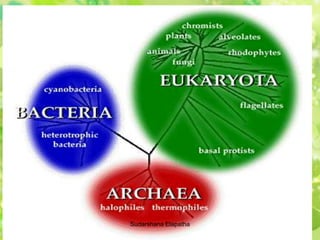
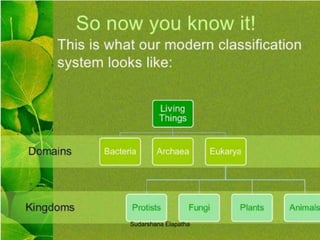
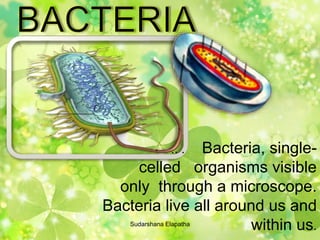
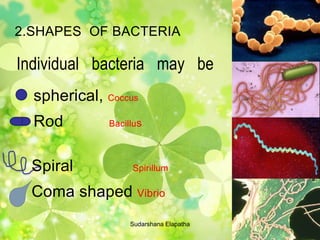
The document discusses bacteria, protists, and fungi. It describes their basic structures, shapes, modes of nutrition, reproduction, distribution, and provides examples for each. Key points covered include that bacteria are unicellular prokaryotes, protists are eukaryotic organisms that are not plants or animals, and fungi absorb nutrients from organic materials and can be unicellular or multicellular.