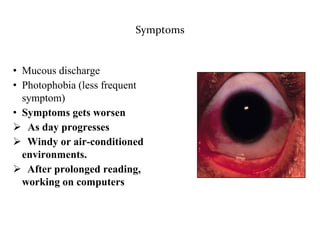
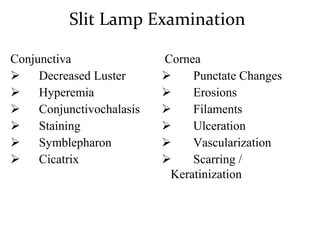
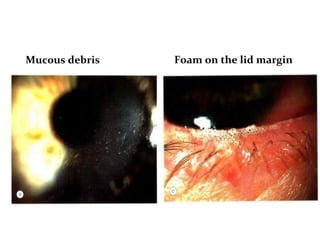
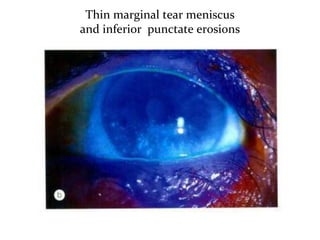
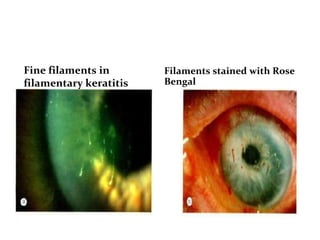
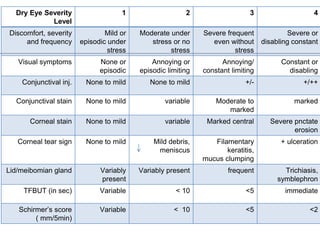
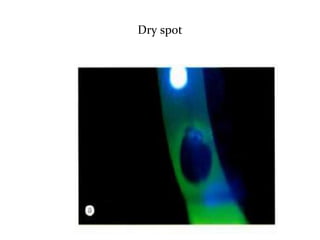
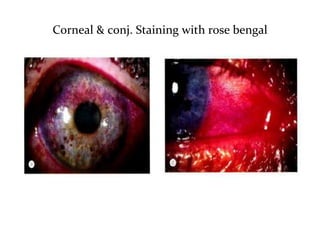
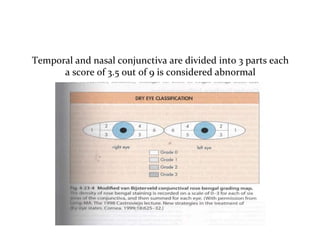
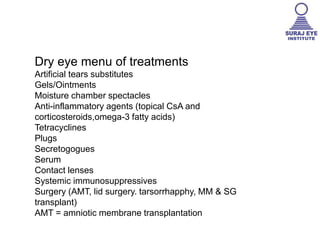
Dry eye, also known as dysfunctional tear syndrome, is a multifactorial disease of the tears and ocular surface. It results in symptoms of discomfort, visual disturbance, and tear film instability, and can potentially damage the ocular surface. The document discusses the prevalence, classification, signs, symptoms, and diagnostic tests and tools for dry eye. The prevalence increases significantly with age and is higher in women. Diagnosis involves evaluating symptoms, performing a slit lamp exam to check for signs of damage, and conducting tests to assess tear film stability, tear secretion, and ocular surface damage. Management involves classifying dry eye severity levels based on signs and symptoms to determine appropriate treatment.