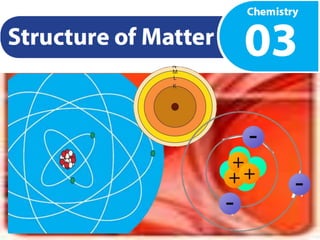
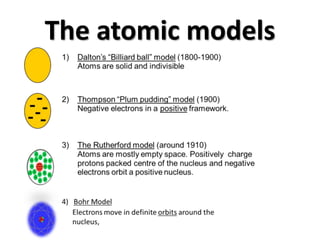
Matter is anything that takes up space and has mass. It can be classified as solids, liquids, or gases based on physical properties, and as pure substances like elements and compounds or mixtures based on chemical composition. Atoms are the building blocks of matter and contain protons, neutrons, and electrons. The Rutherford and Bohr atomic models showed electrons orbiting a nucleus containing protons and neutrons. An atom's atomic number equals its protons, while its mass number equals protons plus neutrons. Electrons fill energy levels in an atom's electronic configuration.