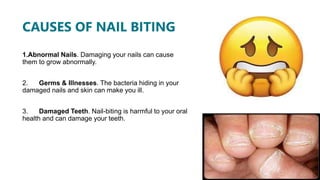
Nail biting, also known as onychophagy, is a common oral habit where a person bites their fingernails. Freud believed it was a sign of an "oral receptive" personality from the oral stage of development. Nail biting can be caused by genetics, anxiety, boredom, or psychological issues like ADHD or OCD. It can lead to abnormal nail growth, germs/illnesses, and damage to teeth. Ways to stop include keeping nails trimmed, using bitter polish, regular manicures, replacing with a good habit like fidget toys, identifying triggers, and gradually stopping the habit one nail at a time.