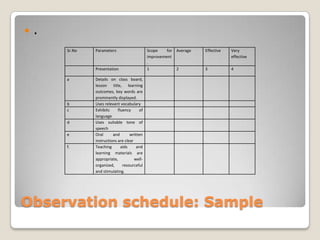
This document outlines a constructive model for peer observation and feedback in English language teacher training programs. It discusses moving from unstructured observation, which tends to provide only positive or negative feedback, to more structured observation involving tasks. Sample tasks are provided to help observers focus on specific aspects of teaching and provide qualitative feedback. The model was tried with B.Ed trainees and found to develop critical thinking skills while creating a supportive environment. Structured observation with tasks is recommended as an effective learning tool for both observers and observed teachers.